![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
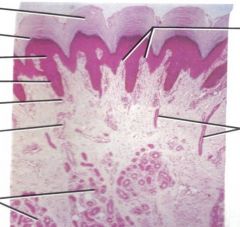
Identify structures
|
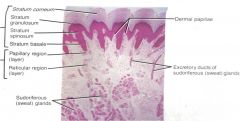
|
|
|
Name the 3 main layers of skin structure;
|
Epidermis
Dermis Subcutaneous fatty tissue |
|
|
Skin is the largest organ, measuring approx:
|
18 square feet and weighing 12 lbs
|
|
|
Name at least 5 functions of skin;
|
protective barrier
light touch sensation thermoregulation regulates and preserves body fluid assist with excretion begins endogenous production of vitamin D Cosmetic covering and personal identity |
|
|
T or F, normal pH of skin is acidic?
|
True, 4.2 to 5.6 normally
|
|
|
T or F, the statum corneum, granulosum, spinosum and basale are all part of the epidermis?
|
True
|
|
|
The dermis consist of what two layers?
|
papillary (layer) region and the reticular (layer) region
|
|
|
Stratum basale is the ( ) layer.
|
deepest
|
|
|
The statum lucidum is mainly composed of?
|
clear, flat, dead keratanocites
|
|
|
T or F, the stratum corneum is the thickest layer of skin, the visible outer layer, and all its cells are alive?
|
False, cells are dead
|
|
|
Name 4 epidermal cell types:
|
keratinocytes
melanocytes langerhans cells merkel cells |
|
|
The most abudant cell type in the epidermis is?
|
keratinocytes
|
|
|
This cell is responsible for skin pigment.
|
melanocyte
|
|
|
These epidermal cells detect foriegn material.
|
langerhans cells
|
|
|
Merkel cells are ( ) detectors.
|
sensory
|
|
|
The papillary layer of the dermis consist of mainly?
|
loose fibers and ground substance
|
|
|
The reticular layer of the dermis consist of dense fibers and provides ( ).
|
structural support
|
|
|
T or F, the epidermis is very vascular?
|
False, its avascular and relies on the dermis for its blood supply
|
|
|
The reticular layer is important for ( ) and is where your ( ) are.
|
elasticity
vessels |
|
|
Name at least 5 dermis cell types.
|
fibroblast
macrophages WBC Mast cells Meissner's corpuscles Pacinian corpuscles |
|
|
These cells are the builders when a wound occurs.
|
fibroblast
|
|
|
These cells cause the release of histamine.
|
Mast cells
|
|
|
These cells are in the papillary layer and are sensitive to light touch.
|
Meissner's corpuscles
|
|
|
In the reticular layer, these cells sense pressure.
|
pacinian corpuscles
|
|
|
T or F, humans have control over erector pille muscles?
|
False, activated when were cold or scared (think goosebumbs)
|
|
|
Name 3 functions of the dermis:
|
supports and nourishes epidermis
houses epidermal appendages assist with infection control (phagocytosis) assist in thermoregulation provides sensation |
|
|
Briefly describe how vessels of the dermis assist with thermoregulation.
|
Vessels in the dermis restrict when we are cold causing warm blood to move to the core of the body so vital organs are taken care of. When were flushed from heat exposure, these same vessels dialate to help dissapate heat.
|
|
|
The subcutaneous layer consist mainly of?
|
adipose tissue
fascia deep lymphatics |
|
|
Name the 4 functions of adipose tissue (fat).
|
heat insulation
cushioning provides energy stores fat-soluble vitamins |
|
|
This tissue appears black in wounds and should be removed.
|
necrotic
|
|
|
A wound that penetrates the epidermis and dermis, but not completely thru the dermis is considered a?
|
partial thickness wound
|
|
|
This type of wound is often the result of abbrasions, 1st degree burns and only penetrates into the epidermis.
|
Superficial
|
|
|
This wound penetrates into the subcutaneous tissue (subdermal).
|
full thickness
|
|
|
Wound healing occurs in 3 phases:
|
Latent phase
proliferative phase repair phase remember different books will have different names |
|
|
T or F, all phases of healing overlap?
|
True
|
|
|
The epidermis heals by ( ) from the wound edges.
|
epithelialization
|
|
|
epitheliazation typically takes how long in a healthy individual
|
2 wks
|
|
|
If the dermis is destroyed, healing must occur through?
|
granulation and contraction or through grafting- may take weeks, months, or years
|
|
|
Rubor, calor, tumor, and dolar are all signs that you are in what phase of healing?
|
inflammatory phase
|
|
|
The inflammatory phase generally last?
|
24 - 48 hrs and up to two weeks
|
|
|
Brief description of the inflammatory phase:
|
purpose is control bleeding and prevent bacterial invasion, sends signals to other cells to begin repair process, vascular and cellular responses occur
|
|
|
Part of the vascular response of the inflammatory phase consist of allowing blood to leak out of injured vessels, this blood is called?
|
transudate
|
|
|
Transudate is responsible for:
|
localized edema which creates pressure and serves to restrict blood loss
|
|
|
Clots seal lymph channels off which causes:
|
more swelling
|
|
|
During inflammation, activated platelets release chemical mediators such as?
