![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe difference between a tree, shrub, and herbaceous plant |
Tree- often single stem, mature trees 13 feet or greater Shrub- often have multiple stems, mature shrub 13 feet or less Herbaceous plant- lacks woody cells found in trees and shrubs and are much shorter |
|
|
Difference between a species and sub species |
Species- largest group within which interbreeding produces viable offspring Subspecies- a group which can interbreed successfully with other subspecies, but do not do so in practice |
|
|
Describe the process of photosynthesis. What is needed and what results from this process. Where do the items needed in this process come from |
Photosynthesis- process of using light collected by leaves to create energy/food for plant Materials needed- carbon dioxide, water, and light are taken in by leaves through respiration and other processes. chlorophyll used inside of plant to create energy plant leaves absorb co2 and sunlight through leaves, turned into oxygen and energy in the form of sugars. Co2 comes from the air absorbed by plant leaves. |
|
|
Describe 4 functions cell wall provides plants |
Structural support- rigid cell wall allows plant to keep shape Protects against herbivory- Limits water loss- Protects against temp extremes- |
|
|
Describe primary pit field and plasma membrane, describe difference between the two |
Primary pit field- an area connecting one cell to another which allows the transfer of chemicals between the two Plasma membrane- seperates interior of cell from outside -Basic function of cell membrane is to protect cell from surroundings, primary pit field transports nutrients and waste between cells |
|
|
Describe wilting and plasmolysis, including difference between the two |
Wilting- the loss of rigidity in a plant due to water shortages -cell and cell wall collapse -non reversible -death of cell Plasmolysis- extra solution moves through cell wall into middle lamella as plant cell shrinks due to water shortages -reversible |
|
|
Describe transpiration, include two mechanisms or processes involved |
Transpiration- water loss through leaves 2 processes -evaporation- changing water into water vapor -diffusion- movement from high to low concentration to teach equilibrium |
|
|
Diagram and describe internal structure of leaf |
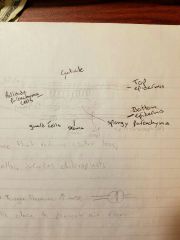
Cuticle- waxy surface that reduces water loss Pallisade parenchyma- middle cells, includes chloroplasts |
|
|
Describe how leaves lose water to surrounding atmosphere, include where water originates in leaf and processes involved |
- |
|
|
Describe three features of leaf that result in reduced water loss |
-cuticle- waxy surface on leaf that reduces water loss -guard cells close at night to prevent air from entering -stomates underneath leaf |
|
|
Describe three different sections of a tree and two functions performed by each |
Canopy- creates sugar/food/energy Trunk- connects roots to leaves, gets leaves to light Roots- brings in water and nutrients, anchors tree |
|
|
Describe respiration, list materials needed for respiration and byproducts |
Plant uses glucose and oxygen to create carbon dioxide, water, and energy used in photosynthesis Materials needed- glucose, carbon dioxide Byproducts- carbon dioxide, water, atp |
|
|
Describe how each section of tree uses one or more of these processes (photosynthesis, respiration, synthesis) to sustain life of tree |
- |
|
|
Describe difference in roots between monocots and dicots |
Monocots- primary tap root hours deep with smaller offshoots Dicots- fibrous roots that stay near surface |
|
|
Diagram and describe different types of cells in roots |
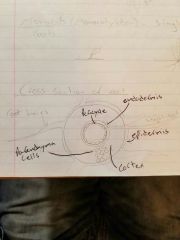
Epidermis- protective cells on outside of root Endodermis- protective layer of cells on inside of root Cortex- unappreciated cells found inside of root Parenchyma cells- cells composing the cortex |
|
|
Diagram and describe different types of cells and their functions in mature trunks |

Pericycle- unspecialized parenchyma cells Primary xylem- transports water upwards to leaves Primary phloem- transports nutrients down to roots Vascular cambium- allows root to grow |
|
|
Describe how tree rings arise and cell responsible |
Meristematic tissue- tissue that allows growth |
|
|
Describe meristem, how do primary and secondary meristem differ |
Meristem- regions of undifferentiated cells |
|
|
Describe three different types of meristem based on their location in tree |
Apical meristem- found at root and shoot tips, increases root and canopy depth/height and spread Intercalary meristem- found between mature tissue Lateral meristem- parallel to trunk, responsible for increased diameter |
|
|
Describe process of how shoot tips continue to elongate while producing new materials |
- apical meristems divide through mitosis with lower cells beginning to differentiate info new woody cells while upper cells remain undifferentiated |
|
|
Diagram and describe cells and their function in apical meristems |

Cells go through mitosis,lower cells start to become differentiated, upper cells remain undifferentiated |
|
|
Describe three differences between gymnosperms and angiosperms |
Angiosperms- rely on pollinators, have seeds that are enclosed in an ovary, Gymnosperms- rely on wind for pollinations, have unenclosed seeds on surface of scales or leaves, |
|
|
Diagram and describe relationship between temperature and photosynthetic activity for coniferous and deciduous trees |

Conifers are more photosynthetic active in colder temps, while deciduous trees are more active in warmer |
|
|
Describe three differences between coniferous trees and deciduous trees that allow deciduous to dominate in high northern latitudes |
-Keep needles all year, allows for jump start in photosynthetic activity earlier in year -heavy waxy deposits on needles to reduce water loss -longer narrower tracheids causes fewer bubbles in water transportation |
|
|
Describe how conifers and deciduous trees modify soil nutrient availability to benefit them |
Deciduous- drop leaves annually, pouring nutrients back into soil, leaves break down quickly Conifers- |
|
|
3 ways conifers modify their environment to increase possibility of return of fire/are adapted to periodic fire |
-needles have heavy waxy deposits, making them flammable -thick bark helps with fire resistance -few branches between roots and crown |

