![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is most common immune mediated dermatosis
|
pemphigus foliaceus
|
|
|
what breeds are predisposed to pemphigus foliaceus
|
akita
chow chow dachsunds DSH 4-5 yrs of age |
|
|
What are characteristics of pemphigus foliaceus
|
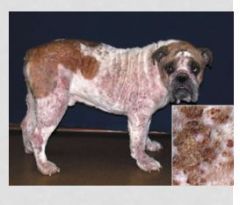
+/- pruritis
pustular dermatitis - dry crusts, scale, alopecia, erosions, epidermal collarettes |
|
|
Where does PF first present
|
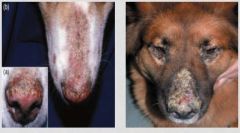
face and ears in dog and cats
-feet -clawpad -can become generalized -cat: paronchya, nipples, bilateral and symmetrical |
|
|
What are differentials from pemphigus foliaceus
|
bacterial folliculitis
dermatophytosis dermodicosis seborrheic skin diseases PE D and SLE cutaneous adverse drug rxn |
|
|
What is auto-ab against in pemphigus foliaceus
|
Desmosome autoantigen
Dogs: desmoglein 1 |
|
|
What is pathophysiology of pemphigus foliaceus
|
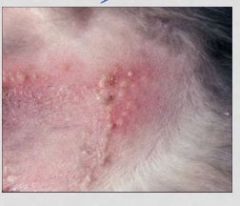
produce autoab against desmosomes - complement activation and inflammation
loss of epidermal cell-cell adhesion creates blisters impairment of integrity of epidermal tissues |
|
|
What can cause pemphigus foliaceus
|
Idiopathic
drug induced drug triggered paraneoplastic systemic disease chronic allergies made worse by UV light |
|
|
what drugs have been implicated in casing PF
|
penicillin
sulfa drug cephalosporins promeris certifect |
|
|
How do you diagnose pemphigus foliaceus
|
Do database to R/o other causes
histopath - acantholytic cells, subcorneal pustules, neutrophils |
|
|
What can cause acantholysis
|
pemphigus foliaceus
Dermatophytosis bacterial folliculitis |
|
|
How do you treat pemphigus foliaceus
|
Dog:
Glucocorticoid: 2-4 mg/kg daily then EOD Azathioprine: |
|
|
what is the effect of glucocorticoids
|
effect humoral and CMI
inhibit inflammatory mediators suppress autoab |
|
|
what are SE of glucocorticoids
|
PU/PD
DM increased infection risk calcinosis cutis demodicosis / dermatophytosis GI ulcer |
|
|
What is MOA of azathioprine
|
antagonize purine metabolism
interfere with RNA and DNA syntehsis cytoxic to T cells |
|
|
what are SE of azathioprine
|
myelosuppression
hepatotoxicity |
|
|
what is PF treatment in cats
|
Glucorticoids
Chlorambucil |
|
|
what is MOA of chlorambucil
|
alkylating agent
affects cross linking of DNA |
|
|
what are SE of chlorambucil
|
myelosuppression
diarrhea anorexia |
|
|
what is long term monitoring for PF treatment
|
taper med based on response and evidence of active disease
review SE routine lab work |
|
|
What needs to be done every 2-4 weeks with PF
|
recheck exam
CBC chem UA cytology |
|
|
during PF treatment you see new lesions what should you do
|
skin scrape - R/o demodicosis
Trichogram |
|
|
what is prognosis with PF
|
guarded
Cost SE may be difficult to achieve remission |

