![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
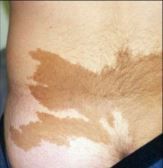
What is this?
|
A macule
(This one is cafe-au-lait) |
|
|
What are the properties of a macule?
|
Flat
Color change |
|
|
What are causes of macules?
|
Hyperpigmentation
Hypopigmentation Vascular abnormalities Dilated capillaries |
|
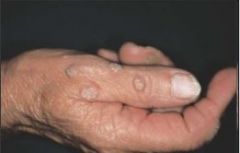
What is this?
|
Papule
|
|
|
What is the difference between a papule and a plaque?
|
Papule: < 1 cm
Plaque: > 1 cm |
|
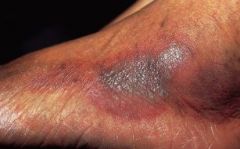
What is this
|
Plaque
|
|
What is this?
|
Nodule
|
|
|
What are the properties of nodules?
|
BIg, spherically enlargedpapule.
Use different adjecties: firm, painless/painful, etc. |
|
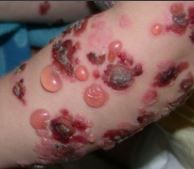
What is this?
|
Bulla
|
|
|
What is the difference between a vesicle and a bulla?
|
Vesicle: < .5 cm
Bulla: > .5 cm |
|
|
What kinds of fluids can be inside a vesicle/bulla?
|
Serum
Lymph Blood |
|
|
What is the definition of a pustule?
|
Circumstcried, elevated lesion containing a purulent fluid
Neutrophils always, bacteria some of the time. |
|
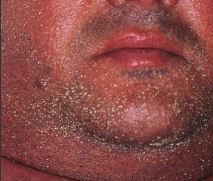
What are the small bumps on the man's face?
|
Pustule
|
|
|
What is the definition of an erosion?
|
Loss of epidermus resulting in a circumscribed, moist, depressed lesion
|
|
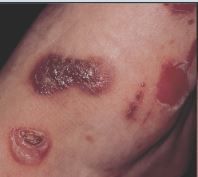
What is this?
|
Erosion
|
|
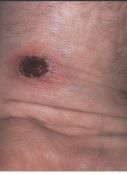
What is this?
|
Crust
|
|
|
What composes a crust?
|
Dried serum, blood, or purulent exudate
|
|
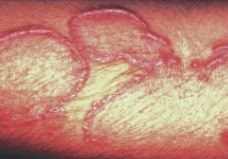
What kind of a lesion is this?
|
Annular lesion
Active periphery, the middle is less active. |
|
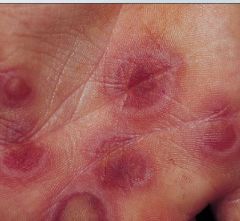
What kind of a lesion is this?
|
Targetoid
|
|
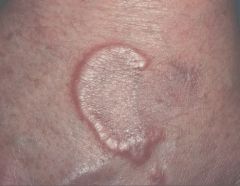
What kind of a lesion is this?
|
Arciform
|
|
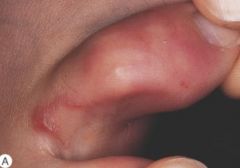
What kind of a lesion is this?
|
Serpiginojs
|
|
|
If vesicles are grouped, what do you call it?
|
Herpetifom
|
|
|
If lesions follow a dermatome, what do you call it?
|
Dermasomal
OR ZOSTERIFORM |
|
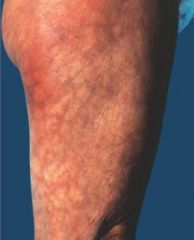
What kind of a lesion is this?
|
reticular
|
|
|
What types of lesions are seen in impetigo?
|
Vesicula/Bulls
|
|
|
What are the causes of impetigo?
|
Gram + bacteria:
S. aureus, S. pyogenes |
|
|
How is Impetigo spread?
