![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In the United States, standards for dental materials are developed and administered by the:
(a) FDA (Food and Drug Administration) (b) ADA (American Dental Association) (c) AADR (American Association for Dental Research) (d) OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) |
(b) ADA (American Dental Association)
The FDA is the regulatory agency, whereas the ADA develops standards and administers those standards and guidelines. The AADR is a professional organization for dental researchers. The OSHA mandates the practice of standard (universal) precautions for bloodborne pathogens. |
|
|
All of the following are reasons for a dental hygienist to have knowledge and understanding of dental materials EXCEPT:
(a) Explaining the different types of restorative materials available to the patient (b) Assessing the patient's oral condition (c) Deciding which material is best for the patient's restoration (d) Understanding the behavior of dental materials |
(c) Deciding which material is best for the patient's restoration
It is not within the scope of dental hygiene practice to choose the restorative material for the patient. This is the responsibility of the dentist. Understanding how dental materials behave, educating the patient, and assessing the patient are all patient care responsibilities of the hygienist. |
|
|
An amalgam restoration located on the gingival third of tooth #3 would be a Class ____ restoration.
(a) I (b) II (c) III (d) IV (e) V (f) VI |
(e) V
Gingival third caries, anterior and posterior and both lingual and facial, are defined as Class V. |
|
|
The biologic nature of the oral environment and the size of the oral cavity restrict the use of dental materials. One restriction is the degradation of restorations.
(a) The first statement is true; the second statement is false. (b) The first statement is false; the second statement is true. (c) Both statements are true. (d) Both statements are false. |
(c) Both statements are true.
The degradation of teeth and dental materials, biocompatibility, biting forces, esthetic demands of the patient, and temperature changes are all restrictions that limit the use of dental materials. |
|
|
When the temperature changes in the mouth, the teeth and most restorative material expand and contract by the same amount. No leakage occurs around the restoration.
(a) The first statement is true; the second statement is false. (b) The first statement is false; the second statement 1s true. (c) Both statements are true. (d) Both statements are false. |
(d) Both statements are false.
When the temperature changes in the oral cavity, no dental material expands and contracts by exactly the same amount as the natural tooth structure. Over time, this expansion and contraction may cause leakage around the restoration and tooth sensitivity. |
|
|
Which of the following oral tissues provides feedback to the individual regarding the forces placed on the tooth?
(a) Pulp (b) Dentin (c) Periodontium (d) Gingival tissue |
(c) Periodontium
The periodontium supports the tooth in a stable condition and gives feedback on the forces being placed on the teeth. The gingival tissues seal out undesirable agents and attach to the teeth, forming a barrier. The pulp serves to respond to thermal stimuli, as it contains the nerve cells. |
|
|
Which of the following restorations are utilized when a substantial amount of a tooth is missing?
(a) Crown (b) Pontic (c) Implant (d) Fixed partial denture |
(a) Crown
When a significant amount of tooth structure is missing from a particular tooth, a crown will encircle and support the remaining tooth structure. A pontic is the “false tooth” on a bridge, whereas an implant replaces the entire tooth, including the root. A fixed partial denture replaces teeth that may be missing in an arch and is cemented in place. |
|
|
The design of a cavity preparation aids in the retention of a restoration. The walls of an amalgam preparation diverge while the walls of an inlay converge.
(a) The first statement is true; the second statement is false. (b) The first statement is false; the second statement is true. (c) Both statements are true. (d) Both statements are false. |
(a) The first statement is true; the second statement is false.
It is true that the cavity preparation design helps to secure the restoration in place. But because gold castings such as an inlay are cemented in place and must be first seated without cement as a “try-in,” the walls must diverge so that it can be removed and then cemented. The converging walls of an amalgam preparation, as well as the added undercut areas, help to retain it in the cavity prep. |
|
|
If a restoration is fabricated on a replica (positive reproduction) of a patient's teeth, It is referred to as a:
(a) Student model (b) Cast (c) Diagnostic cast (d) Any of the above terms may be used |
(b) Cast
Technically, the only terms that would be interchangeable are study model and diagnostic cast. This replica is used to study the size and position of the oral tissues. If a restoration is constructed on the replica, it is called a cast. |
|
|
An example of an indirect restorative material would be:
(a) Amalgam (b) Glass ionomer cement (c) Composite (d) Ceramic (porcelain) |
(d) Ceramic (porcelain)
Amalgam, composites, and glass ionomers are all direct restorative materials. They are placed directly into the cavity preparation once all the decay is removed. Porcelain materials must be fabricated in a dental laboratory because they are fired in an oven at high temperatures. Temporary restorations are usually made for the patient to be used between appointments while indirect restorations are being fabricated. |
|
|
Medical devices are grouped into three categories according to Medical Device Amendment of 1976. Which class of devices is most regulated?
(a) I (b) II (c) III (d) IV |
(c) III
Class III devices are the most regulated and require premarket approval. Class I are the least regulated. There is no Class IV. |
|
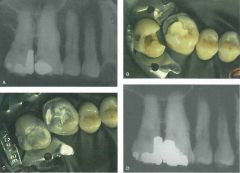
Using Figures 1. 9 A and D, which of the following best describes the roots of the teeth?
(a) Calculus is visible on the distal of tooth #2. (b) Calculus is visible on several roots. (c) The roots are radiographically foreshortened. (d) The roots are radiographically elongated. |
(a) Calculus is visible on the distal of tooth #2.
Calculus is visible on the distal surface of #2 but not others. Do not confuse the crestal bone with calculus. The teeth appear radiographically correct and no distortion has occurred during exposure. |

