![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
nuclear medicine pharmaceuticals
|
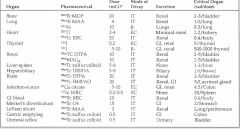
|
|
|
quality assurance for radiopharmaceuticals
|
generator
aluminum bkthg < 10ug/ml molybdenum bkthg <0.15 uci/1mci of tc99m Mo bkthg determined by counting the eluate in a well counter without and with a lead shield radiochemical purity determined by thin layer chromatography free tco4 migrates in saline and methanol tc99m migrates in saline only |
|
|
vq mismatch
|
pulmonary embolism
vasculitis, radiation therapy, wegeners, autoimmune tumor compression of PA pleura effusion radiation therapy hypoplastic PA |
|
|
PE causes
|
venous thrombus (most common)
fat embolism tumor embolism amniotic fluid embolism parasites,esp schistosomiasis talc embolism in IV drug use, widespread micronodular dz of lungs oil embolism from ethiodol following lymphangiogram mercury embolism air embolism |
|
|
matched vq defects
|
any primary pulmoary parenchyma abnormality may result in 2ndary arteriolar constriction causing vq defect
consolidation, pneumonia, edema copds atelectasis tumor bullous disease pneumonectomy, surgery pneumonia enlarged hilar nodes edema fibrosis pulmonary infarction |
|
|
decreased perfusion in one lung
|
embolus
pneumothorax massive effusion tumor pulmonary agenesis or hypoplasia swyer-james syndrome |
|
|
false negative thallium studies
|
submaximal exercise (high splachnic uptake)
noncritical stenosis (<40%) small ischemic area coronary collaterals multivessel disease medications blunted cardiac response to exercise-beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin) altered myocardia extraction (furosemid, lidocaine, dipyrimadole, dexamethasone, isoproteranol) |
|
|
false positive thallium
|
any cardiomyopathy
aortic valve stenosis mitral valve prolapse left bundle branch block infiltrative cardiac disease (sarcoidosis, chagas disease, amyloidosis) |
|
|
paradoxical septal movement
|
septal ischemia
previous cardiac surgery rv overload lbbb or pacer placement |
|
|
pyrophosphate uptake
|
MI
unstable angina lv aneurysm cardiomyopathy valvular calcification any cause of myocardial injury contusion or surgery cardioversion myocarditis pericarditis |
|
|
gb not visualized on HIDA
|
give morphine to increase pressure or cholecystokinin to contract GB
acute cholecystitis prolonged fasting recent meal |
|
|
biliary system not visualized on HIDA
|
biliary atresia
long-standing bile duct obstruction |
|
|
low hepatic activity, renal activity on HIDA
|
severe hepatocellular disease
neonatal hepatitis, pt. can be pretx with phenobarbital 5mg/kg for 5 days |
|
|
bowel not visaulized on hida
|
choledocholithiasis
ampullary stenosis |
|
|
abnormal tracer collections on HIDA
|
bile leak
choledochal cyst caroli's disease duodenal diverticulum |
|
|
false negative HIDA
|
duodenal diverticulum simulating GB
accessory cystic duct |
|
|
false positive HIDA
|
recent meal in 4 hours
prolonged fasting, ICU patients, parenteral nutrition pancreatitis hepatocellular dysfunction right lower lobe pneumonia cholangiocarcinoma involving cystic duct |
|
|
focal liver uptake with tc99m sulfur colloid
|
FNH
regenerating nodule budd chiari syndrome (hot caudate lobe) vena cava obstruction (umbilical vein delivery to segment 1) |
|
|
bleeding studies
|
uptake conforming to bowel with no change over time-IBD, faulty labeling with free tech excreted into bowel
uptake conforming to bowel with progressive accumulation over time-hemorrhage upatke not conforming to bowel, aneurysm |
|
|
RLQ activity on meckel scan
|
meckels diverticulum or other duplication cysts with ectopic gastric mucosa
renal (ectopic kidney, ureteral stenosis) very active bleeding sites tumors IBD |
|
|
rapid gastric emptying
|
postoperative-BI, BII
peptic ulcer disease, ZE syndrome drugs-erythromycin, metoclopramide, domperidone sprue vagotomy with distal partial gastrectomy |
|
|
delayed gastric emptying
|
diabetes
hyperglycemia acidosis ileus chronic gastritis chronic ulcer disease drugs-opiates, antacids, gastrin |
|
|
focal renal defects
|
tumor-solid, cystic
infections-abcess, cortical scarring congenital-duplex system trauma vascular-complete stenosis |
|
|
focal hot renal lesions
|
collecting system
urinary leak cross-fused ectopia horshoe kidney |
|
|
dilated ureter or collecting system
|
reflux
obstructed ureter |
|
|
delayed uptake and excretion
|
prerenal (unilateral, poor flow and uptake)
arterial stenosis venous thrombosis renal (bilateral) ATN, normal flow, poor uptake glomerulonephritis, poor flow and poor uptake chronic renal failure postrenal obstruction-dilated calyces |
|
|
nonvisualized kidney
|
nephrectomy
ectopic kidney pelvis, fused ectopia renal artery embolus renal artery occlusion |