|
Direct person-person contact
|
|
|
What's the most common kind of impetigo?
|
Non-bullous
|
|
|
What bacteria usually causes Non-bullous impetigo?
|
S. aureus
Some are caused by S. pyogenes |
|
|
What are the properties of lesions from non-bullous impetigo?
|
Red macule-->vesicle-->crust
|
|
|
Generally, where does non-bullous impetigo occur?
|
Nose, mouth, extremities
Sites of trauma |
|
|
What bacteria causes Bullous impetigo?
|
S. Aureus
A toxin causes the problems. |
|
|
What population gets bullous impetigo?
|
Neonates
|
|
|
What are the treatments?
|
Clean skin/remove crust
Ointment |
|
|
Widespread papula on a 18 year old who has a hot tub: what do you think?
|
Pseudomonas folliculitis
|
|
|
What is the time course for pseudomonas folliculitis?
|
Starts up 8 - 48 hours after exposure
|
|
|
What's the treatment of pseudomonal folliculitis?
|
It's normally self-limited
IF IMMUNE COMPROMISED: Oral fluoroquinolone |
|
|
What is the cause of lyme disease?
|
Borrelia burgdorferia
|
|
|
What are the initial findings of Lyme disease?
|

Erythema migrans
|
|
|
What is the treatment of lyme disease?
|
Doxy
Amoxicillin |
|
|
Grouped vesicles are seen in what disease?
|
Herpes simplex
|
|
|
What type of herpes usually causes orolabial herpes? Genital?
|
Orolabial: HSV-1
Genital: HSV-2 |
|
|
What is the mechanism of transmission of herpes?
|
Direct contact
|
|
|
what are the symptoms of an active herpes infection?
|
Pain
Tenderness burning Fever ymphadenopathy |
|
|
How does herpes establish latency?
|
Skin--> Dorsal root ganglion along the nerve
It can then go back down to the skin to reactivatex |
|
|
What virus causes chicken pox?
|
VZV
|
|
|
What's the transmission of VZV?
|
Airborne droplets
DIrect contact with the vesicles |
|
|
What's the typical pattern on the body for VZV?
|
Scalp-->trunk-->extremities
|
|
|
In what stage is VZV contagious?
|
When things aren't crusted over.
|
|
|
What disease should you think of when they say, "Dew drop on a rose petal?"
|
VZV
|
|
|
What virus causes shingles? How does it happen?
|
VZV
You get a reactivation of the VZV |
|
|
What condition causes a reticular pattern?
|
Erythema infectiosum
|
|
|
What virus causes erythema infectiosum?
|
Parvovirus B19
|
|
|
How is erythema infectiosum transmitted?
|
Respiratory droplets
|
|
|
What is the pattern of the rash travelling in erythema infectiosum?
|
Initial rash on the cheeks
Later, a reticulate rash on the extremities |
|
|
What are serious complications to erythema infectiosum?
|
ANEMIA
Can happen seriously in newborns |
|
|
What causes swimmers itch?
|
Schistosomes
|
|
|
What animals are involved in swimmers itch?
|
Duck are the host, crap out the eggs, gets picked up in the snails, then humans can get it.
Causes lots of papules. |
|
|
What causes a serpingenous lesion?
|
SCABIES!
They show a burrow sign |
|
|
What are the symptoms of scabies?
|
ITCHING!
|
|
|
How do you diagnose scabies?
|
Look for the little bugger in the skin: scrape it and look in a scope.
|
|
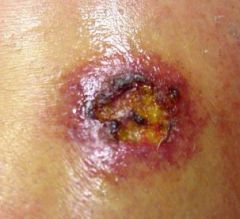
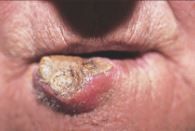
What is this?
|
Erosion/ulceration
|
|
|
What kind of a spider can cause an ulcerating lesion?
|
BROWN RECLUSE!
|

