![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the types of sinus rhythms.
|
sinus rhythm
sinus bradycardia sinus tachycardia sinus arrhythmia SA block sinus arrest |
|
|
List EKG leads and whether they are frontal or horizontal and bipolar or unipolar.
|
frontal
-bipolar → lead I, II, III -unipolar → aVL, aVR, aVF horizontal + unipolar → V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6 |
|
|
List the 3 functional activities of the heart.
|
1. automaticity
2. conductivity 3. contraction |
|
|
List frontal and horizontal leads and whether they are bipolar or unipolar.
|
FRONTAL:
bipolar → leads I, II, III unipolar → aVR, aVL, aVR HORIZONTAL: unipolar → V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6 |
|
|
List the limb leads.
|
standard → leads I, II, III
augmented → aVR, aVL, aVF |
|
|
List the precordial chest leads.
|
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6
|
|
|
List the steps for interpreting an EKG.
|
1. rate
2. rhythm → regular or irregular (regularly irregular or irregularly irregular)? 3. p wave → present or absent, upright or inverted, followed by QRS complex? 4. pr interval → 3-5 small boxes, fixed or variable? 5. QRS complex → <3 small boxes? 6. ST segment → isoelectric, elevated or depressed? 7. T wave → upright or inverted? |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of normal sinus rhythm.
|
1. rate → 60-100 bpm
2. rhythm → regular 3. p wave → present, upright, followed by QRS complex 4. pr interval → 3-5 small boxes, fixed 5. QRS complex → <3 small boxes 6. ST segment → isoelectric 7. T wave → upright |
|
|
Torsades des Pointes
|
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hyponatremia?
|
no significant changes
|
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hypernatremia?
|
no signficant changes
|
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hypokalemia?
|
flattened R wave
widened QRS complex peaked T wave |
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hypokalemia?
|
flattened or inverted T wave
prominent U wave |
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hypocalcemia?
|
prolonged QT interval
|
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hypercalcemia?
|
shortened QT interval
|
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hypomagnesemia?
|
diminished p wave
diminished and slightly widened QRS complex flattened T wave prominent U wave |
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with hypermagnesemia?
|
prolonged pr interval and QRS complex
elevated T wave |
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen with digitalis?
|
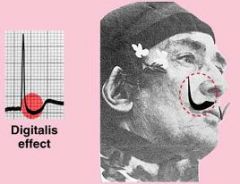
downsloping ST segment (think Salvador Dali's mustache)
|
|
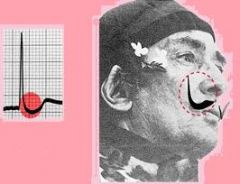
What does this EKG indicate?
|
digitalis effect
|
|
|
What leads indicate a bundle branch block?
|
V1, V2
|
|
|
If a right bundle branch block is present, you cannot diagnose hypertrophy, axis, or MI, true or false?
|
false
you can't diagnose hypertrophy or axis but you can diagnose MI |
|
|
If a left bundle branch block is present, you cannot diagnose hypertrophy, axis, or MI, true or false?
|
true
|
|
|
What is the intrinsic heart rate of the SA node, atria, AV node, bundle of his, purkinje fibers, and ventricles?
|
SA node → 60-100
atria → 55-60 AV node → 50-55 bundle of his → 45-50 purkinje fibers → 40-45 ventricles → 35-40 |
|
|
What is overdrive suppression?
|
Suppression of the automaticity and independent
depolarization of cells with pacemaker potential by tissues firing at a higher intrinsic rate of automaticity. This is why the SA node normally functions as the pacemaker of the heart, despite the presence of other tissues that possess automaticity. |
|
|
What is the only route of conduction from the SA node to the left atria?
|
Bachman's bundle
|
|
|
What is the only route of conduction from atria to ventricles?
|
bundle of His
|
|
|
Describe Einthoven's Triangle.
|
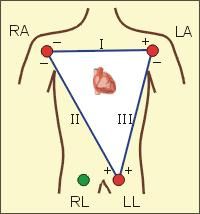
|
|
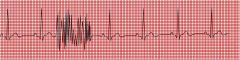
|
artifact
|
|
|
List common causes of artifact.
|
AC interference
loose electrode or broken wire muscle tremor |
|
|
What are the 4 ways to calculate rate?
|
1. 6 second method → count number of QRS complexes in 30 boxes → multiply by 10
2. large box method → count number of large boxes between 2 QRS complexes → divide by 300 3. small box method → count number of small boxes between 2 QRS complexs → divide by 1500 4. sequence method → count down 300-150-100-75-60-50-43 (each number falls on a big box starting at a QRS complex and ending at the next one) |
|
|
What is the only method you can use to calculate rate if the rhythm is irregular?
|
6 second method
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of sinus bradycardia.
|
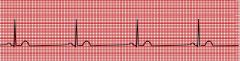
1. rate → <60 bpm
2. otherwise normal *can be clinically normal in athletes or during sleep |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of sinus tachycardia.
|
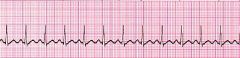
1. rate → 101-180
2. otherwise normal |
|
|
What are the characteristics of sinus arrhythmia?
