![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Gastroenterology |
Deals with the structure function diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the stomach and intestines |
|
|
|
Digestive process |
Are five basic activities ingestion movement of food digestion absorption defecation |
|
|
|
Mechanical vs chemical digestion |
Mechanical Break down is the physical breakdown of food
chemical breakdown is the chemical reactions that break food molecules by enzymes which help speed up the chemical reaction |
|
|
|
Organization |
GI tract is Continuous tube extending from mouth to anus
Accessory structures Teeth tongue salivary gland liver gallbladder pancreas
|
|
|
|
Histology of GI Tract |
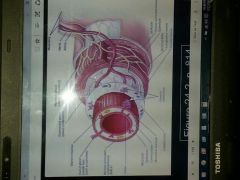
Four layers Mucosa which has 3 layers epithelium has direct contact with content in stomach ,lamina propria is an areolar connective tissue , and muscularis mocosae smooth muscle tissue
Submucosa areolar connective tissue highly vascular regulate secretion of blood vessels constriction contains lymphatic tissue Muscularis inner circular fibers Outer longitudinal fibers Skeletal muscle in mouth pharynx superior esophagus external anal sphincter Smooth muscle Contains nerve supply of GI tract Serosa Most Superficial serous membrane also called visceral peritoneum inferior to diaphragm
|
|
|
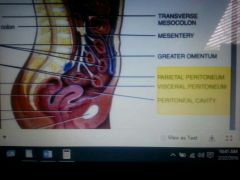
Parietal peritoneum,visceral peritoneum,peritoneal cavity |
Parietal peritoneum Lines the body wall of the abdominopelvic cavity Visceral peritoneum Covers organs within the cavity also termed the Serosa Peritoneal cavity The space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum contains serous fluid |
|
|
|
Mesentery |
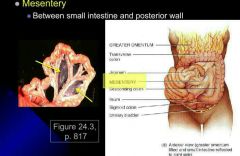
Between small intestine and posterior |
|
|
|
Mesocolon |
•Binds the large intestine to the abdominal wall •Carries blood and lymphatic vessels to the intestines |
|
|
|
Falciform ligament |
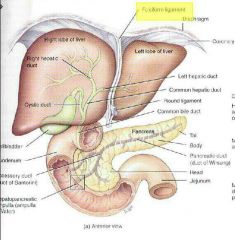
•Attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm •Liver is only organ attached to the anterior abdominal wall |
|
|
|
Lesser omentum |
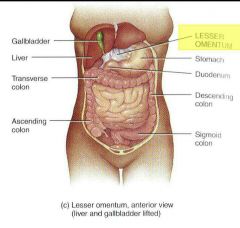
From stomach to liver and duodenum Along lesser curvature stomach |
|
|
|
Greater omentum |
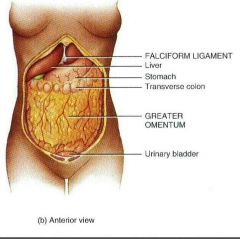
From the stomach ,draping over the transverse colon and in front of the small intestine Contains adipose tissue and many lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Mouth oral cavity |
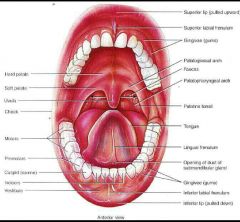
Cheeks Lips Labia frenulum the split that connects your lip to your gum Vestibule bind gum and teeth together Faucet throat Hard palate roof of u your mouth Oral cavity Soft palate bottom of the mouth Uvulva muscular process hanging from the free border Palatoglossal arch Plato pharyngitis arch Palatine tonsils between arches Lingual tonsils at the base of the tongue |
|
|
|
Tongue |
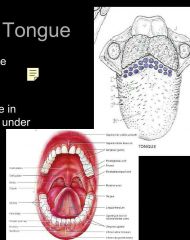
Extrinsic muscles Originate outside the tongue and insert •moves tongue Intrinsic muscles Originate and insert in the connective tissue •Alter the shape and size of tongue for speech and swallowing
Median septum Divides the tongue symmetrically Lingual frenulum Midline of the under tongue Filiform anterior of tongue Fungiform near tip Circumvallete in V on posterior |
