![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
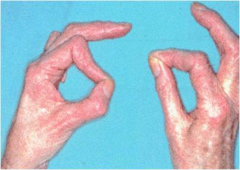
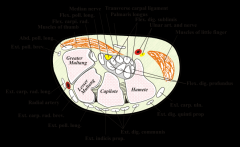
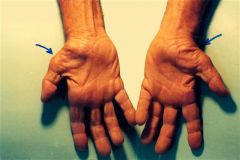
72yo F c/o progrssv weaknss w/ grasp & key pinch in L hand. PE hand: (+) dec'd senstn on volar aspect 4 & 5 digits. Dorsal senstn throughout the hand= nl. b/l key pinch Fig A. What is cause of compressn?
|
1-Accessory head FPL; 2-FCU; 3-Osborne's lig; 4-Ganglion w/in Guyon's canal; 5-Anconeus epitrochlearis:: Comprssn ulnar n w/in Guyon's canal= ulnar tunnel syndrm, MC caused by a ganglion cyst.Ans4
|
|
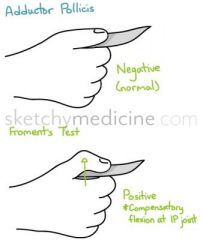
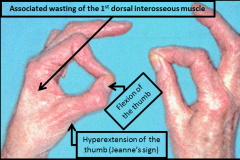
1 Froment sign
2 Wartenberg sign 3 Presentation of compression within Guyon's canal causing tarsal ulnar tunnel syndrome |

1 IP flexion compensating for loss of thumb add when attemptg to hold a piece of paper, loss of MCP flex & add by adductor pollicis (ulnar n.)compensatory IP hyperflex by FPL (AIN); 2 abd posturing little finger; 3 pure m/s/mix
|
|
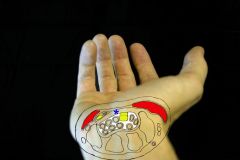
1 CTS mnemonic
2 contents of the carpal tunnel |
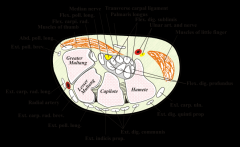
1.MEDIAN STRAP: M-Myxoedema M-mucopolysaccharidosis M-mucolipidosis (CRF); E-Edema premenstrually; D-Diabetes; I-Idiopathic; A-Agromegaly A-Alcoholism; N-Neoplasm;
S-Smoking; T-Trauma hypoT-Thyroid; R-Rheumatoid arthritis; A-Amyloidosis; P-Pregnancy (OBESITY); 2. FPL, FDP, FDS, Med n |
|
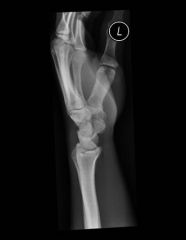
44yo M factry workr c/o 7-mth hx: pn & paresthesias palmar aspect R thmb, indx, lng & radl 1/2 ring fngrs. PMH (+): anemia & obstrctv sleep apnea. Percussion over volar wrst crease -> electric senstn distly hand & wrist flex w/ elbow in extn -> thmb paresthesias w/in 18 sec. Fig A, xray. sensory n conduction velcty test- distal sensory latency- 5.7 ms. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management
|
1-Phonophoresis & 6-wk course Vit B6 (pyridoxine)
2-Open CTS release; 3-Wrist splintg; 4-1-mth course of NSAIDs & PT; 5-1mth course of bumetanide, smokg cessation, & PT:: hx, PE, nerve conduction velocity tests (nl distal sensory latency is <3.5 ms) are consistent w/ CTS. Level 1 & 2 evidnc supportg local steroid injn/ splntg nonoperative tx. neutral wrist splints is most useful for improvg night-time sx.Ans3 |
|
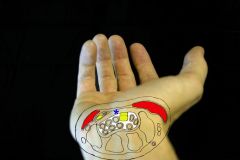
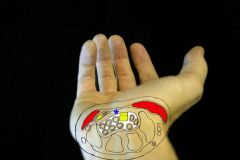
All of the following are contents of the carpal tunnel EXCEPT:1-Flexor pollicis longus (FPL); 2-Flexor digitorum sublimis (FDS); 3-Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP);4-Fexor carpi radialis (FCR); 5-Median n
|
(FCR) is not a tendon w/in the carpal tunnel. In summary, the carpal tunnel contains the median n, FPL & 4 tendons each of the FDP and FDS. Of note, with respect to the FDS tendons, the 3rd and 4th FDS tendons are volar to the 2nd and 5th FDS tendons.Ans4
|
|
All of the following can be found on the (EMG) portion of an electrodiagnostic study during the evaluation of a pt w/ CTS EXCEPT: 1-Fibrillations at rest; 2-(+) sharp waves; 3-Dec. motor recruitment; 4-Incrsd insertional activity; 5-Incrsd distal sensory latency
|
EMG's detect the electrical potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically activated. information about the muscle motor unit and can display the presence: fibrillations, sharp waves, motor recruitment, and insertional activity of the muscle. The n conduction (NCV) portion of the electrodiagnostic study measures the speed at which the nerve impulse travels down the axon. Distal latencies & conduction velocities are measured with NCV's. General parameters for NCV dx of CTS include a distal motor latency of >4.5 msec, a distal sensory latency of >3.5msec, or a conduction velocity of < 52 m/sec.Ans5
|
|
50 yo F is dx-d w/ CTS. She is prescribed a cock-up wrist splint at 30 deg of extension to wear @ night. This splint has what effect on the carpal tunnel? 1. Dec carpal tunnel press; 2-Incr carpal tunnel press; 3-No effect on carpal tunnel press; 4-Enlarges the carpal tunnel volm; 5-Improves nerve conduction studies
|
Use of neutral wrist splints for carpal tunnel syndrome is most useful for improving noctural symptoms. The reason for this is the functional position of the wrist is approximately 30 degrees of extension, and the neutral splints can be functionally limiting when used during productive daytime hours.Ans2
|
|
All of the following are predictive findings for correctly dx'g CTS EXCEPT: 1-Abn hand diagram; 2 Abn. Semmes-Weinstein testg in wrist-neutral position; 3-(+) median n compression test (Durkin's sign); 4-Presence of night pn; 5-Loss of small digit add (Wartenberg sign)
|

