![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1) Define pharmacology
2) Define Medical Pharmacology |
1)The study of substances that interact with living systems through chemical processes
2)Study of substances used to prevent, diagnose, or treat disease |
|
|
Define Toxicology
|
The branch of pharmacology which deals with the undesirable effects of chemicals on living systems
|
|
|
Define Pharmacogenomics
|
relation of the individual’s genetic make-up to his/her response to specific drugs
|
|
|
Define "Drug"
|
Substnce which brings about a change in biological function through chemical actions at a receptor
|
|
|
Define Hormone
|
Drug synthesized within the body
|
|
|
Define poison
|
Drugs that have almost exclusively harmful effects.
|
|
|
Define Toxin
|
poisons of biological origin (from plants or animals)
|
|
|
Define Xenobiotic
|
Drugs not synthesized in the body
|
|
|
1) Optimal drug size is MW= ?
2) Why bad if too low? 3) why bad if too high? |
1) 0.1 - 1 kD
2) may not be specific enough 3) problems with diffusion |
|
|
Which type of drug-receptor bond is ALWAYS short range and is mainly responsible for controlling dissociation and specificity?
|
Hydrophobic (Van der Wall)
|
|
|
Why is SC-558 (approx =Celebrex) selective for COX-2.
|
The additional steric interaction of the drug Sulphonamide moiety with Ile (COX-1) over Val (Cox-2) blocks binding of SC-558 to COX1
|
|
|
Argatroban is an inhibitor of?
|
Thrombin
|
|
|
1) k1 (association constant) is limited by?
2) what factors influence this limit? |
limited by diffusion to 6.5 108 M-1s-1
influenced by dimensionality, electrostatics, solution conditions |
|
|
Specificity is mainly controlled by which kinetic parameter?
|
k-1 ( dissociation constant)
|
|
|
k-1 is limited by?
|
No upper limit
|
|
|
How does the rate of equilibration of a system (L, R, and RL) relate to the timescales of the dissociation and dissociation?
|
Equilibrium is always reached faster than the fastest time scale
|
|
|
How do we calculate a:
1) Association time constant (tau)? 2) Dissociation time constant (tau)? |
1) 1 / (k1 x [L])
2) 1 / k-1 |
|
|
1)Define Kd and give it's units.
2) describe what higher and lower values mean in terms of affinity. |
Kd (M) is the equlibrium dissociation constant which is the concentration of FREE ligand when the receptor is 50% occupied,
2) The lower the Kd, the higher the affinity. |
|
|
Ka is the association constant.
1) What are its units? 2) A higher Ka means what in terms of affinity? |
1) 1/M
2) higher Ka means higher affinity. |
|
|
Give another way to mathematically represent Kd
|
[L]50
|
|
|
Given another way to represent [RL]50
|
[R0] / 2
|
|
|
The more negative the Delta H the ________ the affinity of L for R
|
Higher
|
|
|
The more _________ the delta S, the higher the affinity of L for R
|
positive
|
|
|
Each tenfold increase in __1___ decreases Delta G by ____2____
|
1) Ka
2) 1.4 kcal/mol at 37C |
|
|
delta H greater than zero means ____thermic
|
endothermic
|
|
|
Define induced fit
|
When R binds L, a conformational change occurs
such that RL goes to R*L. R* and L have a greater affinity than R and L. Affinity is enhanced over initial step of recognition |
|
|
Selective binding
|
you know this, it is the thing where R is in an eq with R* and L bind R* to drive the equilibrium in a LeChatelier kind of way.
|
|
|
Define Allosteric binding
|
L binds preferentially (not exclusively) to one conformation
affinity is decreased or increased relative to the step of recognition |
|
|
1)Define Kcat
2) give its units |
1) turn over ate
2) 1/s (per second) |
|
|
1) Define Km
2) give its units |
1) [S] at half Vmax
2) Molar |
|
|
1) What is the specificity constant?
2) units? 3) what limits it? |
1) Kcat/Km
2) M-1s-1 3) diffusion |
|
|
Lineweaver Burk plot:
1) x-int = ? 2) y-int = ? 3) slope = ? 4) units of x-axis? |
1) -1/Km
2) 1/Vmax 3) Km/Vmax 4) 1/[S] 5) 1/Vo |
|
|
Competitive inhibition
1) Change in Vmax? 2) Change in Km? 3) define |
1) no
2) increase 3) I binds only to E |
|
|
Un-competitive inhibition:
1) Change in Vmax? 2) Change in Km? 3) define |
1) Decrease
2) Decrease (proportional) 3) I binds only to ES |
|
|
Non-competitive Inhibition
1) Change in Vmax? 2) Change in Km? 3) define |
1) Decrease
2) same 3) I binds to E or ES |
|
|
Give an alternate way to describe Kcat
|
k for ES to E +P
|
|
|
1) define Tight binding inhibition
2) slope of T vs. [P] curve goes to? |
1) inhibitor binding /dissociation rates are slow
2) constant positive slope |
|
|
1) define Irreversible inhibition
2) slope of T vs. [P] curve goes to? |
1) inhibitor will not release E
2) slope goes to zero |
|
|
what kind of inhibitor
|
competitive
|
|
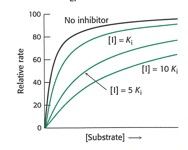
what kind of inhibitor
|
competitive
Vmax same Km increase |
|
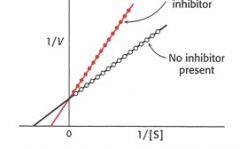
what kind of inhibitor?
|
competitive
Vmax same Km increase |
|
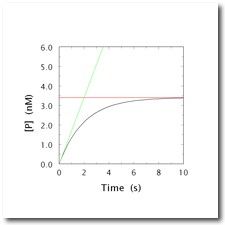
what kind of inhibitor?
|
irreversible
|
|
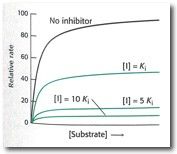
what kind of inhibitor?
|
non-competitive
Km same Vmax Decreases |
|
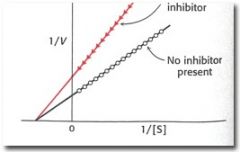
what kind of inhibitor?
|
non-competitive
Km same Vmax Decreases |
|
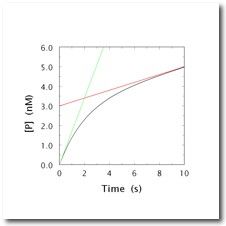
what kind of inhibitor?
|
tight-binding
|
|
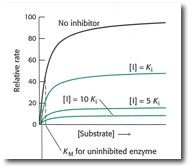
what kind of inhibitor?
|
uncompetitive
Km and Vmax both decrease |
|
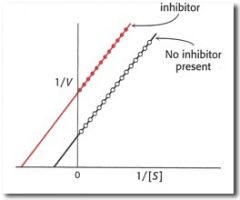
what kind of inhibitor?
|
uncompetitive
Km and Vmax both decrease |

