![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
red line=chorionic membrane
orange line=amniotic membrane in between red & orange lines=chorionic cavity blue=embryo yellow=yolk sac purple=connecting stalk pink=chorionic villi |
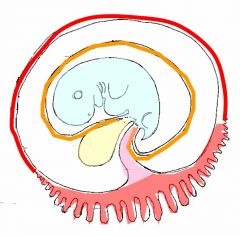
red line?
orange line? in between red & orange lines? blue? yellow? purple? pink? |
|
|
when does fetal period begin
|
begining of 9th week
|
|
|
conceptus
|
everything derived from the embryo including fetus (or embryo) plus all surrounding membranes
|
|
|
importance of yolk sac
|
early nutrient transfer, earliest site of blood cell development, formation of germinal cells
|
|
|
importance of allantois
|
(blind ended sac lined by endoderm) induction of umbilical vessels (aa & vv)
|
|
|
amniotic sac and membrane
|
protects from injury, symetrical growth, regulates fetal temp, fluid exchange
|
|
|
oligo hydramois
|
inadequate fluid levels
|
|
|
What is Chorion
|
Space between amnion and uterus
Filled with fluid early in life Later, as the amnion grows, chorionic space dissappears. Villous chorion eventually becomes placenta |
|
|
chorion dissapears by what period
|
fetal period
|
|
|
describe placenta
|
chorionic villi increase surface area. CV is rich w/ blood vessels to collect nutrients from mothers blood
|
|
|
syncitiotrophoblast
|
embryonic tissue
|
|
|
endometrium
|
side closest to mom
|
|
|
viability of premature birth
|
>500 g, can survive but may or may not thrive
<500 g, usually won’t survive. |
|
|
Estimated day of fertility
|
(=LNMP - 2 wks)
|
|
|
trimesters are approx _____ weeks
1)first trimester 2) second trimester 3)third trimester |
13
1) most critical 2)starts previable ends viable 3)all viable |
|
|
quickening
|
first fetal movements felt (17-20 weeks)
|
|
|
lung maturity assessed by _________
|
amniocentesis surfactant levels
|
|
|
dizygotic twins
|
fraternal - 2 seperate fertilization events; seperate amniotic membranes
|
|
|
monozygoti twins
|
identical - 1 zygote or blastocyst diveds into 2 embryos and often in same cavity
|
|
|
methods of examining fetus in utero (5)
|
1) ultrasound
2)amniocentisis 3) chorionic villus sampling (CVS) 4)fetoscopy 5) radiology |
|
|
ultrasound
|
high frequency sound. generally safe
|
|
|
aniocentesis
|
needle aspiration of amniotic fluid 1/2% rate of spontaneus abortion (can be done as early as 10 weeks; safest 12-18 weeks
|
|
|
chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
|
clip a few placental vili best done 10-12 weeks. can clip off fingers accidentily
|
|
|
fetoscopy
|
fiber optics, limited use
|
|
|
radiology
|
xray - hazerdous to fetus
|
|
|
before ___ week injury to the fetus usually results in death
|
2nd week
|
|
|
developmental defects resulting from external agents act by
|
Interfering with cell division
Interfering with cell migration Delaying cell differentiation |
|
|
cleft
|
failure of fusion
|
|
|
agenisis
|
failure of induction of an organ to develop at all
|
|
|
ectopy
|
abnormal location of development
|
|
|
duplication
|
2 sx forming where only 1 should
|
|
|
red line=chorionic membrane
orange line=amniotic membrane in between red & orange lines=chorionic cavity blue=embryo yellow=yolk sac purple=connecting stalk pink=chorionic villi |
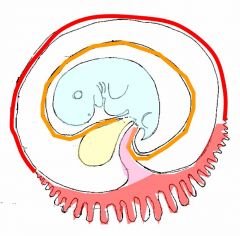
red line?
orange line? in between red & orange lines? blue? yellow? purple? pink? |
|
|
duplication
|
2 sxs form where only 1 should
|
|
|
stenosis
|
abnormal narrowing
|
|
|
fistula
|
abnormal connection
|
|
|
cyst
|
abnormal fluid containing sx
|
|
|
atresia
|
blind tube
|

