![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the title for chapter 3? |
"Equipment Selection, Specification, and Design" |
|
|
|
What are the 2 classes that equipment can be classified to ? |
(1) Proprietary - Equipment such as pumps, compressors, filters, centrifuges, and dryers, which are designed and manufactured by specialist firms. (2) Nonpropriety - Equipment which are designed as special, one-off items for particular process, eg; reactors, distillation columns, and heat exchanger. |
|
|
|
Describe solid-solid separation process . |
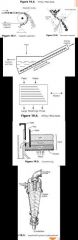
• To separate valuable solids from unwanted materials and for size grading of solid raw materials and products. (1) Screening : • Aka sieving. • Small particles - woven cloth, or wire screen. • Large particles - perforated metal plates, or grids. (2) Liqud-Solid Cyclones. (3) Hydroseparators and Sizers. (4) Hydraulic Jigs. (5) Tables. (6) Magnetic/Electrostatic Separators. |
|
|
|
Describe Liquid-solid Separation. |
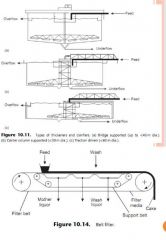
(1) Thickeners and Clarifiers : • Thickener - to increase relatively large quantity of suspended solids concentration. • Clarifier - to remove a small quantity of fine solids to produce clear liquid effluent.
(2) Filtration : • Using vacuum, pressure, or centrifugal force to drive liquid through deposited cake of solids.
(3) Centrifuges.
(4) Hydrocyclones (Liquid-cyclones).
(5) Pressing. |
Figure : Thickener and clarifier, and filtration. |
|
|
Describe Separation of Dissolved Solid. |
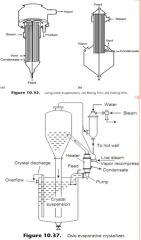
• Evaporation and crystallization are main process to recovery dissolved solid.
(1) Evaporator.
(2) Crystallizer. |
|
|
|
Describe liquid-liquid separation. |
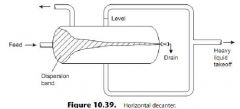
(1) Decanters (Settlers). (2) Plate Separators. (3) Centrifugal Separators. |
|
|
|
Describe crushing and grinding. |
•Crushing is the first step in size reduction, reducing large lumps to manageable-sized pieces. |
|
|
|
What are the main factors to be considered when selecting equipment for crushing and grinding? |
(1) Size of feed. (2) Size of reduction ratio. (3) Particle size distribution of product needed. (4) Throughput. (5) Properties of materials such as hardness, abrasiveness, stickiness, density, toxicity, and flammability. (6) Permissible for wet grinding. |
|
|
|
Describe mixing equipment. |
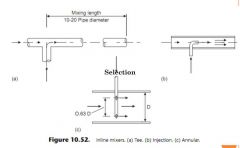
• Liquid and solid mixing usually carried out as batch process. |
|
|
|
Describe Reactors . |
(1) It is the heart of chemical process. (2) The only place raw materials are converted into products. (3) The reactor design is a vital step in overall process design. |
|
|
|
What characteristics normally used to classify reactors design ? |
(1) Mode of design : • Batch or continuous. (2) Phases present : • Homogeneous or heterogeneous. (3) Reactor geometry : • Flow pattern and manner of contacting the phases. Example reactors : • Stirred tank reactor - consists of a vessel with mechanical agitator and cooling jacket or coils which operated as batch or continuous. • Tubular reactor - use gasesous reactions but also suitable for some liquid-phase reactions. • Packed bed, fixed and moving. • Fludised bed. |
|