most predictive factors for correctly dxg (CTS)= abn hand diagram, abn sensibility by Semmes-Weinstein testg in wrist-neutral position, (+) Durkan's test, & night pain, the probability that carpal tunnel syndrome will be correctly dx'd is 0.86.
highest sensitivity were Durkan's compression test (89%), Semmes-Weinstein testing after Phalen's maneuver (83%), and hand diagram scores (76%). Night pain was a sensitive symptom predictor (96%). The most specific tests were the hand diagram (76%) and Tinel's sign (71%). the diagnostic power of the combination of these 4 clinical tests, and proceedg with surgical release is appropriate even if the EMG is nl.Ans5 |
|
Approxily what % of pre-op grip strength would be expected 3 mths p/ carpal tunnel release? 1-10%; 2-25%; 3-50%; 4-100%; 5-150%
|
grip strength = 28% of preoperative level at 3 weeks; 73% by 6 weeks, returnED to the preoperative level by 3 months, 116% at 6 months.
Pinch strength =74% of preoperative level at 3 weeks, 96% at 6 weeks, 108% at 3 months, and 126% at 6 months.Ans4 |
|
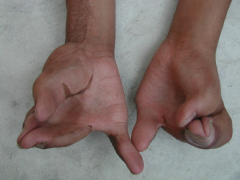
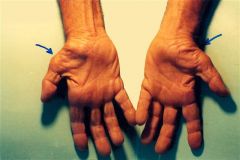
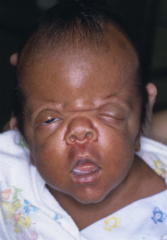
4yo child has flattened facial features, wide set eyes, and the hand deformity pictured in Fig A. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1-Apert's syndrm 2-Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia; 3-Cleidocranial dysplasia; 4-Noonan syndrm 5-Achondroplasia
|

The primary deformity of the hands and feet is severe syndactyly, often with fusion of the digits. The index, middle, and ring fingers are affected most often.Ans 1
|
|

Apert's syndrome is caused by a mutation in what gene? 1-Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2)
2- (FGFR3); 3. Collagen type II alpha 1 chain (COL2A1) 4. SED late (SEDL); 5. Fibrillin |
Mutations in the FGFR2 gene cause Apert syndrome. 2: Achondroplasia is abn FGFR3, not FGFR2.
3: SED congenita is caused by mutations in COL2A1 (type II collagen alpha 1 chain) These result in abnormal type II collagen. 4:The X-linked form of SED tarda is caused by mutation in (SED late) gene. 5: Marfan syndrome is defects in the fibrillin gene.Ans1 |

