![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common demyelinating disease in humans? Does it affect central or peripheral nervous system? What is the pathologic lesion?
What is the most common form of the disease? |
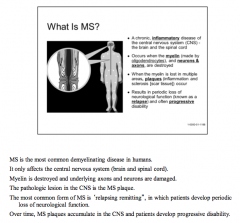
|
|
|
What is a relapse? |
New neurologic disability that lasts greater than 24 hours |
|
|
What is the clinical definition of MS? |

Two relapses that occur during two different times in a person's life. Two different areas of the CNS. |
|
|
What is used to diagnose MS? |
MS plaques on MRI Inflammatory profile in spinal fluid IgG index and oligoclonal bands Some lymphocytes but NEVER neutrophils! |
|
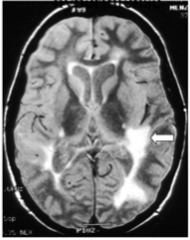
What are the bright white areas? Diagnosis?
What are they often enhanced with? |
MS plaques
Gadolinium => does not normally enter brain parenchyma, but does in the case of new acute MS plaque where active inflammation and breakdown of BBB allows gadolinium to enter brain parenchyma. |
|
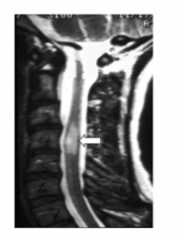
Can MS also affect the spinal cord? |
Yes |
|
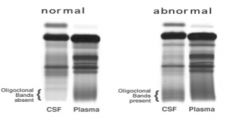
What is shown here? |
Oligoclonal bands of IgG |
|
|
How is the visual evoked response effected with MS? |

How quickly the occipital cortex detects light input from the retina |
|

Review |

|
|
|
Where are plaques located? Luxol fast blue stains normal myeline what color? |
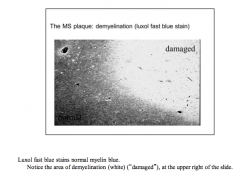
Deep white matter and periventricular areas |
|
|
Are axons also damaged in MS? |
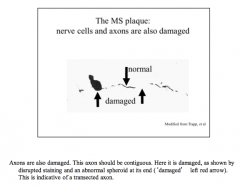
|
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of MS? |
Unknown
Genetically susceptible individuals => triggers => leukocytes penetrate BBB and secrete inflammatory cytokines => T-cells, B-cells, and macrophages autoimmune attack against myelin antigens => demyelination and axonal loss |
|
|
More detailed pathogenesis of MS: |
TH1 activated in systemic circulation => cross BBB and initiate autoimmune response => stimulate B cells to make antibodies and macrophages to demyelinate and cause axonal damage
TH2 => regulate and reduce pro-inflammatory response of TH1 |
|
|
Age of diagnosis of MS? Sex? Distance from equator? |
Between 20-40 2/3 female
Incidence of MS increases with distance from the equator |
|
|
What are the two types of MS? |
Relapsing Progressive |
|

Relapsing or progressive? |
Relapsing |
|
|
Steady progression of disability with few or no exacerbations. Relapsing or progressive? |

|
|
|
Draw the graph of benign MS. Remitting MS. Secondary progressive MS. Natural progression of primary MS. |
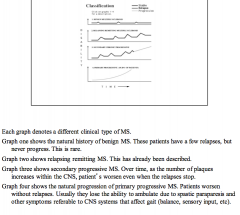
|
|
|
What if life expectancy of MS? What is average relapse per year? Median time to reach EDSS? |

|
|
|
What will you see evaluated in spinal tap in MS patient? What type of evoked potentials are used? |
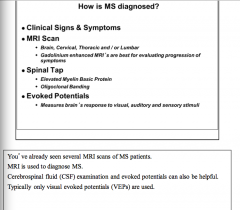
|
|

What are these the symptoms of? |
MS |
|

What are these all symptoms of?
Acute, subacute, or chronic |
MS
Subacute |
|

What is the effect of increased temperature on demyelinated segments? |

|
|
|
What are the two most common presenting symptoms in MS? |

Sensory symptoms in arms/legs, unilateral vision loss |
|
|
Where are MS plaques located? |
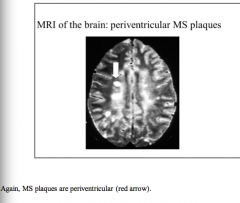
Periventricular |
|
|
Protein level in MS CSF? Normal or abnormal Lymphocyte count? Elevated or not?
What are the markers of MS in the CSF?
|
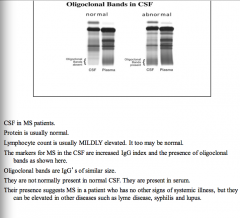
|
|
|
If the optic nerve is demyelinted from MS, what will be the delay in VER? |

|
|
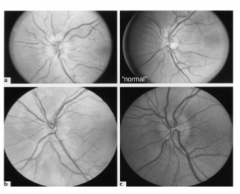
What is shown here? |
Optic neuritis in MS |
|
|
Will patients with MS sometimes have an APD? |
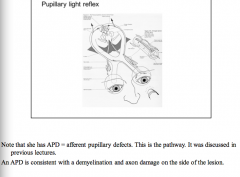
|
|

