![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
inoculations
|
sample placed in container of medium supporting its growth
|
|
|
inspection
|
cultures observed
|
|
|
incubation
|
placed in incubator to promote growth
|
|
|
magnification
|
enlarge objects
|
|
|
resolving power
|
shows detail
|
|
|
agar
|
.solid @room temp, liquefies @100°, resolidifies @42°
.provides framework to hold moisture & nutrients .not digestible for most microbes |
|
|
hyaluronic acid
|
found in connective tissue
|
|
|
strep
|
catalase -
chains of cells sensitive to drying, heat & disinfectants |
|
|
staph
|
catalase + (hydrogen peroxide bubbles)
|
|
|
staph
|
cluster of grapes
|
|
|
group b strep
|
can be transferred from mother to baby
|
|
|
viridans group
|
most serious infection - sub acute endocarditis
|
|
|
prokaryotic
|
simple cell
unicellular no nuclei no organelles ex. bacteria and archaea |
|
|
eukaryotic
|
complex cell
unicellular and multicellular nucleus membrane organelles ex. animals. plants. fungi.protists |
|
|
microbes
|
bacteria
fungi algae virus protozoa helminth |
|
|
Leeuwenhoek
|
first to observe microbes
|
|
|
holmes
|
mothers give birth in home fewer infections
|
|
|
semmelweis
|
correlated infections with physicians coming directly from autopsy room to maternity ward
|
|
|
Lister
|
introduced aseptic techniques
|
|
|
Pasteur
|
microbes caused fermentation
disproved spontaneous generation developed pasteurization germ theory of disease |
|
|
koch
|
identified cause of anthrax. tb and cholera
developed culture methods |
|
|
Koch's postulates
|
sequence of experimental steps that verified the germ theory
|
|
|
classifications
|
domain. kingdom. phylum. class. order. family. genus. species
|
|
|
folliculitis
|
inflammation of hair follicle
|
|
|
furuncle
|
boil. inflammation of hair follicle that progresses into abcess
|
|
|
carbuncle
|
larger and deeper lesion created by aggregation of cluster of furuncles
|
|
|
impetigo
|
bubble like swelling that can break and peel away. common in newborns
|
|
|
osteomyelitis
|
infection of bone in metaphysis. abscess forms
|
|
|
bacteremia
|
bacteria in blood. endocarditis possible
|
|
|
food intoxication
|
ingestion of heat stable enterotoxins. gastrointestinal distress
|
|
|
staph scalded skin syndrome
|
toxin induces bright red flush. blisters. desquamation of epidermis
|
|
|
toxic shock syndrome
|
toxemia leading to shock and organ failure
|
|
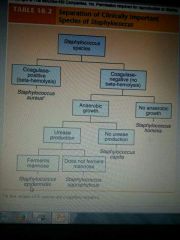
|
.
|
|
|
mrsa
|
methicillin resistant s. aureua.
|
|
|
erysipelas
|
pathogen enters through a break in skin and spreads to dermks and subq . can become systemic
|
|
|
streptococcal pharyngitis
|
strep throat
|
|
|
scarlet fever
|
strain of s. pyogenes carrying prophage that codes for erythrogenic toxin
|
|
|
rheumatic fever
|
follows pharyngitis in children. carditis.arthritis. chorea. fever
|
|
|
acute glomerulonephritis
|
nephritis. ^ bp. HF. kidney failure
|
|
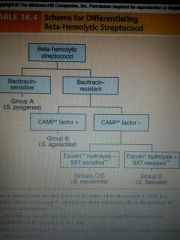
|
.
|
|
|
bright field
|
specimen darker than surrounding field. used for live and preserved stained specimens
|
|
|
dark field
|
illuminated specimens surrounded by dark field. used for live and unstained
|
|
|
phase contrast
|
transforms subtle changes in light waves passing passing through specimen. best for observing intracellular structure
|
|
|
fluorescence
|
uv radiation . uses dye . used for diagnosing infections
|
|
|
scanning confocal
|
uses laser beam. integrates images to allow focus on multiple depths
|
|
|
electron
|
forms image with electrons. waves are 100,000 x shorter than waves of visible light.
|
|
|
basic dyes
|
cationic positively charged
|
|
|
positive staining
|
surfaces of microbes are negatively charged and attract basic dyes
|
|
|
acidic dyes
|
anionic. negatively charged
|
|
|
negative staining
|
microbe repels dyes. dye stains background
|
|
|
selective media
|
contains one or more agents that inhibit growth of some microbes and encourage growth of desired microbes
|
|
|
differential media
|
allows growth of several types of microbes and displays visible differences among them
|
|
|
gram positive bacteria
|
thick cell wall composed of peptidoglycan and cell membrane
|
|
|
gram negative bacteria
|
outer cell membrane. thin peptidoglycan layer and cell membrane
|
|
|
peptidoglycan
|
composed of a repeating framework of long glycan chains cross linked by short peptide fragments
|
|
|
rickettsias
|
very thin gram negative
pathogenic obligate intracellular pathogens cannot survive outside of host rocky mountain spotted fever |
|
|
chlamydias
|
tony
obligate intracellular parasites not transmitted by arthropods |
|
|
archaea
|
most closely related to eukarya
contain unique genetic sequenses in RNA unique membrane lipids and cell walls |

