![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pancreatic Divisum |
1. Failure of fusion of the dorsal & ventral primordial fetal duct system 2. Predisposes to chronic pancreatitis |
|
|
Annular Pancreas |
1. Band-like ring of pancreatic tissue around the second part of the duodenum 2. Risk of intestinal obstruction |
|
|
Acute Pancreatitis |
1. Inflammation and hemorrhage of the pancreas; associated with acing cell injury 2. Autodigestion of parenchyma by pancreatic enzymes activated by trypsin. 3. Liquefactive hemorrhagic necrosis of the pancreas and fat necrosis of peripancreatic fat. |
|
|
Acute Pancreatitis: Causes |
1. Alcohol and Gallstones (80%) 2. Trauma, hypolipidemia 3. Drugs, Scorpion Stings, Mumps 4. Rupture of posterior duodenal ulcer |
|
|
Acute Pancreatitis: Clinical Features |
1. Epigastric pain that radiates to the back 2. Nausea and vomiting 3. Periumbilical and flank hemorrhage 4. Elevated serum lipase and amylase; lipase is more specific 5. Saponification; calcium binds w/ released fatty acids in areas of fat necrosis |
|
|
Acute Pancreatitis: Complications |
1. Shock (result of hemorrhage and kinin system) 2. Pancreatic pseudocyst 3. Abscess 4. DIC and ARDS |
|
|
Acute Pancreatitis: Morphology |
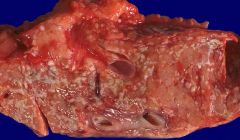
1. Proteolytic destruction of pancreatic tissue 2. Necrosis of blood vessels w/ subsequent interstitial hemorrhage 3. Fat necrosis by lipolytic enzymes 4. Associated acute inflammatory reaction |
|
|
Chronic Pancreatitis |
1. Repeated bouts of mild to moderate pancreatic inflammation 2. Damaged tissue replaced by fibrosis 3. Seen most often in middle-aged alcoholic males |
|
|
Chronic Pancreatitis: Causes |
1. Alcohol (Adults)
2. Cystic Fibrosis (Children) 3. Longstanding obstruction of duct by gallstones 4. Pancreas divisum |
|
|
Chronic Pancreatitis: Clinical Features |
1. Epigastric abdominal pain that radiates to the back 2. Pancreatic insufficiency- results in malabsorption w/ steatorrhea and fat soluble vitamin deficiencies. 3. Dystrophic calcification; "chain of lakes" pattern due to dilatation of ducts 4. Secondary Diabetes Mellitus 5. Increased risk for Pancreatic Carcinoma |
|
|
Chronic Pancreatitis: Morphology |
1. Densely fibrotic organ w/ atrophic exocrine glands 2. Chronic inflammation around the lobules 3. Ducts w/ proteinaceous plugs 4. Calcification seen grossly |
|
|
Pancreatic Pseudocyst |
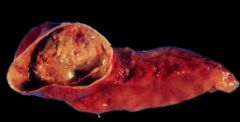
1. Cystic space formed by wall of fibrosis and filled w/ blood & necrotic tissue 2. No true epithelial lining 3. Caused by acute and chronic pancreatitis 4. May present as abdominal mass |
|
|
Tumors of the Pancreas |
1. Cystadenoma 2. Intraductal mucinous neoplasms 3. Adenocarcinoma **Arises from the exocrine portion of the pancreas, associated with cigarette smoking** |
|
|
Tumors of the Pancreas: Associations |
1. 60-70% arise in the head of the pancreas 2. Adenocarcinomas arise from ductal epithelium 3. Lesions of the head obstruct bile flow at the ampullary region 4. Body and tail lesions remain silent and invade adjacent tissue |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas |
1. Arises from ducts; very aggressive tumor 2. Associated with CA19-9 marker 3. Usually metastasized by presentation |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas: Risk Factors |
1. Tobacco Use 2. Chronic Pancreatitis (> 20 years) 3. Diabetes 4. Age > 50 years 5. Jewish and African American Males |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas: Clinical Features |
1. Abdominal pain radiating to the back 2. Weight Loss (due to malabsorption) 3. Migratory Thrombophlebitis- redness and tenderness on palpation of extremities (Trousseau Syndrome) 4. Obstructive jaundice w/ palpable, nontender gallbladder |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas: Treatment |
1. Whipple Procedure 2. Chemotherapy, Radiation |

