![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Gout is a disorder of, dx, Mnemonics gout?
|
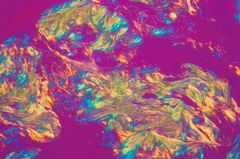
nucleic acid metabolism grt monosodium urate crystal deposition in the joints. dx made by joint aspiration and crystal analysis
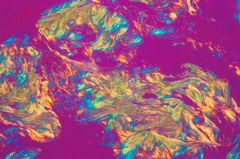
BRAGN = “birefringent: blue right angle gout negatively”. I.e. gouty urate crystals are negatively birefringent: blue when perpendicular to the plane of polarization. |
|
Gout is caused; The biologic precursor to gout is
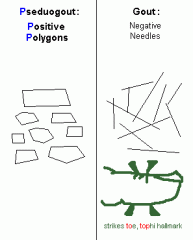
psuedogout crystals are |
caused by monosodium urate crystal deposition in tissues grt: djd, soft tissue masses (i.e., tophi), nephrolithiasis, and urate nephropathy.
- elevated serum uric acid levels (i.e., hyperuricemia). Pseduogout crystals are:: Calcium pyrophosphate deposition is found with pseudogout and Positive birefringent Polygon shaped Also, gout classically strikes great Toe, and its hallmark is Tophi. |
|
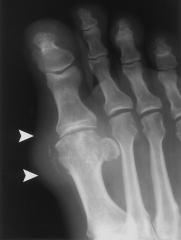
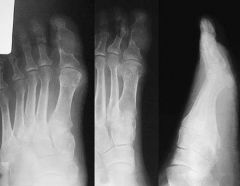
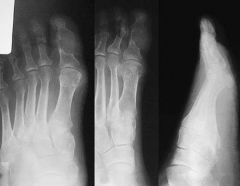
60yo Mc/o pain: R great toe x 2 yrs. What is the most likely cause arrows in Fig A::1 Monosodium urate crystal deposition; 2 Ca pyrophosphate deposition;
3 Renal osteodystrophy; 4 TB; 5 Sarcoidosis:: |
dx is confirmed if monosodium urate crystals are present in synovial fluid." deposition MU crystals in tissues grt=djd, soft tissue masses (i.e., tophi), nephrolithiasis, and urate nephropathy. The biologic precursor to gout is elevated serum uric acid levels:::Ans1
|
|
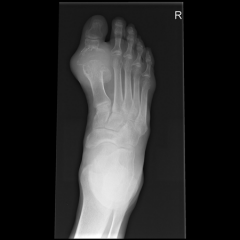
Which of the following foot radiographs is most consistent with the diagnosis of gout? ddx of gout & tx of, Mof Action 1 arthritis mutilans in psoriatic arthritis; 2 Freiberg's infraction; 3 Charcot foot; rheumatoid foot. tx
|
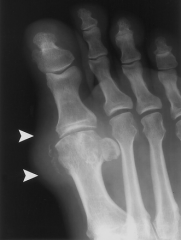
asymmetric polyarthropathy, well-defined erosions w/ sclerotic margins, overhnging bony edges, tophi. well-defined punched out periarticular erosion w/sclerotic overhang'g borders w/in forefoot, consistent w/gout::
tx= indomethacin (indocin) 50mg TID-inhibits phagocytosis ; colchicine-inhibits inflammatory mediators |
|
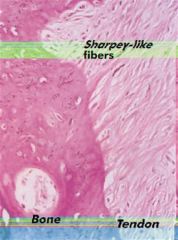
Ligaments attach to bone by both direct insertion & indirect insertion. Which of the following most accurately describes the order of the four transition zones of direct insertion?
|
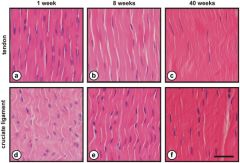
1 Lig > fibrocartilage > mineralized fibrocartilage > b1; 2 Lig > mineralized fibrocartilage > fibrocartilage > b1;
3 Ligt > mineralized fibrocartilage > periosteum > b1; 4 Lig > Sharpey's fiber > periosteum > b1; 5 Lig > periosteum > fibrocartilage > b1:::ans1 |
|
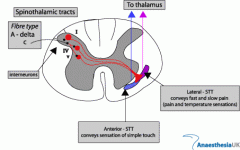
spinal cord pain travels through what tracts?
|
they both sound the SAME":
Sensory=Afferent, Arrive Motor=Efferent, Exit Spinal cord: converting ventral/ anterior/ motor/ efferent and dorsal/ posterior/ sensory/ afferent A limousine: The motor of limo is ventral and anterior on the car. The Aerial is sensory and on the dorsal and posterior of the limo. · Note 1: 'A' is Afferent, and also, in a limo, the aerial on the top of the trunk has a capital 'A' shape. · Note 2: An aerial is a sensory thing: picks up radio waves. · Note 3: If picked a limo up in your hand, can only see motor on ventral, since dorsal is covered by the hood/bonnet. |
|
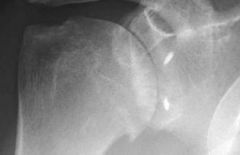
35yoMc/o pain, limited ROM x3 mthsp/ SARK. postop: intra-articular infusion pump x 3 D, sling x 4 wks, passv ROM @4 wks & active ROM, isotonic strengthening program @ 9 wk. Which options is MOST appropriate tx?1 Reassurance & appropriate f/u
|
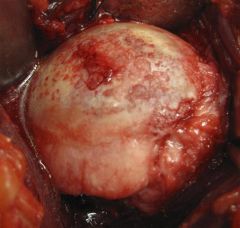
; 2 Focused PT- aggressive ROM exercises and modalities; 3 Intra-A injection of corticosteroids to dec post-op inflammn; Shoulder xrays- assess for chondrolysis; 5. Arthroscopic vs open Bankart revision surg for failed repair:::ans4 (FDA) has issued a warning on the adminstration of continuous intra-articular infusion of local anesthestics for pain control.
|
|

What is the most appropriate delivery route for pain medication to a morbidly obese post-operative patient to insure a therapeutic plasma concentration? 1 PO tab; 2 PO liq solution; 3 SubQ inj; 4 IV PCA based on actual body wt; 5 IV PCA based on ideal body wt
|

in the morbidly obese = IV PCA based on the pt's ideal body weight. This method of analgesia has the best chance of avoiding respiratory depression while also adequately controlling the patient's pain::ANS5
|

