![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Age does not equal.... |
cognitive impairment |
|
|
Changes in cognitive ability should be... |
aggressively assessed and treated |
|
|
Abrupt-onset confusion state involving: •Disturbance of consciousness •Change in cognition •Develops over a short period •Fluctuates during the day •Always secondary to another condition•Complete recovery can occurn |
Delirium (Acute Confusion) |
|
|
•Intoxications/withdrawals •Infections •Metabolic disorders—fluid& electrolyte imbalances, hypoxia, hypo/hyperglycemia •Drugs—CNSdepressants, digitalis, lithium, steroids, benzodiazepines •Neurologicaldiseases—headtrauma, seizures •Cancer—primary or metastatic lesions •Psychosocialstressors—sensorydeprivation/overload, relocation, pain, immobility, sleep deprivation |
Causes of delirium |
|
|
Causes of delirium? |
Drugs Environment Low O2 Infection Intracranial (tumor) Under hydration Metabolic Sleep deprivation |
|
|
•Specific for delirium •Takes less than 5 minutes. •Very helpful in noting change in cognition. •Delay in Treatment can have serious consequences. |
CAM tool (Confusion Assessment Method) |
|
|
CAM tool Feature 1 & feature 2 must be present as well as.... |
Feature 3 or 4. |
|
|
RASS (Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale) score identifies if patient is |
sedated or agitated |
|
|
Dementia is a _________ confusion. It is the __________ loss of function. Majority of which is irreversible. Most common cause is ___________ disease. |
Chronic Progressive Alzheimer's |
|
|
Brain damage caused by multiple strokes. |
Vascular dementia |
|
|
abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits, called Lewy bodies, affect chemicals in the brain whose changes, in turn, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. |
Lui Body dementia |
|
|
a group of disorders caused by progressive nerve cell loss in the brain's frontal lobes (the areas behind your forehead) or its temporal lobes (the regions behind your ears). |
Frontal temporal dementia
|
|
|
The disease process is associated with plaques and tangles in the brain. |
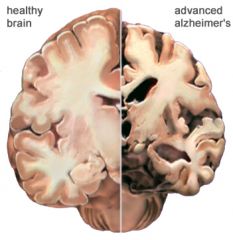
Alzheimer's |
|
|
(mild)—forgetfulness; possible depression
|
Stage 1 |
|
|
(moderate)— Confusion Memory gaps Self-care gaps Apraxia (motor function) Labile (easily altered) mood. |
Stage 2 |
|
|
(moderate to severe)— Can't identify objects/people Agnosia (sensory perception) Apraxia (Motor function) |
Stage 3 |
|
|
(late)—end-stage: Agraphia (writing) Hyperorality (combo pica or overeating) Hypermetamorphosis (touching everything) |
Stage 4 |
|
|
Over time experiences difficulty remembering words Loss of language ability |
Anomia Aphasia |
|
|
Cardinal symptoms |
–Anomia (Name recall) –Aphasia (Speak) –Apraxia (Purposeful Action) –Agnosia (Interpret sensations) |
|
|
Defensive behaviors |
–Denial –Perserverationv (repetition of a particular response) –Avoidance of questions –Confabulation (fabricated stories without the conscious intention to deceive) |
|
|
Diagnosis is based on... |
history of symptoms. (lab tests + imaging) |
|
|
Cholinesterase inhibitors (↑acetylcholine to slow progression) |
–donepezil –rivastigmine –galantamine |
|
|
NMDA receptor antagonist (↓effectsof glutamate, CNS excitation) |
–Memantine |
|
|
SSRI’s for depression |
–paroxetine –sertraline |
|
|
Sleep aids and antipsychotics are used ___________ with patients who have dementia. |
sparingly |
|
|
Never say “No” or “You can’t”
___________ may cause agitation – depends on stage of disease |
Orientation |

