![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
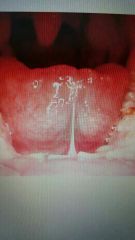
Ankyloglossia |
Short lingual frenum; tongue-tied. Frenectomy as treatment. |
|
|
|
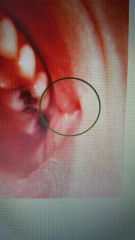
Commissural lip pits |
A deep depression at the label comissurre; may be shallow or several millimeters deep. |
|
|
|
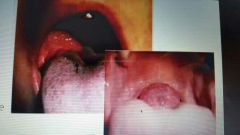
Lingual thyroid |
Mass of tissue located on the tongue which is not the normal location of your thyroid gland. Results as a failure of primitive thyroid tissue to migrate to its location. treatment is removal |
|
|
|
Radicular cyst (periapical cyst) |
Most common cyst of the jaw occurs apex of necrotic tooth caused by pulpal inflammation. Treatment is tooth extraction or endodontic trestment. |
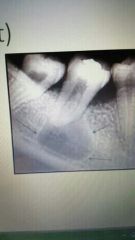
Odontogenic |
|
|
Residual cyst |
Radicular cyst that was left behind. Treatment involves removal of cyst |
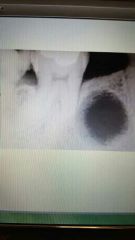
Odontogenic |
|
|
Dentigerous cyst (follicukar cyst) |
Seen around the crown of an impacted or unerupted tooth. Second most common type of cyst. Most commonly seen around third molars followed by maxillary canine. Treatment is removal of tooth. |
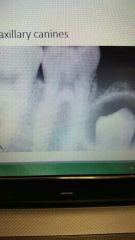
Odontogenic |
|
|
Eruption cyst |
Similar to Dentigerious as it is found around the crown of an erupting tooth. No treatment usually needed as the tooth and errupts through the cyst. |
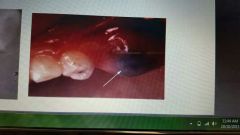
Odontogenic |
|
|
Primorfial cyst |
Occurs in place of a tooth because the tooth never came in. Common in area of third molars. Treatment is removal of the cyst |

Odontogenic |
|
|
Odontogenic keratocyst |
Very aggressive unilocular or multilocular radiolucency with a high occurrence rate. surgical excision is necesary. |
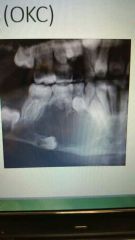
Odontogenic |
|
|
Lateral periodontal cyst |
Common location between roots of mandibular premolars. surgical excision is necessary |
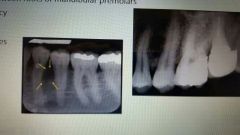
Odontogenic |
|
|
Nasopalatine canal/duct cyst |
Also called incisive canal cyst. Can appear "heart shaped" due to anterior nasal spine. Treatment is surgery |
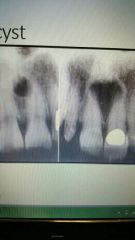
Non- odontogenic |
|
|
Globulomaxillary cyst |
Seen between maxillary lateral incisor and canine. Treatment is surgery |
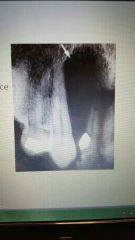
Non- odontogenic |
|
|
Nasolabial cyst |
Also called nasolacrimal cyst. No alveolar bone involvement; soft tissue cyst. Trestment is surgery. |
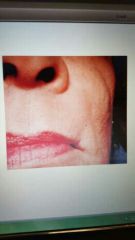
Non- odontogenic |
|
|
Abodontia |
Congenitally missing teeth. Total or partial |
Most common third molars, then maxillary lateral incisors, then mandibular second premolars. |
|
|
Supernumeary teeth |
Extra teeth. Treatment is removal to prevent cysts. |
Most common is between the maxillary central incisors. Second mist common is a 4th molar. |
|
|
Microdontia |
Small teeth |
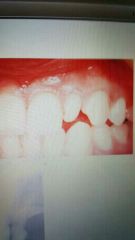
Peg latetal most common, then maxillary thrid molar. |
|
|
Macrodontia |
Larger than normal teeth. |
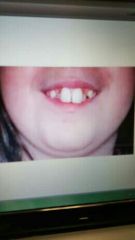
|
|
|
Gemination |
Development of two teeth (or two crowns) within a single root with one pulp canal. |
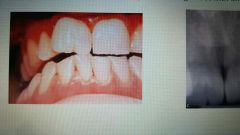
|
|
|
Fusion |
The joining of two tooth germs. clinically appear as a single large crown, radiographically appear as separate or fused roots. |
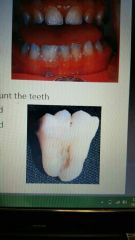
|
|
|
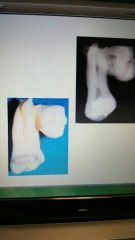
Concrescense |
A form of fusion; the teeth are joined by cementum only |
|
|
|
Dilaceration |
And abnormal curve or angle in the root, or less common in the crown, of a tooth caused by trauma to the tooth germ during root development. Extractions and endodontic treatment might be difficult. |

|
|
|
Enamel pearl |
Usually seen in bifurcated or trifurcated areas. Abnormal displacement of ameloblasts may consist of enamel, dentin, and pulp. may need removal if the patient has periodontal problems. |

|
|
|
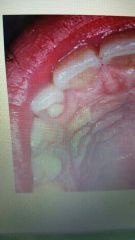
Talon cusp |
And accessory cusp located in the area of the cingulum of maxillary or mandibular permanent incisor |
|
|
|
Taurodontism |
Teeth have elongated, large pulp chambers and short roots. No treatment. |

|
|
|
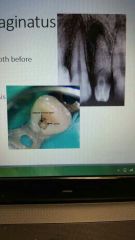
Dens in dente |
Tooth within a tooth. |
|
|
|
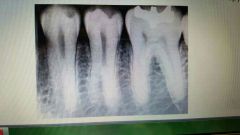
Supernumary roots |
Extra routes common in third molars in mandibular cuspids and bicuspids. |
|
|
|
Enamel hypoplasia |
Incomplete or defective formation of enamel caused by a disturbance or damage to ameloblasts during enamel matrix formation |
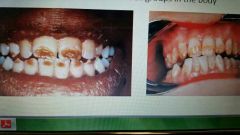
|
|
|
Enamel hypocalcification |
A disturbance of the maturation of enamel characterized by localized chalky white spots on the middle third of smooth crowns. Enamel may be soft underneath |
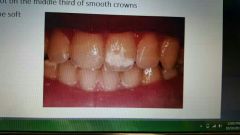
|

