![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Rooting Reflex |
Allows searching for and locating feeding source; movement of tongue, mouth and/or head towards the stimulus Onset: 28 weeks gestation Integration: 3 months Stimulus: stroke corner of mouth, upper lip and lower lip |

|
|
|
Suck and Swallow Reflex |
Allows ingestion of nourishment; strong rhythmical sucking Onset: 28 weeks gestation Integration: 2-5 months Stimulus: place finger in infant's mouth with head in midline |

|
|
|
Moro Reflex |
Facilitates ability to depart from dominant flexor posture-protective response; Phase 1-arm extension/abduction, hand opening Phase 2-arm flexion and addiction -Onset: 28 weeks gestation -Integration: 4-6 months -Testing: infant in supine, head midline, support infant's head while child is halfway between supine and upright sitting -Stimulus: rapidly drop infant's head backwards Asymmetry=brain lesion or peripheral nerve problems to the upper extremity |

|
|
|
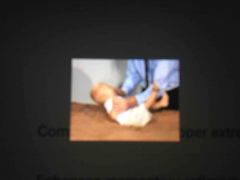
Traction Reflex |
Enhances momentary reflexive grasp; helps stabilize the head before the child has voluntary head control; complete flexion of upper extremities Onset: 28 weeks Integration: 2-5 months Stimulus: grasp infant's wrists and pull up; infant will flex and elevate shoulders, arms and wrists Testing: infant in supine, arms and head in midline |
|
|
|
Plantar Grasp Reflex |
Increases tactile input to sole of foot; Toe flexion Onset: 28 weeks gestation Integration: 9 months Stimulus: apply pressure on ball of infant's foot Testing: infant is supine, head midline, legs relaxed Integrates at the same time that independent gait first becomes possible |

|
|
|
Galant Reflex |
Facilitates lateral trunk movements necessary for trunk stabilization; infant will literally flex toward stimulated side Onset: 32 weeks gestation Integration: 2 months Stimulus: stimulate along paravertebral area from C7 area to buttocks Testing: infant placed prone May persist with atypical children; athetoid CP |

|
|
|
Neck Righting (NOB) |
Maintains head/body alignment; initiates rolling (1st ambulation effort Onset: 34 weeks gestation Integration: 4-6 months Stimulus: infant in supine, fully turn head to one side Testing: infant supine, head midline Transitions between supine, side lying and eventually prone |

|
|
|
Neck Righting (BOB) |
Facilitates trunk/spinal rotation; assists in rolling between supine and prone Onset: 34 weeks gestation Integration: 4-5 months Stimulus: infant in supine, flex one hip and knee toward the chest and hold briefly Testing: infant supine, head midline |

|
|
|
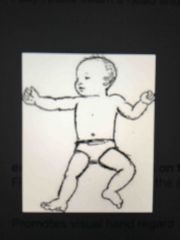
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR) |
Promotes visual hand regard; extension of extremities on the face side and flexion on the skull side Onset: 0-2 months/37 weeks gestation Integration: 4-6 months Stimulus: fully rotate infant's head Testing: supine Persistence of reflex may indicate CNS damage |
|
|
|
Palmar Grasp Reflex |
Increases tactile input on the palm of the hand; finger flexion Onset: 10 weeks/37 weeks gestation Integration: 4-6 months Stimulus: finger in infant's palm from ulnar to palmar surface Testing: infant supine, head midline, arms and hands free |

|
|
|
Palmar Grasp Reflex |
Increases tactile input on the palm of the hand; finger flexion Onset: 10 weeks/37 weeks gestation Integration: 4-6 months Stimulus: finger in infant's palm from ulnar to palmar surface Testing: infant supine, head midline, arms and hands free |

|
|
|
Tonic Labyrinthine Prone Reflex |
Prone=flexor time will dominate Onset: birth Integration: 6 months Stimulus/Testing: place infant in prone Persistence will impede activities that require co-activation of flexor and extensor muscles |

|
|
|
Palmar Grasp Reflex |
Increases tactile input on the palm of the hand; finger flexion Onset: 10 weeks/37 weeks gestation Integration: 4-6 months Stimulus: finger in infant's palm from ulnar to palmar surface Testing: infant supine, head midline, arms and hands free |

|
|
|
Tonic Labyrinthine Prone Reflex |
Prone=flexor time will dominate Onset: birth Integration: 6 months Stimulus/Testing: place infant in prone Persistence will impede activities that require co-activation of flexor and extensor muscles |

