![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The liver acts as a ____________________ through which the sonographer can view many of the internal abdominal structures, including the right kiney, gallbladder, pancreas, biliary ducts, proximal inferior vena cava, and aorta. |
natural acoustic window |
|
|
The right lobe of the liver is covered by the ____________. |
ribs |
|
|
The left lobe of the liver lies in the midline just posterior to the _________. |
sternum |
|
|
The fundus of the stomach lies ____________ and _______________ to the left lobe of the liver. |
posterior; lateral |
|
|
The normal, healthy liver appeares diffusely uniform, meaning it should appear ____________. |
homogenous |
|
|
The normal liver is homogenous and is slightly more ___________ compared to the normal renal cortex. |
hyperechoic |
|
|
What does hyperchoic mean? |
Echoes greater than |
|
|
What does anechoic mean? |
Free of echoes |
|
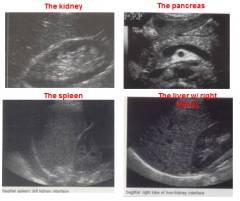
Out of the following structures, which is the most hypoechoic? |
The renal cortex |
|
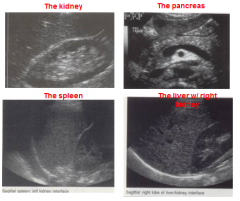
Out of the following structures, which is the most hyperechoic? |
The renal sinus |
|
|
To determine whether the liver's echogenicity is normal, compare the gray scale of the liver to what? |
The cortex of the right kidney |
|
|
The liver parenchyma is only slightly more echogenic than the _____________. |
cortex of the right kidney |
|
|
The cortex of the kidney is slightly more _____________ compared with the normal liver parenchyma. |
hypoechoic |
|
|
The kidneys are isoechoic or ____ echogenic than the liver. |
less |
|
|
The spleen is isoechoic or ____ echogenic than the liver. |
less |
|
|
The pancreas is isoechoic or ____ echogenic than the liver. |
more |
|
|
The liver develops from which region of the primary gut? |
The foregut |
|
|
During prenatal development, which process is responsible for the formation of hepatocytes and the development of the liver? |
Hematopoiesis |
|
|
The surface of the liver which rests upon the abdominal organs is the ________ surface. |
inferior |
|
|
The liver accounts for only 2% of the body's weight, but it receives how much of the body's cardiac output in order to accomplish its functions? |
28% |
|
|
Each liver lobe is divided into thousands of microscopic _________, which are the functional units of the liver. |
lobules |
|
|
The liver is what type of shape? |
Wedge-shaped |
|
|
The liver is surrounded by peritoneum except for the? |
Bare area |
|
|
The bare area is located ___________ to the dome of the liver. |
posterior |
|
|
What quadrant of the abdomen is the liver located in? |
The right upper quadrant (RUQ) |
|
|
The liver takes up almost all of the right __________, the greater part of the _______________, and the left ________________. |
hypochondrium, epigastrium, hypochondrium |
|
|
The craniocaudad approach of measuring the liver measures it from superior to __________? |
inferior |
|
|
Sonographers measure the liver from the tip of the right lobe all the way to the tip of which lobe? |
The left lobe |
|
|
Hepatomegaly is indicated with a greater than _____ inferior-superior dimension or when the right lobe of the liver extends well beyond the lower pole of the right kidey. |
15 cm |
|
|
The hepatorenal pouch or Pouch of Morrison is located between which structures? |
The liver and the right kidney |
|
|
The subphrenic space is located between which structures? |
Either between the liver and the diaphragm or the spleen and the diaphragm |
|
|
_______________ is a tongue-like inferior extension of the right lobe of the liver as far as the iliac crest. |
Reidel's Lobe |
|
|
Reidel's Lobe may be mistaken for ____________ when only measuring the superior-inferior dimension of the liver. |
hepatomegaly |
|
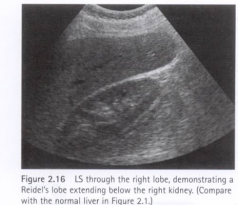
This is an example of a _______________? |
Reidel's Lobe |
|
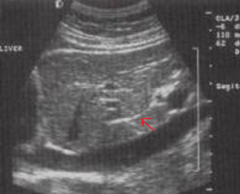
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The ligamentum venosum |
|
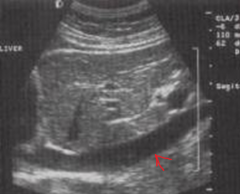
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The inferior vena cava |
|
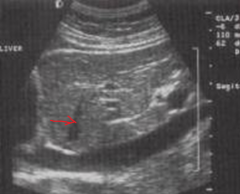
