![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
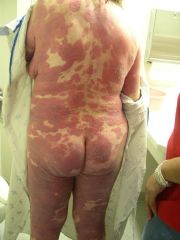
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma - non-nodal
Typically presents with red, scaly patches or thickened plaques of skin that often mimic eczema or chronic dermatitis and are painful |
|
|
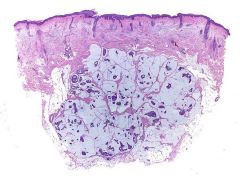
Mucinous carcinoma
Blue areas are pockets of mucin |
|
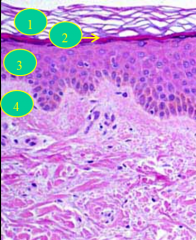
LAYERS (not stratums)
|
1 = horny layer
2 = granular layer 3 = squamous layer 4 = basal layer |
|
|
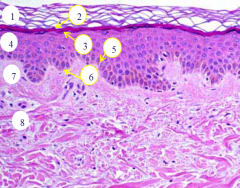
1 = stratum corneum
2 = stratum lucidem 3 = stratum granulosum 4 = stratum spinosum 5 = stratum basale 6 = DEJ 7 = papillary dermis 8 = reticular dermis |
|
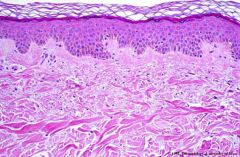
Where is this skin/ what type?
|
Trunkal skin (on trunk/ more proximal extremities)
|
|
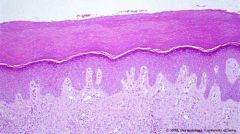
Where is this skin/ what type?
How is it different from other skin? |
Acral skin (palms and soles - specialized areas without hair)
Has a thicker corneum and a well defined graular layer |
|
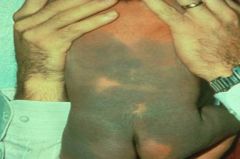
What is this and when/ why does it arise?
|
Mongolian spot
Children of mixed race at birth because the pigment higher in the skin is brown/black but in deeper areas it is bluer and in newborns the pigment is still migrating superficially |
|
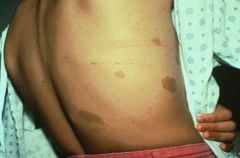
|
Cafe au lait macules
|
|
|
Minocycline hyperpigmentation
(from fillings) |
|
|
Hemangiomas - this is a patch
Sometimes also as plaques Congenital |
|
|
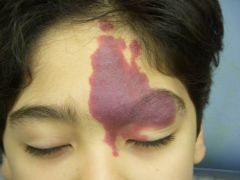
Nevus flamus aka port wine stain
Congenital |
|
|
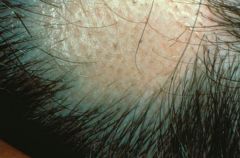
Allopecia areata - autoimmune
Considered a patch even though there is no visible pathology |
|
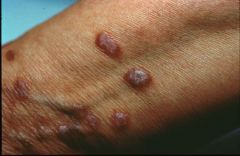
Also, what is a common area to see this?
|
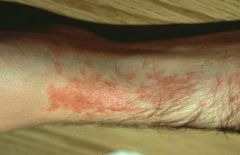
Lichen planus, common on extensor surfaces (wrist here)
Note: pruritic, violaceous, flat-topped papules |
|
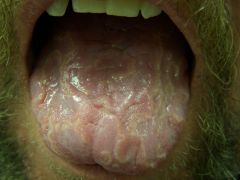
|
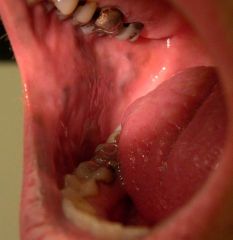
Lichen planus on oral mucosa
Note: pruritic and scaley, flat topped |
|
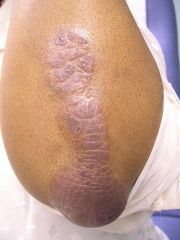
|
Psoriasis
Note: scaley plaques, common on joints - well demarcated and erythematous |
|
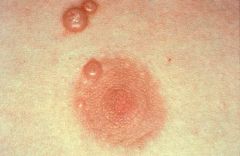
|
Molluscum contagiosum
Note: bowl-shaped lesion with central depression (full of keratin and viral particles) |
|
|
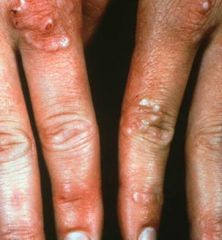
Granuloma annulare
Note: plaques and papules both present, filled with granulomatous deposits |
|
Also, how does this arise?
