![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What should you do to visualize mites / FB
|
move condensor stage down
|
|
|
What should you do to visualize eosinophils / parasites
|
close the aperture diaphragm
|
|
|
Describe the steps for kohler illumination
|
1. focus on slide using 10x objective
2. Lower condenser stage 3. Close field diaphragm and aperture diaphragm 4. Slowly raise condenser stage until a small circle of light is seen 5. Open field diaphragm until light fills objective view 6. Adjust aperture diaphragm for objective n.a. |
|
|
What are key microscope care points
|
-keep scope clean and lubricated
-cover when not in use -clean leans daily to remove oil and debris -USe a different scope for fecal exams if possible -adjust the scope using Kohler illumination |
|
|
What objective should be used to view mites, FB, hair and fungal hyphae
|
2-4x
|
|
|
what are rules for slide submission
|
Make extra slides -Send off slides and then keep a copy
send unfixed air dried slides and stained slides package in protected cases do not send in same package as formalin |
|
|
What is the definition of cytology
|
Collection of cellular material and or fluid for microscopic examination
use on skin to diagnose and monitor |
|
|
Where can you use cytology
|
Skin: impressions, papules, draining tracts, nodules, tumors
Ears Anal sacs Claw folds |
|
|
What are you looking for on cytology
|
-Inflammatory vs non-inflammatory
-Presence of infectious agents -evidence of neoplasia -Presence of acantholytic cells |
|
|
What is skin
what is normally found on it |
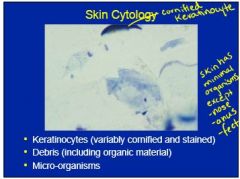
Cornified layer
-keratinocytes -debris -minimal micro-organisms |
|
|
How long does skin take to mature
|
- 21 days to mature
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Melanin
|
- Variable amount, size and shape in groups or clumps
-Brown - reddish orange in color - Some pigment will look like bacteria |
|
|
Who makes melanocytes
|
Melanocyte (dendritic cell)
- Located in basal layer of the epidermis - Keratocytes phagocytize the melanin |
|
|
What locations may give a contaminated smaple
|
Ulcer
draining tract oral cavity (SImonsiella) |
|
|
What is normal finding of an anal sac
|
ketatinocytes
mixed bacterial population |
|
|
What are findings consistent with anal sacculitis
|
Neutrophils
predominance of 1-2 types of bacteria |
|
|
How can you perform cytology sample collection
|
fine needle aspiration (masses, ln)
Impression smears Scrapings Lanced pustules or papules swabs (facial fold) Anal sac - express and touch to slide |
|
|
When should you not use squash preparation
|
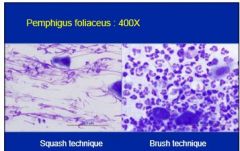
pustular material (use brush)
weight of two slides is damaging to friable neutrophil in the lesion |
|
|
What specimens should not be heat fixed
|
wet or pustular material
|
|
|
When is heat fixing useful
|
greasy preps
impressions smears ears Malassezia |
|
|
What stains can be used for fungi and yeast
|
Silver stain
Periodic acid-Schiff |
|
|
What stain is used for Mycobacteria and Nocardia
|
Acid fast
|
|
|
What stain is used for Mast cells
|
Giemsa
|
|
|
What are benefits of running cytology
|
-provides rapid diagnostic information
-may provide definitive diagnosis -has high benefit: cost -high profit margin -indicated in most derm cases |
|
|
What are cytologic characteristics of neoplasia
|
-vary in size form normal cells of same tissue
-unsusual shapes and forms -Groups or clusters of cells are more likely -Cytoplasm often stains more basophilic -Inclusions may be present -low cytoplasm:nucleus -nucleoli present -irregular mitotic figures -fine chromatin pattern in nucleus |
|
|
How can you maximize the value of skin biopsies
|
-clip hair short
-do not scrub the lesion -handle tissue gently -rinse specimen -fix appropriately |
|
|
Where should you biopsy
|
take a sample of every lesion that looks different
|
|
|
When is general anesthesia required for biopsies
|
pinnae
nasal planum foot pad oral cavity temperament? |
|
|
When is local anesthesia appropriate for biopsies
|
Skin over trunk
abdomen |
|
|
When is sedation and local anesthesia appropriate for biopsies
|
parts of extremities
head anxious / fussy patients cats |
|
|
What are special consideration of biopsing nasal planum
|
dont go on midline
nose is very rigid suture closed avoid hemorrhage and truama to underlying cartilage |
|
|
What are special consideration of biopsing ears
|
anatomy
trauma to underlying cartilage esthetics use 25g needle insert fluid between cartilage and skin lift skin off bleb and biopsy without cartilage involvement |
|
|
What are special consideration of biopsing foot pad
|
trauma
weight bearing area healing risk of dehisence use wedge biopsy and suture closed |
|
|
How do you biopsy for culture
|
biopsy from side of lesion
scrub first rinse sample with sterile saline sample will be minced for culture other sample should be submitted for histopath |
|
|
when do you biopsy for culture
|
Larger granuloma
|

