![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
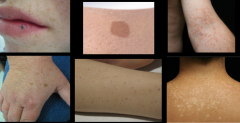
|
macule |
flat (you can't feel it); less than 1 cm; caused by color changes in epidermis or upper dermis |
|
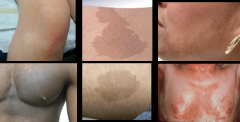
|
patch |
flat but larger than a macule |
|
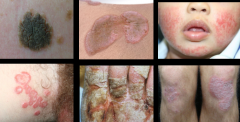
|
plaque |
raised lesions; casts a shadow with side lighting; proliferation of cells in the epidermis or superficial dermis |
|
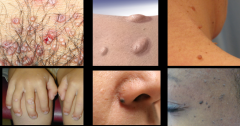
|
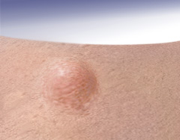
papule |
L. papula (pimple); raised lesion less than a cm; proliferation of cell in epidermis or superficial dermis |
|
|
nodule |
larger deep papule; proliferation of cells down to mid-dermis; raised area in the skin where the overlying epidermis looks and feels normal |
|
|
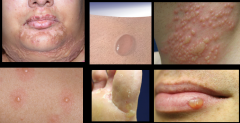
vesicle |
fluid-filled papules; small blisters less than a cm; a bulla is a large blister greater than a cm |
|
|
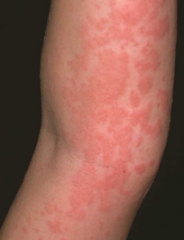
wheal |
elevated and palpable (can be touched); solid transient (changing); variable diameter; paler pink with lighter center; Ex: urticaria, insect bites and dermatographism |
|
|
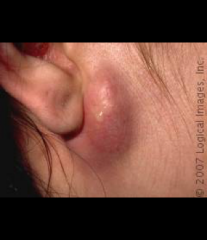
cyst |
elevated, palpable but deep; circumscribed, encapsulated; filled with liquid/semi-solid material; Ex: epidermoid cyst |
|
|
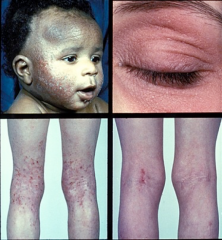
eczematous conditions |
inflamed, pruritic (itchy), dry skin; Papules/Patches; Excoriations/Lichenification; Fissures; Erythematous/Inflamed; Xerotic (dry); moisturize and avoid hot baths/showers; topical/oral corticosteroids; anti-histamine for itch |
|
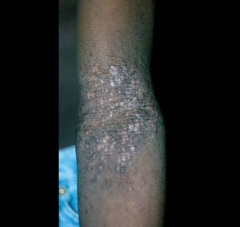
|
eczema/atopic dermatitis |
affects flexor surfaces; barrier dysfunction relation; treatment: control the itch/scratch cycle |
|
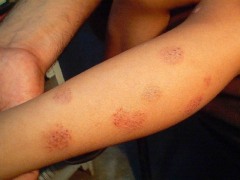
|
nuclear eczema |
|
|
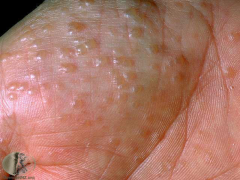
|
dishydrotic eczema |
|
|
|
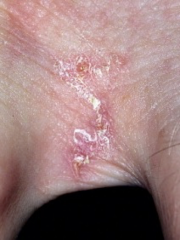
scabies |
|
|
|
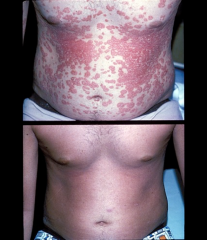
psoriases |
chronic and recurrent; well-circumscribed, silvery, white scaling papules; various-sized plaques; scalp, extensor surfaces: elbows/knees, nail lesions |
|
|
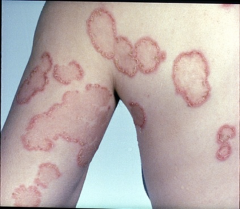
tinea corporis (ringworm) |
skin-skin contact, sandboxes, pets; lesions are round, oval with semicircular or annular appearance; scaly patches with occasional secondary infection |
|
|
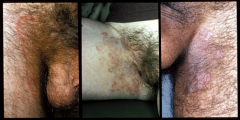
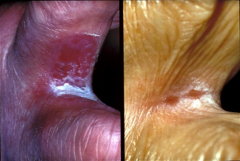
Tinea Cruris |
jock itch |
|
|
Tinea Pedis |
athelete's foot |
|
|
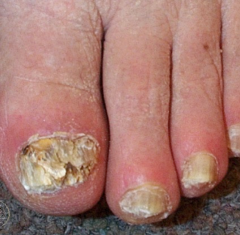
onychomycosis |
Treatment: avoid warm, moist environment; topical antifungals, oral in some cases |
|
|
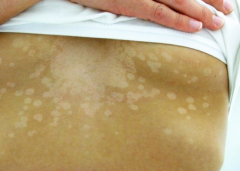
pityriasis rosea |
roubd patch/plaque "herald patch"' that becomes a christmas tree pattern; peaks in Fall and Spring; lasts 5-6 weeks; topical steroids: comfort; oral antihistamines control itch; prodrome suggests viral infection |
|
|
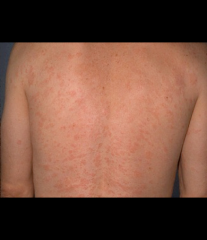
Tinea Versicolor |
lesion: tan and irregularly shaped (macules/papules) on upper back, neck, chest and arms (may de-pigment); recurrent for years and worse in the summer; a KOH lab would show fungal spores; wood lamp/ black light shows a yellow appearance |
