![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
peritoneum |
Visceral and parietal layers, Peritoneal cavity |
|
|
mesentary |
Folds of peritoneum |
|
|
intraperitoneal |
situated within or administered by entering the peritoneum |
|
|
retroperitoneal |
the space between the peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall that contains especially the kidneys and associated structures, the pancreas, and part of the aorta and inferior vena cava |
|
|
Ingestion |
swallowing, Skeletal muscle up to top 1/3 of esophagus |
|
|
Peristalsis |
Major means of propulsion (smooth muscle) |
|
|
Segmentation |
Rhythmic local contractions of the intestine that mixes food with digestive juices (small intestine) |
|
|
Digestion |
Enzymatic Breakdown (mouth, stomach and small intestine) |
|
|
Absorption |
Small Intestine (main site) Into blood vessels (simple sugars and amino acids) Into lacteals (fats only)
Large Intestine (mainly water) |
|
|
Defecation |
exiting the body |
|
|
4 layers of GI tract? |
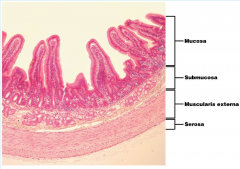
Serosa, muscularis externa, submucosa, mucosa |
|
|
Functions of Peritoneum and Mesenteries |
Holds organs in place, Sites of fat storage, Provides a route for circulatory vessels and nerves |
|
|
Mucosa Layer |
innermost layer, Contains some glands |
|
|
Submucosa Layer |
Contains glands, blood vessels, lymphatics, submucosal nerve plexus |
|
|
Muscularis externa |
Circular muscularis, Inner layer
Longitudinal muscularis, Outer layer |
|
|
Serosa |
is a smooth membrane consisting of a thin layer of cells which secrete serous fluid, and an underlying thin epithelial layer |
|
|
Explain the enteric nervous system |
Enteric means “gut"
Resides solely in the walls of the alimentary canal |
|
|
Myenteric nerve plexus |
Lies between circular and longitudinal muscularis
Controls movement (peristalsis and segmentation) |
|
|
Submucosal nerve plexus |
Lies in submucosa
Signals glands to secrete |
|
|
Salivary glands function |
Saliva moistens the mouth, dissolves food chemicals, binds food into a bolus
Saliva contains -Water, ions, Mucus, Enzymes |
|
|
Esophagus function |
muscular tube Begins as a continuation of the pharynx, Joins the stomach inferior to the diaphragm |
|
|
Cardiac sphincter |
closes lumen to prevent stomach acid from entering esophagus |
|
|
Stomach function |
Site where food bolus is churned into chyme
Protein digestion begins
Food remains in stomach approximately 4 hours |
|
|
Regions of the stomach |
Fundus
Body
Pyloric part |
|
|
Microscopic Anatomy of the Stomach |
Mucosa dotted with gastric pits
Gastric glands-deep to gastric pits |
|
|
3 regions of Small Intestine |
Site of most enzymatic digestion and absorption
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum |
|
|
Duodenum |
Receives digestive enzymes and bile from the liver/gallbladder and pancreas |
|
|
Modifications to increase surface area for absorption in small intestine |
Circular folds, Villi (finger like projections), Microvilli (brush border) |
|
|
Absorptive enterocytes |
(in intestinal wall) Uptake digested nutrients |
|
|
Goblet cells |
(in intestinal wall) Secrete mucus that lubricates chyme |
|
|
Enteroendocrine cells |
(in intestinal wall) Secrete hormones |
|
|
function of large intestine |
Absorb water and electrolytes |
|
|
Cecum |
Blind pouch
Beginning of large intestine |
|
|
Appendix |
Contains lymphoid tissue
Neutralizes pathogens |
|
|
Colon |
Ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon |
|
|
Teniae coli |
3 thin strips of longitudinal muscularis |
|
|
Haustra |
Puckering created by teniae coli |
|
|
Anal canal has what kind of epithelium |
Lined with stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
liver functions |
Largest gland in the body
Performs over 500 functions
Digestive function, Bile production |
|
|
Hepatocyte |
functional cells of the liver |
|
|
Hepatic macrophages |
destroy bacteria |
|
|
Portal triad composed of |
Bile duct
Branch of hepatic portal vein
Branch of hepatic artery |
|
|
Gallbladder function |
Stores and concentrates bile
Expels bile into duodenum
Bile emulsifies fats |
|
|
Pancreas function |
Exocrine function
Produces most enzymes that digest food in the small intestine |

