![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
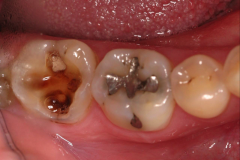
Dental Caries - Breakdown of teeth due to bacteria (most common cariogenic bacteria = streptococcus mutans) - Bacteria use carbohydrates and produce lactic acid which breaks down enamel Most susceptible teeth - Molars |
|
|
Dental Caries Defense and Prevention |
Saliva - washes away bacterial acids, and supplies calcium and phosphate toremineralize and repair damaged tooth surfaces. - contains antimicrobial enzymes Oral Hygeine Diet |
|
|
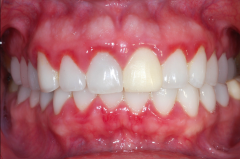
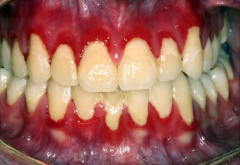
Gingivitis - Inflammation of gingiva without destruction of underlying bone - Can progress to periodontitis (loss of supporting bone) Causes - Dental plaque or calculus - Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy) |
|
|
Gingivitis |
|
|
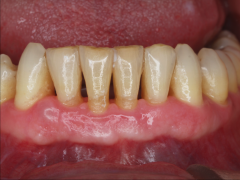
Periodontitis - Bone loss from chronic gingivitis - may need radiographs |
|
|
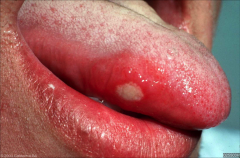
Recurrent aphthous ulcerations "Canker sore" - Painful oral lesions that appear as localized,shallow, round to oval ulcers with a grayish or yellow base - Almost exclusively occurs on non-bound (non-keratinized) mucosa Causes - Pathogenesis is not well-defined - Nutritional deficiencies in 20% of patients - Trauma Treatment - Resolves in 1-2 weeks - Mild corticosteroid gel or cream (ex. triamcinoloneor chlorhexidine gluconate rinse) |
|
|
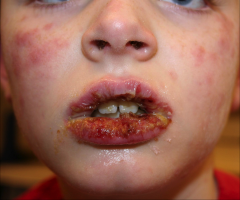
Erythema Multiforme - Acute, self-limiting, inflammatory mucocutaneous disease - 50% caused by a hypersensitivity run to HSV Treatment - Supportive care: systemic/topical analgesics - Severe cases: systemic/topical steroids - acyclovir at the first sign of EM can controlthedisease in 50% of patients |
|
|
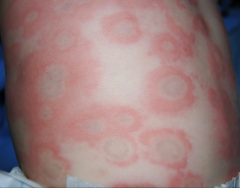
Erythema Multiforme - Acute, self-limiting, inflammatory mucocutaneous disease - 50% caused by a hypersensitivity run to HSV |
|
|
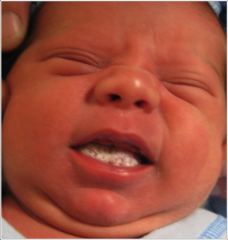
Oral Candidiasis - fungal infection caused by Candida Albicans - White lesion rubs off leaving a red surface Common in - Young infants - older patients w/ dentures - Diabetics - Immunodeficient Treatment - Nystatin 100,000 units/mL oral suspensionDisp: 300 mL Sig: Rinse with 1 teaspoon (5 mL) for 2 minutes 4-5x/daily and spit out - Mycelex (clotrimazole) 10 mg troches Disp: 70 troches Sig: Dissolve 1 troche in mouth 5x/daily until gone |
|
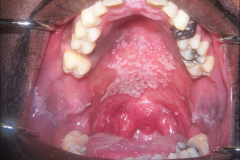
|
Pseudomembranous candidiasis |
|
|
Erythematous candidiasis |
|
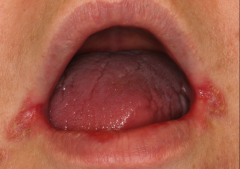
|
Angular Cheilitis Treatment - Nystatin and triamcinolone acetonide ointment Disp: 30g tube Apply to corners of mouth 4x/day for 2 weeks |
|
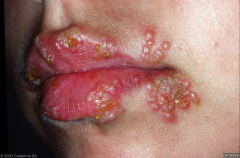
|
Herpes Labialis - HSV 1 or 2 - HSV undergoes latency and persists in the trigeminal neural ganglia,thereby preventing elimination of thevirus by immune responses Recurrent infection is common Tx: Acyclovir |
|
|
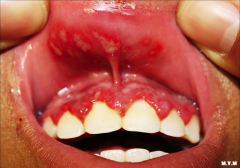
Primary herpes stomatitis - Primary: Keratinized or non-keratinized oral surfaces - Usually in young children, acute onset of numerous painful ulcerations - Patient will present with fever as well Recurrent infection is common DDx. - Primary: may overlap with aphthous ulcers or hand foot mouthdisease
Tx: - Acyclovir |
|
|
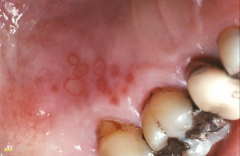
Secondary herpes stomatitis - Secondary: Primarily non-keratinized surfaces (in healthy hosts)Often induced by stress, trauma, or injury - Vesicles are painful and will pop DDx: - Secondary: may overlap with varicella zoster Tx: Acyclovir |
|
|
Oral Lichen Planus |
- T-cell mediated inflammatory run that attacks basal cell layer - Red, white and yellow flat lesions - Characteristic Wickham's striae more common in middle aged adults, women Can present in conjunction with cutaneous or genital disease 3 clinical subtypes - Reticular (white) - Erythematous (red) - Erosive (yellow) |
|
|
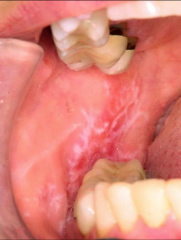
Oral reticular lichen planus - Wickham’s striae: characteristic of reticular lichen planusMost common presents bilaterally on the buccal mucosa - Affectsbuccal mucosa, tongue or gingiva - Atrophicor ulcerated erythematous areas with surrounding border of white lines Treatment - Topicalsteroid gel ex. clobetasol propionate gel 0.05% |
|
|
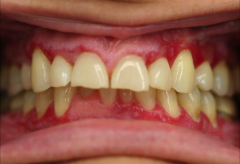
Oral (erythematous and erosive)lichen planus - Affectsbuccal mucosa, tongue or gingiva - Atrophicor ulcerated erythematous areas with surrounding border of white lines Treatment - Topicalsteroid gel ex. clobetasol propionate gel 0.05% ordapsone for symptomatic (erosive/erythematous) |

