![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is ephaptic conduction?
|
After nerve injury, increased spontaneous firings from newly formed nerves form. Atypical connections develop between neighboring neurons leading to "cross-talk" or ephaptic conduction"
|
|
|
What are the imaging McDonald's Criteria?
|
3 out of the following:
1) 1 Gd enh lesion or 9 T2 hyperintense lesions 2) 1 juxtacortical 3) 1 infratentorial 4) > 3 periventricular |
|
|
What are Dawson's fingers?
|
ovoid shaped, abutting ventricles about 3 mm in size, perpendicular to ventricles. These result from T cell damage along the venules that are perpendicular to the ventricles.
|
|
|
What are the 4 subtypes of MS?
|
Relapsing Remitting
Progressive Relapsing Secondary Progressive Primary Progressive |
|
|
What percentage of patients have pleoctyosis?
|
more than 1/3 of patients
|
|
|
What percentage of patients have positive oligoclonal bands?
|
90% in definite MS *at some point in disease
**Usually they have at least 2 OCBS |
|
|
How often do Gd Enhancing lesions last in MS?
|
4-6 weeks
|
|
|
What is the maximum dose of Baclofen
|
80 mg/day divided into 4 doses
|
|
|
What is the maximum dose of Tizanidine?
|
36 mg daily
SE: somnolence,asthenia, dry mouth, liver toxicity rare, orthostatic hypotension, careful in elderly and renal impairment |
|
|
What is the pop sensation correlate to anatomically during a lumbar puncture?
|
Puncture of the ligamentum flavum
|
|
|
What are the layers you enter with your spinal needle?
|
1) Skin/Subcutaneous tissue
2) Supraspinous ligament 3) Interspinous ligament 4) Ligamentum flavum 5) Epidural space venous plexus 6) Arachnoid 7) Subarachnoid |
|
|
What percentage of patients with MS present with optic neuritis?
|
25%
|
|
|
What is balo's concentric sclerosis?
|
MS variant with bands of demyelinating and remyelinating disease
|
|
|
What is Schilder's disease?
|
variant of MS with aggressive disease course, deafness or cortical blindness and demyelination involving entire hemisphere or corpus collosum
|
|
|
What is Cogan's syndrome?
|
interstitial keratitis + inner ear abnormality
|
|
|
What is Alport's syndrome?
|
sensorineural hearing loss + interstial nephritis X linked
|
|
|
What is Usher's syndrome?
|
sensorineural hearing loss+ retinitis pigementosa (autosomal recessive)
|
|

What are the significant pathologic findings in this patient with susppected PML?
|
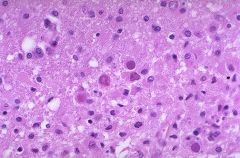
Bizzare astrocytes, lipid-laden ballooned oligodendrocytes with ground glass inclusions
|