|
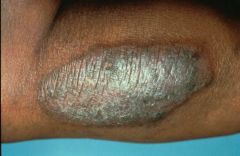
Lichen simplex chronicus
Circular phenomenon from rubbing (like a callous) |
|
Name both and describe
|
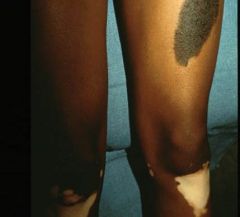
Top: congenital nevus, a plaque (mole)
Bottom: vitiligo, a patch (autoimmune attack on melanocytes) |
|
Name and characterize
|
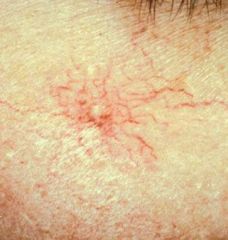
Spider angioma - vascular lesion
Radiating macule (non-palpable) |
|
|
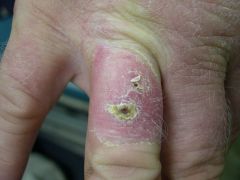
Spider bite
|
|
Name and cause
|
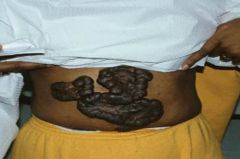
Keloid - tumor like proliferation of raised scars caused by excessive synthesis of type III collagen
Common in blacks |
|
|
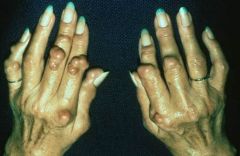
Rheumatoid nodules
|
|
|
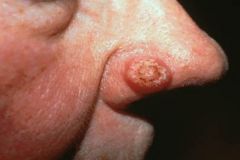
Basal cell carcinoma
Note: raised nodule (can also be papule) with a central crater |
|
|
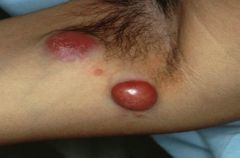
Cutaneous B-cell lymphoma - nodal
|
|
|
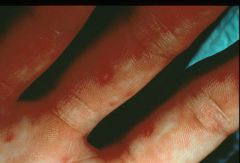
Hand, foot and mouth disease
Note: fragile blisters high in the dermis |
|
Name and associated with what?
|
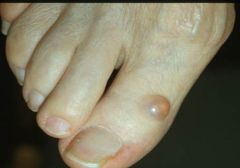
Myxoid cyst
Associated with osteoarthritis Filled with gelatinous substance |
|
|
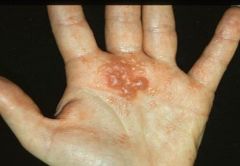
Dishydrotic Eczema - usually affects palms and sides of digits
Intensely puritic |
|
|
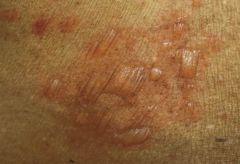
Bullous pemphigoid
Note: subepidermal vesicles |
|
|
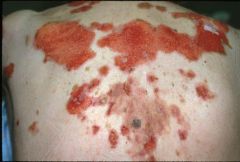
Pemphigus vulgaris
Note: superficial blisters rupture easily - why you only see erosion here |
|
|
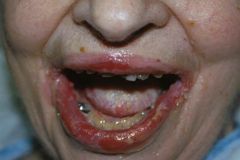
Pemphigus vulgaris
Note: intraepithelial (above basal layer) vesicles, superficial and easily ruptured |
|
|
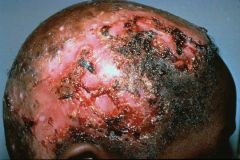
Tinea capitus
Note: circular or ring shaped patches that are highly inflammatory with allopecia, erosion, ulceration and scarring |
|
|
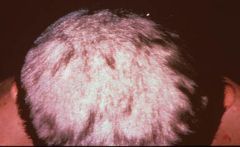
Tinea capitus (less progressed)
Note: black dot is present where hair has broken off |
|
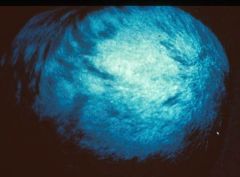
Test and indication
|
Positive Wood's lamp test - indicates causative organism of the tinea capitis as Microsporum (not trichophyton)
|
|
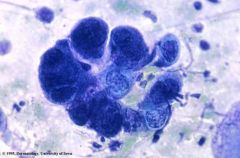
Test and indication - associated diseases
|
Tzanck prep showing giant multinucleated cells
Indicative of herpes virus - herpes zoster, herpes simplex, varicella, pemphigus vulgaris, cytomegalovirus |

