![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the most common elements in living things?
|
-Carbon C
-Hydrogen H -Oxygen O -Nitrogen N |
|
|
State the name of elements other than C,H,O and N that are needed by living organisms
|
-Sulphur S
-Calcium Ca -Phosphorus P -Iron Fe -Sodium Na |
|
|
What is the role of Sulphur?
|
Important element in some amino acid
|
|
|
What is the role of Calcium?
|
Found in bones and teeth
|
|
|
What is the role of Phosphorus?
|
Found in cell membranes and nucleotides (DNA)
|
|
|
What is the role of Iron?
|
Found in haemoglobin (oxygen carrier in red blood cell)
|
|
|
What is the role of sodium?
|
Needed for nerve impulse
|
|
|
Draw a water molecule
|
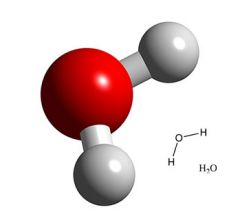
|
|
|
Outline the thermal properties (heat capacity) of water
|
Water has a large heat capacity. Blood is mainly composed of water and can carry heat from warmer part of the body to cooler part. It is a transport medium for heat.
|
|
|
Outline the thermal properties (boiling point) of water
|
Water has a high boiling point (100C). It is below boiling point and above freezing point in most area on earth. As a liquid it can act as the medium for metabolic reaction.
|
|
|
Outline the thermal properties (cooling effect) of water
|
Water molecules can evaporate below boiling point. Evaporation from plants (transpiration) and from human skins (sweat) has useful cooling effect. Water can be used as a coolant.
|
|
|
Outline the cohesive properties of water
|
Water molecules stick to each other because of the hydrogen bond between them.
|
|
|
Outline the solvent properties of water
|
Many different substances dissolve in water because of its polarity. Water is the medium for metabolic reaction and can also be used as a transport medium
|
|
|
Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds
|
Organic = compounds containing carbon
Inorganic = no carbon |
|
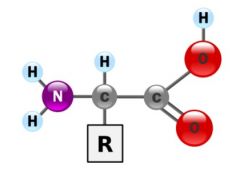
Identify the molecule
|
Amino acid
|
|
Identify the molecule
|
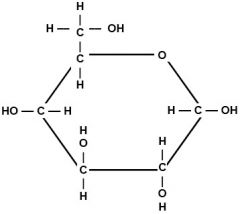
Glucose
|
|
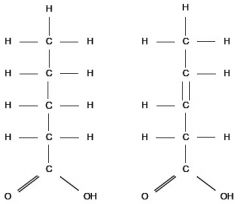
Identify the molecule
|
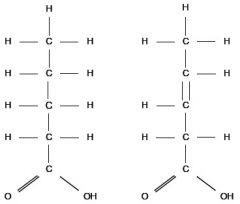
Fatty acid
|
|
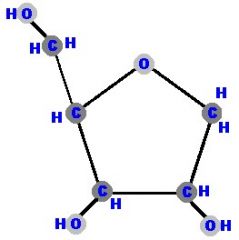
Identify the molecule
|
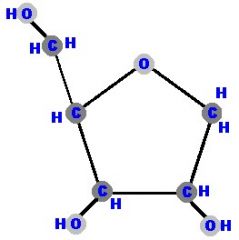
Ribose
|
|
|
List three examples of monosaccharides
|
-glucose
-galactose -fructose |
|
|
List three examples of disaccharides
|
-maltose
-lactose -sucrose |
|
|
List three examples of polysaccharides
|
-starch
-glycogen -cellulose |
|
|
State one function of glucose in animals
|
Transport energy to cells throughout the body
|
|
|
State one function of lactose in animals
|
Sugar in milk, provided energy to young mammals
|
|
|
State one function of glycogen in animals
|
Store energy in liver and muscle cells
|
|
|
State one function of fructose in plants
|
Used to make fruit sweet-tasting
|
|
|
State one function of sucrose in plants
|
Carried by phloem to transport energy throughout the plant
|
|
|
State one function of cellulose in plants
|
Used to construct the cell wall
|
|
|
State three functions of the lypids
|
-energy storage (fat in humans and oil in plants)
-heat insulation -buoyancy |
|
|
State the name of the four bases in DNA
|
-adenine A
-guanine G -thymine T -cytosine C |
|
|
Outline the DNA structure
|
-sugar (deoxyribose)
-base -phosphate |
|
|
How are DNA nucleotides linked together?
|
By covalent bonds
|
|
|
How is the DNA double helix formed?
|
-complementary base pairing (A-T and C-G)
-hydrogen bonds between bases |
|
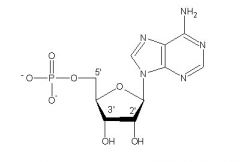
Identify the structures of the nucleotide
|
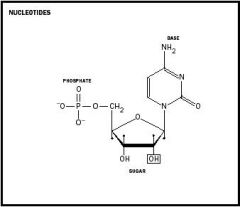
|
|
|
What is the name of the enzyme that unzips the DNA strands?
|
Helicase
|
|
|
Outline the process of DNA replication (SL only)
|
-Helicase unwinds DNA double helix and separates strands
-formation of complementary strands by DNA polymerase |
|
|
What is the name of the enzyme that links the nucleotides on the new strand during DNA replication? (SL only)
|
DNA polymerase
|
|
|
Compare the structure of DNA and RNA
|
DNA vs RNA
-double strand vs single strand -thymine base vs uracil base -deoxyribose vs ribose |
|
|
Outline DNA transcription
|
-formation of a RNA strand complementary to the DNA strand
|
|
|
How many bases form a codon?
|
Three
|
|
|
What is the name of the enzyme used in DNA transcription?
|
RNA polymerase
|

