![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Origins of development gap |
Colonialism Ww2 construction 1970s oil price spike Debt crisis |
|
|
Classifying causes of development |
Economics- stages of industrial development/dependency on industries/location of TNCs/trade links/economic groupings Political- commitment of gvts/debt levels/corruption/colonial legacy Social- population and dependant levels/birth rates and population policies/education and workforce skills/infrastructure quality Physical- harsh environment/water/minerals/agricultural potential |
|
|
indicators |
Social- PQLI (physical quality of life index) measuring basic literacy rates/infant mortality/ life expectancy at 1 Economics- GDP/GNI/GDI Environmental- living planet index |
|
|
Official definition the development gap |
Difference in income and quality of life between the richer and poorest |
|
|
Official definition the development gap |
Difference in income and quality of life between the richer and poorest |
|
|
Two different definitions of the development gap |
1980 Brant report defined the development gap as a North south divide World bank redefined the development gap as high/middle/low incomes where the middle is then split into two (high and low) |
|
|
Modernisation theory |
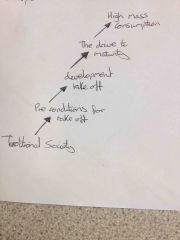
Aka Rostow model- shows how development progresses over time, still large gap between least and most developed countries |
|
|
Dependency theory |
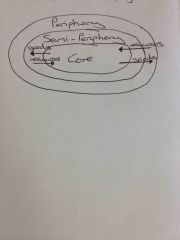
Aka world systems theory (Wallerstein) - shows the interdependency between core developed countries and peripheral developing countries) |
|
|
List of trade development strategies |
-fair trade (NGOs) -Structural adjustment programmes (SAP) -Special economic zones (SEZs) -free trade (Doha Development round) -trade agreements and trade blocs |
|
|
List of Aid development strategies |
-Humanitarian aid -Top down (official development assistance ODA/ bilateral aid/ multilateral aid) -Bottom up (voluntary aid/development aid) -Tied aid |
|
|
Debt reduction/cancellation strategies for development gap |
-make poverty history -HIPC initiative |
|
|
Friedmans core theory |
Showing how some areas have become more economically developed than others hence wealthier/poorer. Some of the factors involved in this include geographic reasons such as OPEC countries being located on rich oil supplies |
|
|
Positive impacts of countries bridging the development gap |
- increased investment from FDI - rising personal incomes from improved range of employment - new projects to extend infrastructure, some high profile extend influence of country Improved international status, membership of WTO etc - expansion in core cities should trickle down to the peripheries and to the poor - increasingly "switched on" by technology of mobile phones/internet |
|
|
Negative impacts of a country bridging the development gap |
- over reliance on export led growth - increasing indebtedness to international banks for loans - increasing reliance on TNCs who can dominate decision making - increasing pressure on services us has health, education and waste - increasing pressure on land and ecosystems due to expanding development - increasing pressure on resources for energy - increasing levels of air and water pollution from industrialisation - increasing congestion from traffic - pressure on cultural traditions and values |
|
|
Examples of disadvantaged groups for whom the development gap has negative consequences |
- women (e.g sub Saharan Africa where girls rarely get to complete secondary) - lower castes and untouchables (India and Sri Lanka- poorer access to facilities) - disabled/old people (in LDCs there's no state support system) - White farmers (black Zimbabwe where their land has been seized and many have moved out) - contract migrant workers (Indians working in Gulf states, or illegal ls- exploited with very little pay) - religion |

