![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Urticaria mediated by which immune substance.
|
Histamine
Allergic. Transient. Move around. Acute and chronic. Circular +/- centres In small children can look like purpura (d/t fragile Bvs) |
|
|
What drugs commonly cause acute urticaria
|
Asprin/NSAIDS
|
|
|
Chronic urticaria definition?
|
>6wks.
Nearly always idopathic Immune dysreg. |
|
|
Management of urticaria
|
Antihistimines
Exclusion diet Investigation not necessary in acute urticaria and not helpful in chronic urticaria Very occasionally immunesuppression |
|
|
Immune pathogenesis of urticaria?
|
Antigen interacts with IgE on mast cells degranulate releasing histamine
Also, IgG antibody to IgE receptors on mast cells leading to more serious clinical presentation |
|
|
Angioedema – what is it?
|
Deep form of urticaria
Swelling. Painful rather than itchy. May occlude airway or eye |
|
|
Anaphylaxis – what is it?
|
Overwhelming IgE mediated allergy
CPx depends on where the mast cells degranulate: Circu collaps Airway obstruction Severe bronchospasm Abdo pain/diarrhoea |
|
|
How quickly after exposure can anaphylaxis occur
|
1-30 mins
|
|
|
Management of anaphylaxis
|
MET CALL
ABC Adrenaline SC/MI/IV Antihistamines IVI hydrocortisone |
|
|
Acutely itch, rapidly spreading erythematous reaction. Maybe oedematous with blistering. What is it?
|
Allergic contact dermatitis.
Type IV cell mediated allergy. |
|
|
Can allergic contact dermatitis be idopathic?
|
No. usually always identifiable cause.
|
|
|
Allergens involved in contact dermatitis?
|
Plants, nickel, topical meds, perfuse, preservatives, dye, latex, sunscreen (usu only when in sun), glues
|
|
|
What’s the characteristic spread of contact dermatitis?
|
Typically rash extends beyond area of contact
|
|
|
Angioedema – what is it?
|
Deep form of urticaria
Swelling. Painful rather than itchy. May occlude airway or eye |
|
|
Anaphylaxis – what is it?
|
Overwhelming IgE mediated allergy
CPx depends on where the mast cells degranulate: Circu collaps Airway obstruction Severe bronchospasm Abdo pain/diarrhoea |
|
|
How quickly after exposure can anaphylaxis occur
|
1-30 mins
|
|
|
Management of anaphylaxis
|
MET CALL
ABC Adrenaline SC/MI/IV Antihistamines IVI hydrocortisone |
|
|
Acutely itch, rapidly spreading erythematous reaction. Maybe oedematous with blistering. What is it?
|
Allergic contact dermatitis.
Type IV cell mediated allergy. |
|
|
Can allergic contact dermatitis be idopathic?
|
No. usually always identifiable cause.
|
|
|
Allergens involved in contact dermatitis?
|
Plants, nickel, topical meds, perfuse, preservatives, dye, latex, sunscreen (usu only when in sun), glues
|
|
|
What’s the characteristic spread of contact dermatitis?
|
Typically rash extends beyond area of contact
|
|
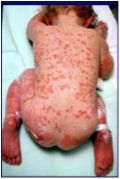
Baby receives abx then gets this reaction - is very unwell.
|
Toxic epidermal necrolysis Most serious of cutaneous drug reactions
Common causes: antiepleptics (lamotragine), sulphur containing abx Mgt in ICU. Give IVIG. |

