![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
3 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acute kidney failure - RENAL FAILURE
|
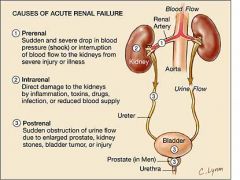
Acute kidney failure is the rapid loss of ones kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in the body (rapid means less than 2 days).
|
|
|
OSTEOARTHRITIS - OA
|
Osteoarthritis is a normal result of aging. It is also caused by 'wear and tear' on a joint.
Cartilage is the firm, rubbery tissue that cushions your bones at the joints, and allows bones to glide over one another. If the cartilage breaks down and wears away, the bones rub together. This causes pain, swelling, and stiffness. Bony spurs or extra bone may form around the joint. The ligaments and muscles around the joint become weaker and stiffer. Often, the cause of OA is unknown. It is mainly related to aging. The symptoms of OA usually appear in middle age. Almost everyone has some symptoms by age 70. However, these symptoms may be minor. Before age 55, OA occurs equally in men and women. After age 55, it is more common in women. |
|
|
Atrial fibrillation
|
Atrial fibrillation (A-tre-al fi-bri-LA-shun), or AF, is the most common type of arrhythmia (ah-RITH-me-ah). An arrhythmia is a problem with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat. During an arrhythmia, the heart can beat too fast, too slow, or with an irregular rhythm.
AF occurs if rapid, disorganized electrical signals cause the heart's two upper chambers—called the atria (AY-tree-uh)—to fibrillate. The term "fibrillate" means to contract very fast and irregularly. In AF, blood pools in the atria. It isn't pumped completely into the heart's two lower chambers, called the ventricles (VEN-trih-kuls). As a result, the heart's upper and lower chambers don't work together as they should. |