|
|
|
Salivary gland |
•secrete saliva to lubricate mouth •secrete lingual lipase to digest fat •Buccal gland and minor salivary glands •three pairs of major salivary gland |
|
|
|
Pharynx and swallowing |
Pharynx 3 part Nasopharynx Oropharynx Laryngopharynx
Swallowing •Voluntary •Pharyngeal •Esophageal
|
|
|
|
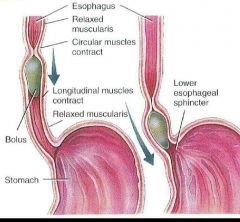
esophagus |
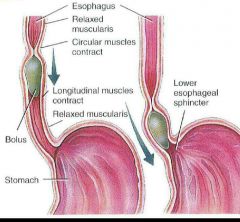
•Muscular tube •lies posterior to trachea •10 inches • begins inferior end if the Laryngopharynx •Pierces diaphragm through Esophageal hiatus •Upper Esophageal sphincter between Laryngopharynx and esophagus •Peristalsis muscle movement that pushes food •Lower esophageal sphincter between esophagus and stomach
|
|
|
|
Stomach |
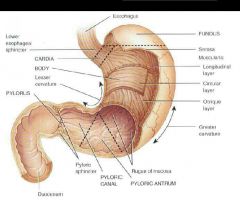
•J shaped enlargement of the GI tract •Inferior to the diaphragm •Function mixing and holding Four main areas Cardia surrounds the superior opening of the stomach Fundus social security in to the left of the cardia Body central portion of the stomach Pylorus region of the stomach connected to the duodenum Pylotic antrum connects to the body of the stomach Pyloric canal leads into the duodenum Rugae larg fold in the mucosa when stomach is empty Lesser curvature medial border Greater curvature lateral border
|
|
|
|
Pancreas |
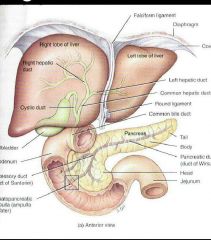
5 to 6 inches 1 inch thick Three parts head body tail It is also posterior to the greater curvature •Two ducts connect to the duedenem • also called duck of wiring Enters the duodenum at the hepatopancreatic •Pancreatic juice controlled by the sphincter of oddi Accessory duct Inters duodenal superior to the hepatopancreatic ampulla |
|
|
|
Liver |
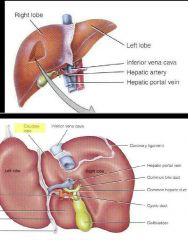
Lobes functional unit of the liver made up of liver cells arranged around the central vein Central vein van in the middle of the lobes responsible for a blood flow Sinusoids large spaces which blood passes instead of capillaries |
|
|
|
Process of bile excretion |
Bile secreted by hepatocytes to emulsify lipids Bile travels through Right&left hepatic ducts Common hepatic duct and cystic forms common bile duct |
|
|
|
Liver |
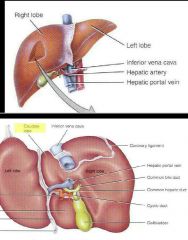
•Bile secretion •Carbohydrates lipids and proteins metabalism •removal of drugs and hormones •excretion of bilirubin •synthesis of bile salts •storage of vitamins •phagocytosis of old blood cells •activation of vitamin D |
|
|
|
Gallbladder |
Function Stores bile concentrate bile |
|
|
|
Small intestine |
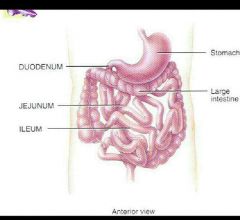
The site of most digestion and absorption three parts duodenum jejunum ileum
|
|
|
|
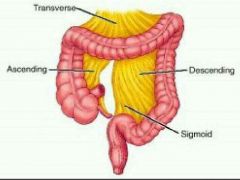
Larg intestines |
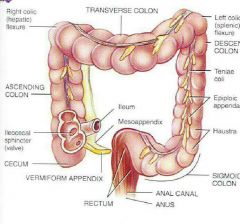
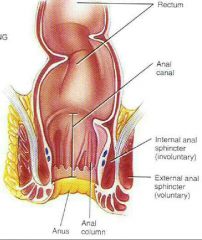
Functions •Completion of absorption • manufacture of certain vitamins •formation of feces and defecation •5 feet long ●4 principal regions •Cecum •Colon = ascending colon goes up transverse colon goes accross descending colon going down sigmoid colon going back toward midline to connect to rectum •rectum and Anal canal •Anal columns folds in the mucous membrane •anus opening to the outside with internal spincter (smooth muscle) •external sphincter cantrol anus (Skeletal muscle) voluntary
|
|