|
|
|
Tonic Labyrinthine Supine Reflex |
Facilitates and Increases extensor tone Onset: birth Integration: 6 months Stimulus/Testing: infant supine Persistence impedes co-activation of flexor and extensor muscles |

|
|
|
Palmar Grasp Reflex |
Increases tactile input on the palm of the hand; finger flexion Onset: 10 weeks/37 weeks gestation Integration: 4-6 months Stimulus: finger in infant's palm from ulnar to palmar surface Testing: infant supine, head midline, arms and hands free |

|
|
|
Tonic Labyrinthine Prone Reflex |
Prone=flexor time will dominate Onset: birth Integration: 6 months Stimulus/Testing: place infant in prone Persistence will impede activities that require co-activation of flexor and extensor muscles |

|
|
|
Tonic Labyrinthine Supine Reflex |
Facilitates and Increases extensor tone Onset: birth Integration: 6 months Stimulus/Testing: infant supine Persistence impedes co-activation of flexor and extensor muscles |

|
|
|
Labyrinthine Head Righting |
Orients head in space; maintains face vertical; necessary to allow the body to turn freely around the head Onset: birth to 2 months Integration: persists through life Stimulus/Testing: hold infant suspended vertically and tilt slowly (45*) to the side, forward or backward |

|
|
|
Palmar Grasp Reflex |
Increases tactile input on the palm of the hand; finger flexion Onset: 10 weeks/37 weeks gestation Integration: 4-6 months Stimulus: finger in infant's palm from ulnar to palmar surface Testing: infant supine, head midline, arms and hands free |

|
|
|
Tonic Labyrinthine Prone Reflex |
Prone=flexor time will dominate Onset: birth Integration: 6 months Stimulus/Testing: place infant in prone Persistence will impede activities that require co-activation of flexor and extensor muscles |

|
|
|
Tonic Labyrinthine Supine Reflex |
Facilitates and Increases extensor tone Onset: birth Integration: 6 months Stimulus/Testing: infant supine Persistence impedes co-activation of flexor and extensor muscles |

|
|
|
Labyrinthine Head Righting |
Orients head in space; maintains face vertical; necessary to allow the body to turn freely around the head Onset: birth to 2 months Integration: persists through life Stimulus/Testing: hold infant suspended vertically and tilt slowly (45*) to the side, forward or backward |

|
|
|
Landau Reflex |
Complete extension of the head; breaks up flexor dominance and facilitates prone extension Onset: 3-4 months Integration: 12-24 months Stimulus/Testing: hold infant horizontal prone suspension |

|
|
|
Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (STNR) |
Breaks up total extensor posture; facilitates static quadruped position (crawling) Onset: 4-6 months Integration: 8-12 months Stimulus/Testing: place infant in craving position and extend head Necessary to achieve quadruped crawling |

|
|
|
Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (STNR) |
Breaks up total extensor posture; facilitates static quadruped position (crawling) Onset: 4-6 months Integration: 8-12 months Stimulus/Testing: place infant in craving position and extend head Necessary to achieve quadruped crawling |

|
|
|
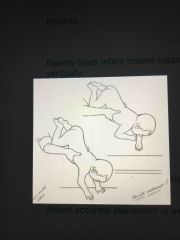
Downward Parachute (Protective Extension Downward) |
Allows accurate placement of extremities in anticipation of a surface Onset: 4 months Integration: persists through life Stimulus/Testing: rapidly lower infant toward supporting surface while suspended vertically Preparation for standing and breaks a fall |
|
|
|
Forward Parachute Reflex (Protective Extension Forward) |
Allows accurate placement of upper extremities in anticipation of supporting surface to prevent a fall; sudden extension of upper extremities/neck extension Onset: 6-7 months Integration: persists through life Stimulus/Testing: suddenly tip infant forward toward supporting surface while vertically suspended Necessary for prop sitting |

|
|
|
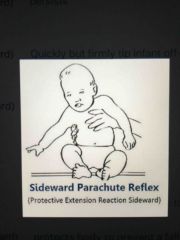
Sideward Parachute (Protective Extension Sideward) |
Protects the body to prevent a fall; supports body for unilateral use of opposite arm Onset: 7 months Integration: persists through life Stimulus/Testing: quickly but firmly tip infant off balance to the side while seated Needed for independent sitting |
|
|
|
Backward Parachute (Protective Extension Backward) |
Protects body from fall; unilaterally facilitates spinal rotation; backward arm extension Onset: 9-10 months Integration: persists through life Stimulus/Testing: quickly but firmly tip infant off balance backward Necessary for independent sitting |

|

