![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are carbohydrates digested generally?
|
by hydrolysis to form oligosaccharides, then free mono and disaccharides.
|
|
|
What is known as the increase in blood glucose after a test dose of a carbohydrate compared with that after an equivalent amount of glucose (as glucose or from a reference starchy food)?
|
glycemic index
|
|
|
Which sugars have a glycemic index of 1 (or 100%)?
|
On hydrolysis lactose, maltose, isomaltose, and trehalose give rise to glucose and galactose. So they have a glycemic index of 1
|
|
|
Which sugars are absorbed less rapidly and have a lower glycemic index?
|
Fructose, sugar alcohols, and sucrose
|
|
|
T/F: the glycemic index of starch varies from 0 to 1.
|
True
|
|
|
Why are foods that have a low glycemic index considered to be healthier?
|
They cause less fluctuation in insulin secretion.
|
|
|
Why do resistant starches and nonstarch polysaccharides cause gas?
|
they provide substrates for bacterial fermentation in the large intestine.
|
|
|
What else do bacteria use from the nonstarch polysaccharides?
|
butyrate and other short chain fatty acids for energy.
|
|
|
The hydrolysis of starch is catalyzed by which enzymes?
|
Salivary and pancreatic amylases.
|
|
|
Which bonds do amylases hydrolyze?
|
they catalyze random hydrolysis of alpha (1-4) glycoside bonds, yielding dextrins then a mixture of glucose, maltose, and maltotriose.
|
|
|
Where are disaccharidases found in the gut?
|
within the brush border
|
|
|
What can cause failure to thrive in infants when they are fed on breast milk or normal infant formula?
|
congenital deficiency of lactase
|
|
|
What enzyme is occasionally deficient among the Inuit, leading to sucrose intolerance with persistent diarrhea and failure to thrive when the diet contains sucrose?
|
Sucrase-isomaltase
|
|
|
What is the transport protein that absorbs both glucose and galactose via a Na+ dependent process in the SI?
|
SGLT 1
|
|
|
T/F: glucose and galactose compete for binding to SGLT 1.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F: other monosaccharides are absorbed by carrier-mediated diffusion.
|
True
|
|
|
What happens when there is a moderately high intake of fructose or sugar alcohols?
|
Some may remain in the lumen and get passed onto the LI where enterocytes ferment it.
|
|
|
What could occur with large intakes of fructose and sugar alcohols?
|
Osmotic diarrhea. (lots of fructose still in the lumen can cause water to follow it, leading to watery stool)
|
|
|
SGLT 1 transporter is coupled to what pump, allowing glucose and galactose to be pumped against their gradients?
|
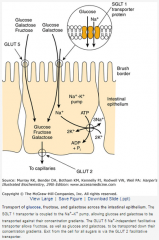
Na+/K+ pump
|
|
|
Which GLUT allows fructose as well as glucose and galactose to be transported down their concentration gradients?
|
GLUT 5 Na+ independent facilitative transporter
|
|
|
Which GLUT allows all sugars to exit cells?
|
GLUT 2
|