What is described here? |
Clinically isolated syndrome |
|
|
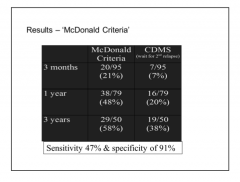
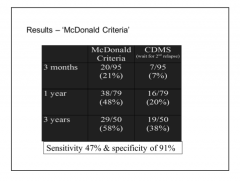
Patient with CIS, how do you determine if they have MS or not? |
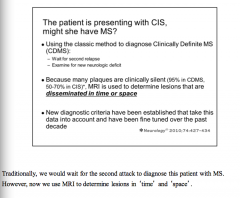
Traditionally = wait for second attack Now = MRI to determines lesions in time and space |
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
How many lessons on MRI do you need if patient presents with one syndrome? |
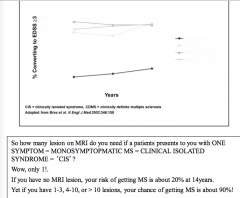
CIS = 1! |
|
|
What drugs are used for acute relapses of MS? |

Steroids
Steroids do not alter the course of the disease |
|
|
|
|

Diagnosis? |
Transverse myelitis No back pack but early urinary retention = SPINAL CORD LESION! |
|

Neurologic exam of what? |
Transverse myelitis |
|
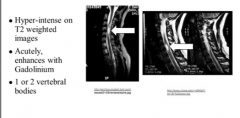
What is shown here? |
Transverse myelitis MRI
Lesion is limited within the spinal cord to only 1-2 vertebral body segments |
|
|
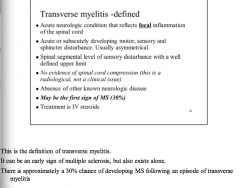
What is an acute neurologic condition that reflects FOCAL inflammation of the spinal cord?
What disturbances may occur? Symmetrical or asymmetrical?
May be the first sign of what condition? What is the treatment? |
|
|

Diagnosis? |
Severe thoracic pain Optic neuritis Acute paraparesis w/ urinary retention
NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA (NMO) |
|

What do these tests indicate? |
Neuromyelitis optic (NMO) |
|
|
How much of spine is involved with NMO? |
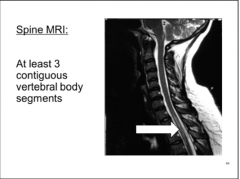
Can involve almost the entire spinal cord |
|
|
What distinguishes NMO from MS? |
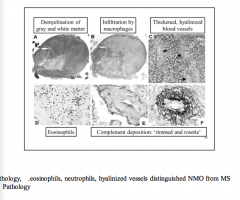
Eosinophils, neutrophils, hyalinized vessels |
|
|
What is the mechanism of NMO? |
Antibody mediated demyelination, axonal injury, and necrosis |
|
|
Optic neuritis + a lesion or two on MRI? Does patient have MS? |
Not technically => increased risk, but need to wait for second "time" factor to be sure |
|

|

|
|
|
Optic neuritis + lesions on MRI + gadolinium enhancing lesion (new)? Does patient have MS? |
Yes, "time" factor satisfied |
|
|
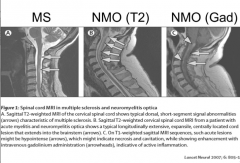
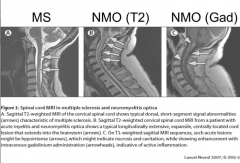
What are the distinguishing factors between MS, and NMO? |
Brain MRI, 3 VB segments PMNs OCB more common in MS |
|
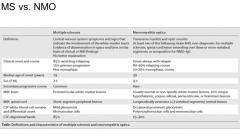
Review this |
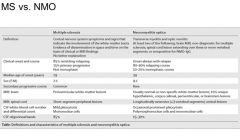
|
|
Review |
|
|

Review |

|
|
|
|
|
|
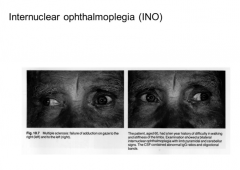
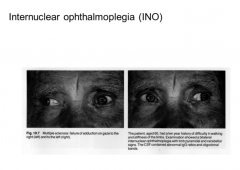
INO results from damage to what?
Where is the lesion located? |
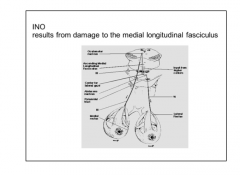
MLF
Lesion is on the side of adduction deficit.
|

