![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the structure-function relationship in the G.I. tract?
|
Length and complexity of gut determined by ease of digestibility and processing of food
Short, simple gut = fast processing (carnivore) |
|
|
What processes are under control in the digestive system?
|
Mechanical processing (smooth muscle contraction)
Secretion of gastric juices Enzymatic breakdown Absorption |
|
|
What are the 2 ways in which digestion is controlled?
|
Neural and hormonal influences
|
|
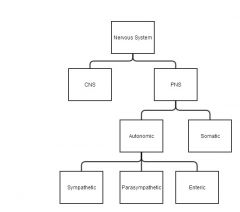
Which parts of the nervous system control the digestive system?
|
Autonomic and enteric
|
|
|
Give some examples of digestive hormones
|
CCK, gastrin, histamine
|
|
|
What is the sympathetic nervous system responsible for?
|
Fight or flight response
|
|
|
Which parts of the autonomic nervous system correspond to the intrinsic and extrinsic parts of the gut?
|
Intrinsic - enteric NS
Extrinsic - Parasympathetic and sympathetic |
|
|
Which part of the nervous system can reach the G.I. tract without communicating with the enteric NS?
|
Sympathetic NS
|
|
|
Which nerve connects the parasympathetic NS to the ENS?
|
Vagus (oesophagus to small intestine) and pelvic (large intestine)
|
|
|
What are pre-ganglionic fibres in the sympathetic nervous system?
|
Fibres from CNS to prevertebral ganglia (where synapse occurs e.g. coeliac ganglia)
|
|
|
What are post-ganglionic fibres in the sympathetic nervous system?
|
Fibres between prevertebral ganglia to effector organ
|
|
|
What are the neurotransmitters in the pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic fibres?
|
Pre-ganglionic - acetylcholine
Post-ganglionic - noradrenaline |
|
|
What is the difference between post-ganglionic fibres in the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
|
Post-ganglionic fibres in the parasympathetic NS are enteric neurones because pre-ganglionic fibres synapse in the enteric NS
|
|
|
Where do pre-ganglionic fibres of the vagus nerve and the pelvic nerve arise from, respectively?
|
Vagus nerve - medulla
Pelvic nerve - S2 - S4 |
|
|
In the parasympathetic NS, which fibres are excitatory and inhibitory?
|
Pre-ganglionic - excitatory
Post-ganglionic - excitatory or inhibitory |
|
|
What is the neurotransmitter of pre-ganglionic fibres of parasympathetic NS?
|
Acetylcholine
|
|
|
Which parts of the digestive system are innervated somatically?
|
Pharynx/oesophagus
External anal sphincter For swallowing and defaecating |
|
|
Which nerves control swallowing and defaecating?
|
Swallowing - vagus nerve
Defaecating - pudendal nerve |
|
|
Does the enteric NS need CNS control?
|
Reflexes can operate independently of CNS
|
|
|
What does the enteric NS control?
|
Motility, fluid movement and blood flow
|
|
|
Where is the myenteric plexus found?
|
Between the outer longitudinal muscle and the inner circular muscle of muscularis propria layer
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of neurone found in the enteric NS?
|
Motor
Sensory Interneurone |
|
|
What is an interneurone?
|
The connection between motor and sensory neurones
|
|
|
Name 4 enteric neurotransmitters
|
Vasoactive intestinal peptide
Acetylcholine Substance P Nitric oxide |
|
|
Can more than one neurotransmitter be found in a neurone?
|
Yes (record is 7)
|
|
|
Where is the submucous plexus found?
|
Between inner circular muscle and submucosa
|

