![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What % of lower limb ulceration is caused by venous or arterial disease? |
Leg ulcers 85% - Venous disease 50% - Mixed 15% - Arterial disease 13% Foot ulcers 15% - Arterial aetiology 72%, often have diabetes - Venous 4% - Mixed 2% |
|
|
What is the mechanism behind the common causes of leg ulcers? |
Venous insufficiency - improper functioning of valves in the legs. Increased venous pressure, fibrin deposits, barrier flow of O2/nutrients. Death of skin tissue. Arterial insufficiency - poor blood circulation due to atherosclerosis, fail to deliver oxygen, nutrients to the leg = tissue breakdown. Diabetes - more common on the foot, from sensory neuropathy. |
|
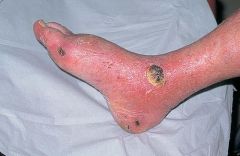
An elderly patient, who smokes, has high BP, presents with painful ankle ulcer that is punched out. What type of ulcer is this like to be? |
Arterial (ischaemic) ulcers - generally localised to the most peripheral areas below the ankle joint, tips of toes, point of heel, pressures points. Often painful at night in bed or legs elevated, pain relieved by lowering legs, punched out, with minimal granulation tissue. Cold, white, blueish shiny feet. Ix - ABPI (ischaemic <0.5, N>0.9) Mx - directed towards repercussion. |
|
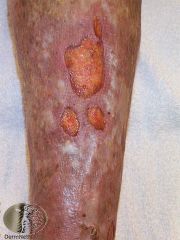
A patient with varicose veins, develops a painless ulcer, associated with leg swelling, surrounded by mottled brown staining and dry, itchy, reddened skin. What type of ulcer is this? |
Venous ulcers - majority of leg ulcers. Chronic venous insufficiency common in elderly. Secondary to deep venous thrombophlebitis. Trophic changes hyper pigmentation, fibrotic thickening, induration and oedema - then venous ulcer. Shallow, more common medial, slow in healing, pain relieved by raising leg. Heal better in a moist, occluded state. Compression stockings. |
|
|
What is the treatment of leg ulcers? |
Reverse the factors that caused the ulcer. Venous leg ulcers - exercise, elevate, compress. Surgery, sclerotherapy, laser to veins may help. Arterial ulcers - if ABPI <0.5 refer to vascular surgeon for reperfusion. Clean, deride wound, treat infection, wound dressings, surgery if fail conservative mx, diet. |
|
|
What are the risk factors for venous ulcers? |
Varicose veins Hx leg swelling Hx DVT Sitting or standing for long periods High BP Multiple pregnancies Previous surgery Fractures or injury Obesity, age, immobility |
|
|
What are the risk factors for arterial ulcers? |
Diabetes Smoking HT High cholesterol Renal failure Obesity RA Clotting and circulation disorders Hx CVA, PVD, cardiac disease |
|
|
How can leg ulcers be prevented? |
Walk and exercise for at least 1hr/day Avoid injury Loose weight, stop smoking Check feet and legs regularly Wear comfortable well, fitting shoes Podiatrist Compression stocking Vascular U/S and consult vascular surgeon |
|
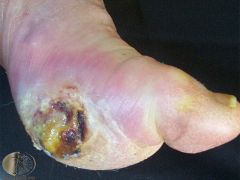
A patient with poorly controlled diabetes presents with an ulcer. What is the cause? |
Diabetic ulcers - similar characteristics to arterial ulcers but are more notably located over pressure points or anywhere the bones may protrude and rub against bedsheets, socks or shoes. In response to pressure, the skin increases in thickness (callus) but with a minor injury breaks down and ulcerates.Ulcer may extend to the bone or joint, prone to infection. Mx - referral to diabetic foot unit, +/- surgery |