|
|
vitiligo |
shows white on woods lamp and black light |
|
|
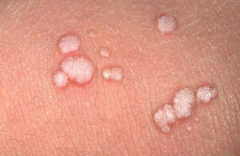
Verrucae (warts) |
most common skin viral infection; common HPV; rough with black dots, tender with pressure, no skin lines; treat with liquid nitrogen and debulking |
|
|
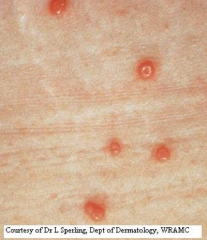
mollusocum contagiosum |
|
|
|
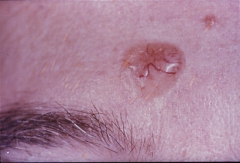
basal cell carcinoma |
most common skin cancer; wound that won't heal; sun exposure, fair skin and radiation exposure are risk factors |
|
|
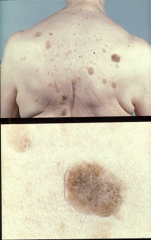
seborrheic keratosis |
light tan macule than becomes more pigmented and elevated over time and becomes a plaque; becomes a warty papule with greasy texture and stuck-on appearance; can be left alone or removed with liquid nitrogen |
|
|
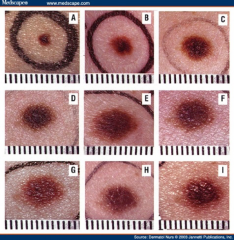
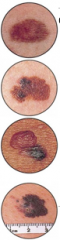
Nevi |
pigmented or nonpigmented skin tumors with nevus cells (orignate from melanocytes); benign nevus pigmentosum, dysplastic nevus, melanoma |
|
|
Asymmetry Borders Color Diameter |
|
|
|
pigmented lesion biopsy |
punch or excisional |
|
|
|
surface lesion biopsy |
shave |
|
|
|
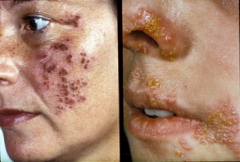
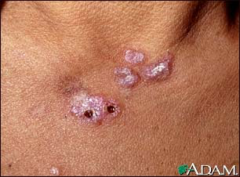
Herpes Zoster (viral) |
painful acute dermatomal infection with reactivation of dormant varicella zoster virus (VZV); common in trunk and first branch of trigeminal nerve (forehead, eyes, nose); nerves don't cross the midline; pain, pruritus, dull ache in dermatome; pustules, erosions and crusts; grouped vesicles on erythematous, tender base; fever, malaise, headache |
|
|
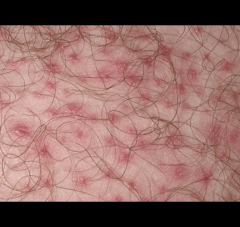
folliculitis |
|
|
|
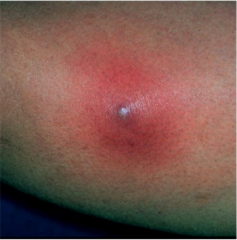
foruncle |
|
|
|
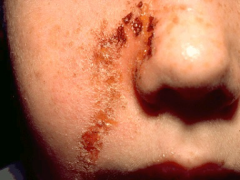
impetigo |
|
|
|
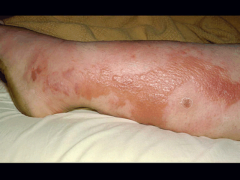
cellulitis |
|
|
|
primary intention |
wound closed with sutures or staples (8 hour rule) |
|
|
|
secondary intention |
heals without closure |
|
|
|
tertiary intention |
closure attempted several days after injury (if no infection shown) |
|
|
|
face stitches |
3-5 days |
|
|
|
chest and ab stitches |
7-10 days |
|
|
|
back stitches |
10 - 12 days |
|
|
|
non-joint upper extremity stitches |
7 - 10 days |
|
|
|
joint upper extremity stitches |
10 - 12 days |
|
|
|
general lower extremity stitches |
7 - 10 days |
|
|
|
lower extremity knee stitches |
10 - 12 days |
|
|
|
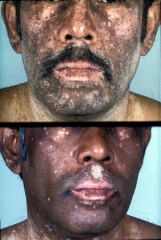
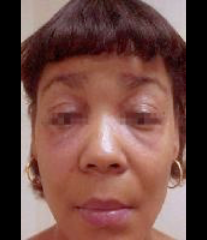
Systemic Lupus Erythemaosus (SLE) |
malar rash associated with Lupus; Skin, joints, lungs, kidneys, blood, heart, nervous system, and membranes of cavities; fever, fatigue, arthralgia, arthritis, photosensitivity, anemia, hair loss, and skin rash; joint tenderness and edema, symmetric polyarthritis |
|
|
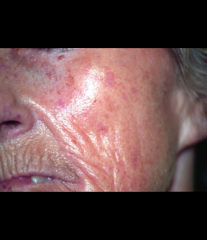
scleroderma |
connective tissue disorder; skin, joints, blood vessels and internal organs; degenerative, inflammatory changes leading to intense fibrosis |
|
|
dermatomyositis |
reddish-purple inflammatory changes in eyelids, periorbital area and erythema of face, neck and upper trunk; skin changes happen; relates to muscle weakness; Gottron's papules |