|
cytokines
growth factors chemotactic agents |
|
|
Cytokines are a kind of?
|
signal protein
|
|
|
Chemotactic factors serve to?
|
attract other cells to help heal the wound
|
|
|
Histamine causes:
|
vasodialation
|
|
|
Part of the inflammatory response consist of the release of?
|
exudate (WBCs and protein)
histamine prostaglandins |
|
|
This cell forms a platelet plug to control bleeding and secretes both growth and chemotactic factors.
|
platelets
|
|
|
This cell is the FIRST cell to the site of the injury, a scavenger, kills bacteria, cleans wound, and secretes inflammatory mediators and MMPs.
|
PMNs
|
|
|
This cell DIRECTS the repair process, assist with killing bacteria, wound cleaning, and secretes GROWTH FACTORS and MMPs
|
macrophage
|
|
|
Secretes enzymes and inflammatory mediators.
|
mast cell (remember histamine)
|
|
|
PMNs (polymorphonuclear neutrophils) are first responders to a wound and work by 3 processes.
|
margination
diapedesis chemotaxis |
|
|
A good indication of the proliferative phase would be?
|
1. the presence of endothelial buds in the wound bed signifies angiogenesis
2. pale pink epithelial cells at wound edge are evidence of epithelialization |
|
|
Angiogenesis, granulation of tissue and contraction all occur in what phase of healing?
|
proliferative phase (at the same time)
|
|
|
Granulation usually occurs ( ) to ( ) days after injury and can occur up to ( ) days depending on the patient.
|
2
4 21 |
|
|
Cell responsible for angiogenesis?
|
angioblasts
|
|
|
angiogenesis is important because?
|
provides nutrition to wound and takes out waste
|
|
|
Matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) are responsible for the?
|
breakdown of materials and which leads to debris during the healing proces
|
|
|
Fibroblast lay down ( ) and fill gaps made by ( )
|
ground substance
MMPs |
|
|
What is very important to remember about tissue layed down during the proliferative phase?
|
its still very delicate
|
|
|
T or F, proper wound healing consist of fibroblast building a disorganized matrix that works its way from the top to the bottom of the wound?
|
False, good wound healing occurs from the bottom UP
|
|
|
Process in which myofibroblast within the matrix of collagen fibers shorten the fibers.
|
wound contraction
|
|
|
granulation tissue is what color?
|
beefy red, shiny and granular in appearance (you want to see this)
|
|
|
T or F, linear wounds heal quicker than circular wounds?
|
true
|
|
|
What is a big concern when a wound crosses a joint in the body?
|
loosing ROM as the tissue contracts
|
|
|
Epithelialization begins?
|
immediately after trauma and occurs concurrently throughout healing
|
|
|
Epitheliazation basically occurs as?
|
cells migrate over oxygen rich scaffolding, and is complete when the wound is completely closed (wound still continues to heal and mature)
|
|
|
Why is smoking not a good idea if you want a wound to heal?
|
proper nutrition is important for epithelialization to occur, so you need blood flow to the injured area. This is inhibited by cigarette smoking.
|
|
|
Remodeling and maturation occur as?
|
new collagen is synthesized and old collagen is broken down by collagenases
|
|
|
Two theories explain how collagen fibers reorientate
|
induction theory and tension theory
both theories are used with scar massage |
|
|
Maturation and remodeling may occur up ( ) yrs after wound closure and will only have about ( )% of its original strength/elasticity.
|
2
80 |
|
|
Surgical incisions and paper cuts often close by
|
primary closure (primary intention)
|
|
|
Tertiary intention or delayed primary closure is used when?
|
time is needed to cleanse and debride the wound because contaminants may still be deep in the wound. Early closure would trap contaminants and lead to an abscess.
|
|
|
When larger, deeper wounds, left open, follow normal phases of wound healing and develop scar tissue, this is called?
|
secondary closure or secondary intention
|
|
|
For secondary closure to occur, ( ) tissue must be produced to fill the wound before epithelialization.
|
granulation
|
|
|
Abnormal wound healing can occur due to:
|
senescent cells (barely alive)
higher levels of MMPs lower levels of tissue inhibitors of matrix (TIMPs) greater numbers of inflammatory cytokines and chronic wound cells |
|
|
What can lead to the abscence of inflammation?
|
high steriod use, elderly, immune disorders
|
|
|
Some common causes of chronic inflammation are?
|
the presence of foreign body in wound bed
repetitive mechanical trauma cytotoxic agents |
|
|
These agents kill healthy skin and prolonge the inflammatory phase.
|
cytotoxic agents
|
|
|
Hypogranulation occurs when?
|
no wound bed is coming up from the bottom of the wound (contact inhibition)
|
|
|
Hypergranulation may be caused by excess use of?
|
whirlpools
|
|
|
Hypertrophic scarring often occurs in?
|
normal skin folds or tension points in the skin
|
|
|
Keloid scars start as an initial wound then.
|
scar spreads all over and is raised
|
|
|
Contractures often occur?
|
when burn scars travel across parts of the body, shorten and restrict movement
|
|
|
Dehiscence is essentially a wound that has
|
opened (usually occurs in diabetics, the malnourished, and obese individuals)
|