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The left hepatic vein |
|
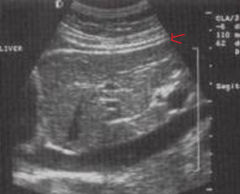
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The peritoneum |
|
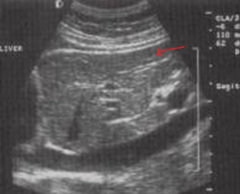
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The left lobe of the liver |
|
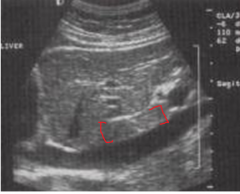
What structure is between the brackets? |
The caudate lobe |
|
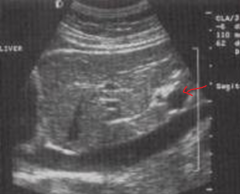
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The left portal vein |
|
|
The duodenum lies adjacent to the right and medial aspects of which lobe of the liver? |
Left lobe |
|
|
The posterior border of the liver lies against the ___________, IVC and aorta. |
right kidney |
|
|
Which structure covers the superior border of the liver? |
The diaphragm |
|
|
The liver is suspended from the diaphragm and abdominal wall by the? |
Falciform Ligament |
|
|
Which lobe of the liver is the smallest lobe? |
The caudate lobe |
|
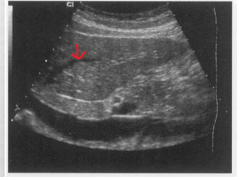
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The left hepatic vein |
|
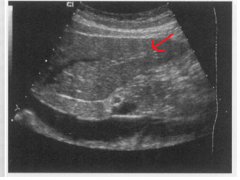
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The left lobe of the liver |
|
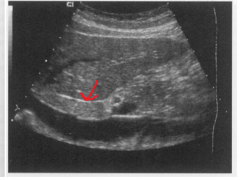
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The ligamentum venosum |
|
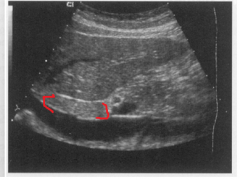
The brackets are surrounding which structure? |
The caudate lobe |
|
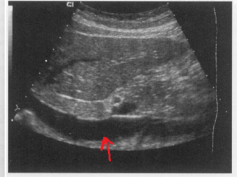
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The inferior vena cava |
|
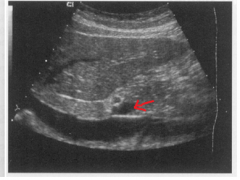
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The main portal vein |
|
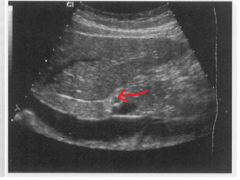
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The hepatic artery proper |
|
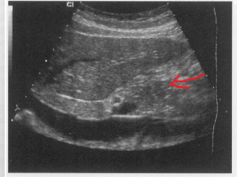
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The pancreatic head |
|
|
The ___________ are intersegmental and interlobar vessels because they course between the lobes and segments |
hepatic veins |
|
|
What type of walls do the hepatic veins have? |
Non-echogenic walls |
|
|
The right and left lobes of the liver are based on the division of the ________________ into its right and left branches. |
main portal vein |
|
|
The main lobar fissure, which contains the ______________, separates the right and left lobe of the liver. |
middle hepatic vein |
|
|
The right lobe is divided into anterior and posterior segments by the ________________. |
right hepatic vein |
|
|
The left lobe is divided into lateral and medial segments by the _________________. |
left hepatic vein |
|
|
The caudate lobe lies between the inferior vena cava and? |
the medial lobe of the liver |
|
|
Which lobe of the liver is the only lobe which is supplied by branches from both the portal and hepatic arterial systems? |
The caudate lobe |
|
|
The caudate lobe is drained by small veins known as the _________________. |
emissary veins |
|
|
What are the vessels that make up the portal triad? |
The main portal vein, the hepatic artery propery, and the common hepatic duct |
|
|
The portal triad is enclosed by a fibrofatty sheath known as _______________? |
Glisson's Capsule |
|
|
The vessels of the portal triad have which type of walls? |
Hyperechoic |
|
|
Which lobe is the liver's largest lobe? |
The right lobe |
|
|
The right lobe of the liver is divided into anterior and __________ segments. |
posterior |
|
|
The right lobe's inferior and posterior surfaces are marked by three fossae, which include? |
The gallbladder fossae, the IVC fossae, and the porta hepatis fossae |
|
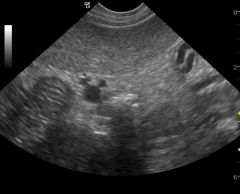
As seen in this picture, the "Mickey Mouse" sign is characteristic of which structure? |
The portal triad |
|
|
Which structure, which contains the right hepatic vein, divides the right lobe into anterior and posterior segments? |
The right intersegmental fissure |
|
|
Which structure, which contains the left hepatic vein, divides the left lobe into lateral and medial segments? |
The left intersegmental fissure |
|
|
The ligamentum venosum is a remnant of what? |
The ductus venosus |
|
|