|
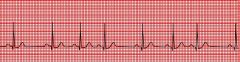
irregular discharge of SA node
|
|
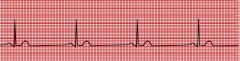
|
sinus bradycardia
|
|
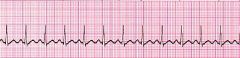
|
sinus tachycardia
|
|
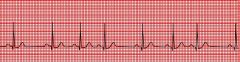
|
sinus arrhythmia
|
|
|
Is sinoatrial block an automaticity or conductivity problem?
|
conductivity → impulse generated by SA node but not conducted to atria
|
|
|
Is sinus arrest an automaticity or conductivity problem?
|
automaticity → impulse failed to generate
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of sinoatrial block?
|
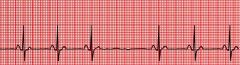
appears as missed beat
underlying rhythm not reset |
|
|
What are the characteristics of sinus arrest?
|
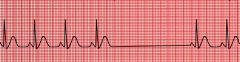
does not correspond with missed beat
underlying rhythm may be reset with ectopic pacemaker |
|
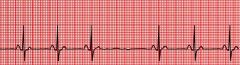
|
sinoatrial block
|
|
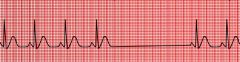
|
sinus arrest
|
|
|
What are the rates of idioatrial, idiojunctional, and idioventricular rhythms?
|
idioatrial → 60-80
idiojunctional → 40-60 idioventricular → 20-40 *can be accelerated above inherent rate |
|
|
How do you differentiate between PJCs and PVCs?
|
both have no p wave
PJCs → QRS complex <3 small boxes PVCs → QRS complex >3 small boxes |
|
|
Which atrial dysrhythmias are due to altered automaticity and which are due to reentry?
|
altered automaticity → PACs, wandering pacemaker, MAT, A-fib
reentry → SVT → AVNRT, AVRT, WPW, A-flutter |
|
|
What are the characteristics of PAC?
|
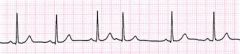
atrial ectopic focus
premature beat p wave present but morphology different than other p waves resets underlying rhythm |
|
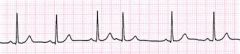
|
PAC
|
|
|
What are the causes of PAC?
|
often innocuous
may be caused by stress, fatigue, atrial enlargement, ischemia, CHF, hyperthyroidism, electrolyte disturbance, drug use, digitalis toxicity |
|
|
Palpitations may indicate what type of rhythm?
|
PAC
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of wandering pacemaker?
|
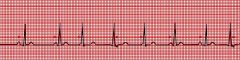
SA node alternating with ectopic atrial foci
rate <100 p wave morphology varies |
|
|
What are the characteristics of multifocal atrial tachycardia?
|
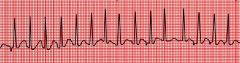
same as wandering pacemaker except rate >100
requires 3 different p wave morphologies |
|
|
Multifocal atrial tachycardia is commonly seen in what patient population?
|
COPD
|
|
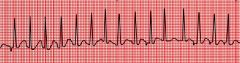
|
MAT
|
|
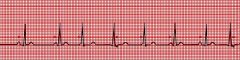
|
wandering atrial pacemaker
|
|
|
Wolf-Parkison-White is a type of what type of dysrhythmia?
|
AVRT
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of WPW?
|
no pr interval
wide QRS complex and delta wave |
|
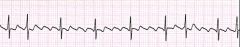
|
atrial flutter
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of atrial flutter?
|
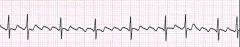
reentrant circuit in atria
regular rhythm sawtooth pattern of p waves |
|
|
Is atrial flutter characterized by a regular or irregular rhythm?
|
regular
|
|
|
How is atrial fibrillation managemed?
|
B-blockers, CCB, digoxin, warfarin
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of atrial fibrillation?
|
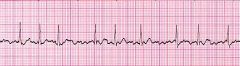
irregularly irregular
no distinct p waves |
|
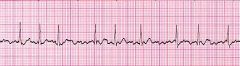
|
atrial fibrillation
|
|
|
The AV node contains pacemakers cells, true or false?
|
false!
|
|
|
What are the EKG characteristics of PJC?
|
p wave absent, inverted, or after QRS complex due to retrograde conduction
pr interval shortened |
|
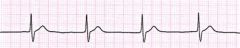
|
junctional rhythm
|
|
|
What are the rates of junctional escape rhythm, accelerated junctional rhythm, junctional tachycardia?
|
junctional escape rhythm → 40-60
accelerated junctional rhythm → 61-100 junctional tachycardia → >100 |
|
|
What are the characteristics of junctional rhythms?
|
rhythm regular
p waves inverted, absent, or after QRS complex |
|
|
What is sick sinus syndrome?
|
tachy-brady syndrome
alternating sinus bradycardia or junctional rhythm with atrial fibrillation |
|
|
What are the characteristics of PVCs?
|
rhythm irregular
inverted T wave |
|
|
What is an R-on-T PVC?
|
PVC that occurs during T wave
can cause V-tach or V-fib |
|
|
What are the causes of pulseless electrical activity?
|
use the mnemonic MATCHED
M - MI A - acidosis T - tension pneumothorax C - pericardial tamponade H - hypoxia, hypthermia, hypokalemia, hypovolemia (most common) E - PE D - OD |
|
|
What is the double-thumbs up sign?
|
refers to axis deviation
both lead I and aVF QRS complexes are positive so no axis deviation |
|
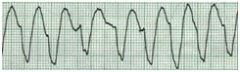
|
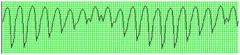
ventricular tachycardia
|

