![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
disintegration of the naturally occurring foodstuff into absorbable forms |
Digestion |
|
|
There are two factors in digestion: |
Primary and Secondary Factor |
|
|
different enzymes found in the juices of the different portions of the digestive tract |
Primary factor |
|
|
Give some examples of Secondary factor in digestion:
|
- Cooking - Mastication - movements of the stomach and intestines or what is known as peristalsis. - absorption from the intestines, - autodigestion |
|
|
the physical movement and breakdown of food which includes: |
-Swallowing -Peristalsis in stomach -contraction of the small intestine -contraction of the large intestine -defecation reflex |
|
|
Bolus is pushed toward the pharynx Voluntary movement |
Buccal stage |
|
|
-Bolus (masticated food with saliva) to pharynx to esophagus to stomach -Involuntary movement |
Pharyngeal and esophageal stage |
|
|
Mixes contents and forces chime thru the pylorus
|
Peristalsis in the stomach |
|
|
Three waves travel down the stomach one at a time
|
Peristalsis in the stomach |
|
|
In peristalsis the three waves, Each beginning every how many seconds near the midpoint of the stomach, lasting about how many minutes ?
|
20 seconds and 1 minute |
|
|
Feedback from the ________ regulates gastric emptying.
|
duodenum |
|
|
2 mechanisms that inhibit gastric motility |
1. Entrogastric reflex which is neuronal 2. Entrogastrone which is hormonal |
|
|
– partially digested food with gastric juices or mixed with gastric juices
|
Chyme |
|
|
Mix with saliva ? |
Bolus |
|
|
What are the 2 phenomenom in the contraction of the small intestine |
Segmenting and Gastroileal reflex |
|
|
rhythmic contractions along a section dividing it into segments |
Segmenting |
|
|
Primarily a mixing action |
Segmenting |
|
|
– the increase in ileal peristalsis and frequency of opening of the ileocecal valve due to the ingestion of food |
Gastroileal reflex |
|
|
2 contraction of the large intestines |
-Haustra -Gastrocolic reflex |
|
|
simultaneous contraction of circular and longitudinal muscle
|
Haustra |
|
|
– infrequent (twice a day) mass movement transferring contents from proximal to distal colon and into the rectum
|
Gastrocolic reflex |
|
|
Occurs shortly after meal |
Gastrocolic reflex |
|
|
a. Distention of rectum triggers intense peristaltic contractions of colon and rectum and relaxation or internal anal sphincter |
Defecation Reflex |
|
|
b. Reflex preceded by voluntary relaxation of external sphincter and compression of abdominal contents |
Defecation reflex |
|
|
DIGESTION in the MOUTH: |
Chemical and Mechanical |
|
|
Mechanical or Chemical; Chewing or mastication
|
Mechanical |
|
|
Mechanical or Chemical: Food manipulated by tongue, ground by teeth, and mixed with saliva
|
Mechanical |
|
|
Mechanical or Chemical ? • Forms bolus |
Mechanical |
|
|
Mechanical or Chemical: hydrolysis of starch by salivary amylase(ptyalin)
|
Chemical |
|
|
Mechanical or Chemical: takes place in the buccal cavity and to a certain extent in the fundic end of the stomach |
Chemical |
|
|
SALIVARY GLANDS RELEASE SALIVA: |
-ordinarily, just enough is secreted to keep mouth and pharynx mosit and clean-when food enters mouth, secretion increase to lubricate , dissolve, and begin chemical digestion. |
|
|
Colorless slightly viscid, opalescent fluid which is a mixture of secretions of the three pairs of salivary glands
|
Saliva |
|
|
three pairs of salivary glands and their location |
Parotid gland- behind the ears Sublingual gland - tounge Submandible gland- mandible |
|
|
section is watery and rich in ptyalin |
Parotid gland |
|
|
secretion is more viscid containing mucin and poorer in ptyalin |
Sublingual gland |
|
|
Organic component of saliva ? |
Water, ptyalin, & mucin |
|
|
Factors influencing the secretion of saliva |
Psychic Mechanical Chemical |
|
|
Identify what Factors influencing the secretion of saliva: Thinking what you are going to eat. |
Psychic factor |
|
|
Identify what Factors influencing the secretion of saliva: Presence of food in the mouth. |
Chemical factor |
|
|
Identify what Factors influencing the secretion of saliva: Chewing of gum |
Mechanical factor |
|
|
Average secretion per day? |
1500cc or ml |
|
|
Percent of organic components of saliva |
99.42 % water 0.58 % solid |
|
|
Organic and inorganic of saliva |
o 2/3 = org. matter (mucin, ptyalin,urea, glucose, lactic acid…)-o 1/3 = inorg. Salts (Cl-, HCO3 of Na, K, - -Ca, SO4 |
|
|
(active stimulation) ph of saliva |
7- 7.3 |
|
|
(resting saliva) ph of saliva
|
6.4-6.9 ph |
|
|
moisten and reduce the foods into a consistency suitable for swallowing |
Saliva |
|
|
SALIVARY AMYLASE Also known as ? |
Ptyalin |
|
|
Endoamylase which acts only on the? |
Alpha 1,4-glycosidic linkages |
|
|
Salivary amylase activators: |
Cl- & Br-; I- & NO3 |
|
|
Splits starch into the disaccharide maltose |
Salivary amylase or ptyalin |
|
|
SALIVARY AMYLASE is inactivated by ? |
Pepsin |
|
|
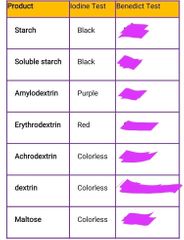
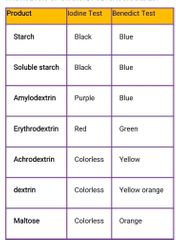
HYDROLYSIS OF STARCH/POLYSACCHARIDES |
>Starch>Soluble starch>Amylodextrin>Erythrodextrin>Achrodextrin>dextrin>Maltose |
|
|
Starch+ iodine |
Black |
|
|
Sol. Starch + iodine |
Black |
|
|
Amylodextrin + iodine |
Purple |
|
|
Erythrodextrin + iodine |
Red |
|
|
Achrodextrin + iodine |
Colorless |
|
|
Dextrine + iodine |
Colorless |
|
|
Maltose+ iodine |
Colorless |
|
|
Positive and negative result of iodine |
+ black to violet - yellow or no change |
|
Identify the result: |
|
|
|
Positive and negative result for benedict test |
+ blue - green to orange |