Which structure separates the caudate lobe from the left lobe of the liver? |
The ligamentum venosum |
|
|
The ___________ classification system divides the liver into functional segments. |
Couinaud |
|
|
Couinaud's segmental division of the liver is based on the distribution of the _____________? |
portal veins |
|
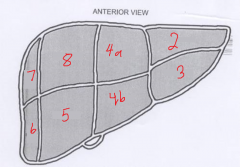
In Couinaud's segmental division of the liver, segment I is? |
The caudate lobe |
|
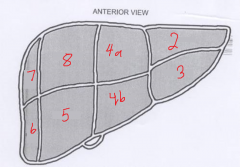
The segment labeled 2 is called? |
Left lateral superior |
|
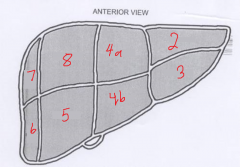
The segment labeled 3 is called? |
Left lateral inferior |
|
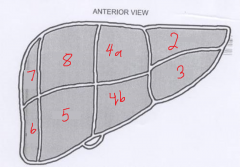
The segment labeled 4a is called? |
Left medial superior |
|
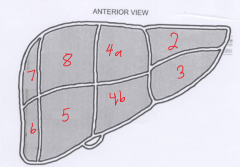
The segment labeled 4b is called? |
Left medial inferior |
|
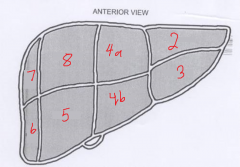
The segment labeled 5 is called? |
Right anterior inferior |
|
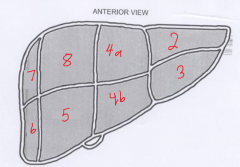
The segment labeled 6 is called? |
Right posterior inferior |
|
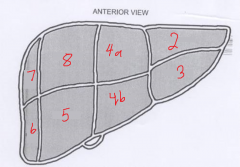
The segment labeled 7 is called? |
Right posterior superior |
|
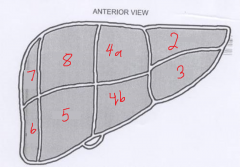
The segment labeled 8 is called? |
Right anterior superior |
|
|
The ligamentum teres is a remnant of the ____________? |
Umbilical vein |
|
|
During prenatal life, the ______________ connects the umbilical vein directly to the inferior vena cava, thus allowing some blood to bypass the liver and flow directly from the placenta to the heart. |
ductus venosus |
|
|
Flow towards the liver, _______________ flow, shows up on ultrasound doppler as the color red and appears above the baseline. |
hepatopedal |
|
|
Flow away from the liver, ______________ flow, shows up on ultrasound doppler as the color blue and appears below the baseline. |
hepatofugal |
|
|
The portal venous system is an example of which type of flow? |
Hepatopedal |
|
|
The liver receives oxygen via the _____________ and the portal vein. |
hepatic artery |
|
|
The portal vein provides ___% of the liver's blood flow and ___% of its oxygen needs. |
75%, 60% |
|
|
______ mm is the upper limits of portal vein diameter. Anything greater than this diameter results in patients with portal hypertension. |
13 |
|
|
Hepatic veins flow towards the inferior vena cava and thus away from the liver and away from the transducer. This represents which type of flow? |
Hepatofugal |
|
|
On ultrasound doppler, the portal veins and hepatic arteries would appear as which color? |
Red |
|
|
On ultrasound doppler, the hepatic veins would appear as which color? |
Blue |
|
|
Which other ligament helps the falciform ligament in suspending the liver from the diaphragm and abdominal wall? |
Coronary ligament |
|
|
These ligaments are peritoneal reflections to the far left and right of the bare area. |
The right and left triangular ligaments |
|
|
The _______________ runs obliquely between the neck of the gallbladder and the right portal vein. |
main lobar fissure |
|
|
The ligaments and fissures inside the liver appear as ____________ on ultrasound because of the presence of collagen and fat within and around them. |
Hyperechoic |
|
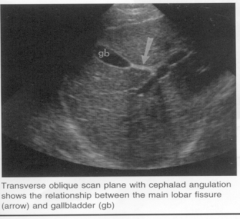
The arrow is pointing to which structure? |
The main lobar fissure |
|
|
The portal venous system is formed by the confluence of the ___________________, ____________________, and the _________________. |
splenic vein, super mesenteric vein, inferior mesenteric vein |
|
|
______________ carry blood from the spleen and bowel to the liver. |
The portal veins |
|
|
The ___________________ drain the blood from the liver to the IVC. |
hepatic veins |
|
|
Which structures carry oxygenated blood from the aorta to the liver? |
The hepatic arteries |
|
|
The ___________________ transport bile to the duodenum. |
bile ducts |
|
|
The liver enzyme test AFP stands for? |
Alphafetoprotein |
|
|
The liver enzyme test ALT stands for? |
Alanine Aminotransferase |
|
|
The liver enzyme test ALP stands for? |
Alkaline Phosphatase |
|
|
The liver enzyme AST stands for? |
Aspartate Aminotransferase |
|
|
The liver function test LDH stands for? |
Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase |

