![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Ingestion |
The consumption of a substance by an organism e.g. drinking through the mouth |
|
|
Define absorption |
The process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across the tissues and organs through diffusion or osmosis, as in absorption of nutrients by the digestive system, or absorption of drugs into the bloodstream |
|
|
Define assimilation |
Combination of two processes to supply cells with nutrients. The first is the process of absorbing vitamins, minerals, and other chemicals from food within the gastrointestinal tract. |
|
|
Define egestion |
The discharge or expulsion of undigested material (food) from a cell in case of unicellular organisms, and from the digestive tract via the anus in case of multicellular organisms. |
|
|
2. Explain the process of peristalsis |
Series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the oesophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed |
|
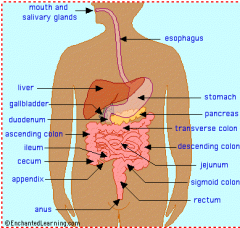
3. List the sequence of parts of the digestive tract that food passes through. |
Mouth and salivary glands Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine |
|
|
two functions of saliva |
-Moisten food, creating food bolus, easily swallowed -Contain the enzyme amylase which breaks down starches into maltose and dextrin5. |
|
|
two functions of the stomach acid |
Prevents amylase from working Carbohydrate digestion stops |
|
|
7. Describei) a physical effect of bile |
??????? |
|
|
Describe A chemical effect of bile. |
????????? |
|
|
8. What is chyme? |
The semifluid mass of partly digested food that is expelled by the stomach, through the pyloric valve, into the duodenum (the beginning of the small intestine). |
|
|
Learn |

|
|
|
10. Where does food get absorbed? |
Large intestine absorbs food molecule and water then transported into bloodstream |
|
|
11. Describe the features (at least 3) of the intestine wall which make absorption efficient |
- 20 feet long, therefore high SA, more nutrient absorbed - Peristalsis slows down movement of chyme to allow more time for absorption - Microvilli increase the SA of small intestine |
|
|
12. To where does the hepatic portal vein take food, and what happens to it there? |
Moves blood from the spleen and gastrointestinal tract to the liver. |
|
|
13. Explain the function of the lacteal inside each villus. |
Absorbs dietary fats in the villi of the small intestine. |
|
|
14. What is the main function of the large intestine? |
Absorb water from indigestible food matter and transit useless waste from body |
|
|
15. Explain the cause of the following digestive disordersa) Constipation |
Bowel movement occur less often than usual or consist of hard dry stools that are painful |
|
|
15. Explain the cause of the following digestive disorders Gastric reflux |
Acid in the stomach rises up into the oesophagus. This occurs because the valve separating the contents of the stomach from the oesophagus does not function properly. |
|
|
15. Explain the cause of the following digestive disorders c) Gastric ulcers |
An open sore usually found in the stomach, oesophagus or upper small intestine |
|
|
What is the epiglottis? |
-The thin elastic cartilaginous structure located at the root of the tongue that folds over the glottis to prevent food and liquid from entering the trachea during the act of swallowing.
|

