![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
metabolic syndrome |
up to 25% of population; insulin resistance exacerbated by obesity, a/w polycystic ovary syndrome; a/w acanthosis nigricans; hyperinsulinemia, lipid abn |
|
|
insulin effects on liver |
incr. glycogen synthesis, incr. lipogenesis, decr. gluconeogenesis |
|
|
insulin effects on adipose tissue |
incr. glucose uptake & lipogenesis, decr. lipolysis |
|
|
insulin effects on striated muscle |
incr. glucose uptake & synthesis, incr. protein synthesis |
|
|
type I DM etiology |
genetics = HLA-DR3 or -DR4; triggered by environmental event (coxsackie B4 virus?); acute insulitis -> most beta cells destroyed |
|
|
type 2 DM etiology |
10% of population > 70; genetics (AD, transcription factor on chromosome 10q); western life style |
|
|
Type 2 DM |
inability of peripheral tissues to respond to insulin (insulin resistance) = decr. # of insulin receptors, reduced GLUT-4 transport; B cell dysfunction (amylin role); obesity |
|
|
acute complications of DM |
decr. tissue glucose utilization; incr. lipolysis (FFA), incr. protein catabolism (AA), glucagon excess -> gluconeogenesis -> hyperglycemia + ketogenesis; polyuria -> volume depletion -> polydipsia |
|
|
diabetic ketoacidosis |
insulin deficiency -> excessive breakdown of adipose stores -> incr. FFA -> oxidized to ketone bodies = metabolic ketoacidosis! esp. in Type 1 |
|
|
non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma |
severe hyperglycemia, dehydration of brain/cerebral cortex, can't drink water; esp. in Type 2 |
|
|
advanced glycosylation end products |
non-enzymatic glycosylation (glucose attaches to protein w/o enzymes) -> form AGE's -> cross link on proteins to trap LDLs + bind to RAGE on inflammatory cells (release infl. cytokines) |
|
|
activation of protein kinase C |
intracellular hyperglycemia -> DAG -> PKC -> proangiogenic VEGF + incr. vasoconstrictor endothelin + incr. profibrinogenic TGF + incr. proinfl. cytokines |
|
|
intracellular hyperglycemia occurs in... |
nerve, lens, kidney, blood vessels |
|
|
intracellular hyperglycemia causes... |
glucose -> sorbitol -> fructose = accelerated decr. in NADPH = less glutathione = cells cannot handle oxidative stress; incr. osmolarity + influx of water; damages Schwann cells & pericytes |
|
|
islet changes in diabetes |
reduced size & number (type 1); degranulation, fibrosis, leukocytic infiltration (type 1); amyloid-like replacement (type 2) |
|
|
diabetic microangiopathy |
thickened BM, incr. collagen type IV, incr. proteoglycans |
|
|
Atherosclerotic vascular disease in DM |
hyperlipidemia (incr. HDL and platelet adhesiveness); many are obese, HTN |
|
|
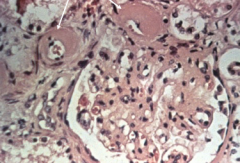
thickening of arterioles in DM |
|
|
nephropathy |
glomerulosclerosis + nephrosclerosis = decr. GFR; incr. bacterial urinary infections and papillary necrosis |
|
|
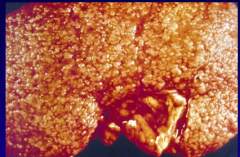
nephrosclerosis due to severe vascular disease |
|
|
small vessel insufficiency |
comes on slowly, doesn't hurt; both nerves & vessels shot due to peripheral neuropathy + atherosclerosis |
|
|
ocular changs |
retinopathy, cataract formation, glaucoma |
|
|
retinopathy |
non-proliferative and proliferative types; microaneurysms (due to loss of pericytes) |
|
|
islet cell tumors |
hyperinsulinism beta cell, zollinger-ellison syndrome, nonfunctional neuroendocrine tumors, multiple endocrine neoplasia |
|
|
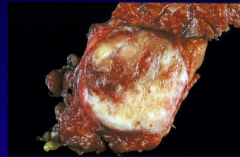
islet cell tumors (non-functional) - neuroendocrine |
|
|
rare islet cell tumors |
glucagonoma (alpha cell tumor), somatostatinomas (gamma cell tumor), VIPoma (watery diarrhea, hypoK, achlorhydria), pancreatic neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumors |

