![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
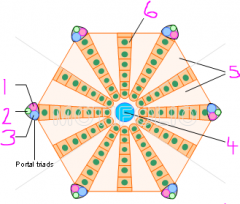
Hepatic lobule
|
1 - hepatic arteriole
2 - bile ductule 3 - portal venule 4 - central vein 5 - Sinusoidal endothelial cells (sinusoids) 6 - Hepatocytes |
|
|
Where do the sinusoids drain into?
|
Central vein
|
|
|
What do the central veins drain into?
|
Hepatic vein into the caudal vena cava
|
|
|
What are adjacent lobules separated by?
|
Connective tissue 9SMALL AMOUNTS EXCEPT IN PIG)
|
|
|
What is the main type of collagen found in the liver?
|
Type III (reticulin)
|
|
|
What does the portal triad consist of?
|
Hepatic arteriole
Portal venule Bile ductule Sometimes lymphatic vessel |
|
|
What is the blood like in the hepatic portal vein compared to the hepatic artery?
|
Portal vein - nutrient rich from GI tract
Hepatic artery - oxygen-rich |
|
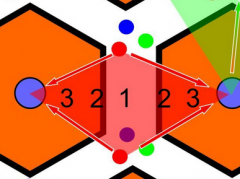
Describe the zones
|
Zone 1 - most oxygenated, closest contact to blood-borne toxins
Zone 3 - least oxygenated, furthest contact from blood-borne toxins |
|
|
Which way does bile drain?
|
From central vein to bile duct
|
|
|
What does bile travel through to reach the bile ductule?
|
Bile canaliculi through canal of Hering
To bile ductule to hepatic ductule |
|
|
What are the 3 types of membrane on the hepatocyte?
|
Apical - exchange with sinusoidal blood
Canalicular aspect - excreting bile Basolateral - communication with other hepatocytes |
|
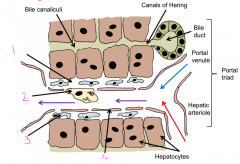
Name the cells
|
1 - Space of Disse
2 - Kupffer cell 3 - Ito (Stellate cell) 4 - Sinusoidal lining cell |
|
|
Name the functions of the liver
|
Metabolic processing of blood
Detoxification of drugs/toxins Activation/processing of drugs Removal of bacteria/erythrocytes Activation of vitamin D Bile synthesis Storage of glycogen Synthesis of plasma proteins |
|
|
What causes prehepatic jaundice?
|
Liver is normal but cannot cope with the excessive breakdown of erythrocytes (immune-mediated haemolytic anaemia), cannot exrete bilirubin fast enough
|
|
|
What causes hepatic jaundice?
|
Damage to the liver, cannot excrete normal bilirubin load
|
|
|
What causes post-hepatic jaundice?
|
Damage, obstruction, compression etc. of gall bladder or common bile duct. Bile cannot empty into small intestine
|
|
|
How may liver damage lead to oedema?
|
Liver not synthesising plasma proteins
Blood loses oncotic pressure, oedema in tissues |
|
|
How may liver damage lead to clotting disorders?
|
If liver not producing clotting factors/proteins
|
|
|
How may liver damage lead to hepatoencephalopathy?
|
Liver not detoxifying ammonia etc., may lead to brain function damage
|
|
|
How may liver damage lead to metabolic disease?
|
If liver unable to process dietary components, e.g. glycogen
|
|
|
Which liver enzyme tests are there?
|
Cell damage:
ALT - liver-specific AST GLDH - large animals Cholestasis: Alkaline phosphatase - cholestasis increased AP Gamma-glutamyl transferase - large animals and cats |
|
|
Which live function tests are there?
|
Bilirubin - increased serum bilirubin = jaundice
Bile acid - increased bile acids in serum after eating |