|
|
testicular anomalies
|
decreased uptake
torsion orchiectomy increased uptake ochioepididymitis ring sign late torsion tumor abscess traume |
|
|
focal hot bone lesions
TIC MTV |
tumor
inflammation osteomyelitis infectious, inflammatory, metabolic arthritis congenital osteogenesis imperfect TORCH metabolic (usually diffuse, multifocal) marrow hyperplasia pagets fibrous dysplasia trauma stress fracture, avulsion injuries osteonecrosis sudecks dystrophy total hip replacement child abuse vascular sickle cell (infection vs infarcts) |
|
|
focal cold bone lesions
|
mets most common 80%
multiple myeloma, lymphoma renal thyroid neuroblastoma primary bone lesions unicameral bone cyst, ABC, EG vascular infarction (acute) aseptic necrosis (early) radiation therapy (endarteritis obliterans) artifact overlying pacemaker, barium, jewelry |
|
|
superscan
diffuse high bone uptake, diminished soft tissue and renal activity, high sternal uptake (tie sign), increased uptake at costochondral junction (beading) |
mets
prostate mets (most common) lung cancer breast metabolic hyperparathyroidism renal osteodystrophy osteomalacia pagets diseaes (hot and cold lesions are typically combined) myeloproliferative diseaes myelofibrosis (large spleen) |
|
|
diffuse periosteal uptake (tram track sign)
|
bilateral diffuse periosteal uptake
hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (lower extremity>upper extremity) child abuse thyroid acropachy |
|
|
extraosseous activity
normally kidneys and bladder are only organs are apparent on bone scan |
increased soft tissue activity
renal failure radiotherapy ports myositis myositis ossificans dermatomyositis rhabdomyolysis tumors with calcifications kidney focal obstruction calcifying mets radiation to kidney rcc diffuse obstruction dehydration mets rcc chemotherapy thalassemia iron overload pyelonephritis breast pregnancy, lactation inflammatory breast lesions steroids stomach, GI free tech hyperparathyroidism bowel infarction liver mets simultaneous/prior administration of sulfur colloid diffuse hepatic necrosis elevated serum aluminum levels colloid formation hepatoma amyloidosis spleen blood dyscrasia chest cardiac infarction lung tumors other urine contamination |
|
|
diffusely increased thyroid uptkae
|
>30% uptake, enlarged gland, pyramidal lobe
graves diseaes (usually hyperthyroid) early hashimoto's thyroiditis (usually euthyroid) rare iodine starvation thyroid metabolism anomalies |
|
|
diffusely decreased thyroid uptake
|
nonvisualized gland or low uptake, salivary glands may show high uptake because of adjusted windowing
thyroiditis painful (subacute granulomatous, deQuervains disease) painless (subacute lymphocytic) late hashimoto's disease medications thyroid hormone therapy iodine iodinated contrast agents vitamin preparations lugols solution PTU Tapazole Thyroid ablation surgery I131 |
|
|
heterogenous thyroid uptake
|
enlarged gland (goiter), hot and cold areas
multinodular goiter multiple autonomous nodules hashimoto's thyroiditis cancer |
|
|
cyclotron or accelerator produced radionuclides
|
used for production of Ga67, I123, 201Tl, F18
|
|
|
fission produced radionuclies
|
I131, 99Mo, carrier free
|
|
|
pet rubidium generator
|
81Rb
|
|
|
99Mo breakthrough test
NRC limit USP limit |
1 microCi 99Mo per mCi 99mTcm
0.15 microCi 99Mo per mCi 99mTc |
|
|
Mo shield test
|
allows 740 and 780 KeV 99Mo photons to be measured by dose calibrator but blocks 140 KeV
|
|
|
Mo chemical test
|
reaction of Mo and phenylhydrazine will form colored complexes on eluate
|
|
|
Al3+ breakthrough test
|
degrades image quality
nrc limit 20 microgram per ml eluate from thermal activation generator 10 microgram per mL of eluate from fission generator chemical evaluation-standard test kit measures Al ion colorimetrically on special test paper strip containing aluminum reagent |
|
|
other impurities
hydrolyzed reduced Tc |
effect RES uptake, poor image quality, increased radiation dose
limit <2% |
|
|
Tc99m eluate other parameters
|
pH 4.5-7.5
other nonparent radionuclide impurities eluate-sodium chloride USP grade pyrogenicity and sterility precautions |
|
|
radiochemical purity
|
chromatography
|
|
|
radiopharmaceutical sterility and pyrogenicity
|
limulus lysate for pyrogens
culture for sterility |
|
|
gamma camera qc
|
intrinsic/extrinsic uniformity
spatial resolution-daily, variable pattern phantoms linearity-daily, parallel line equal spacing phantom and other phantoms energy resolution-6 months sensitivity-monthly temporal resolution-6 months energy registration-6 months accessory devices-6 months center of roration (SPECT), monthly |
|
|
PET systems
|
detector material-BGO, LSO, GSO, NaI
major isotopes for PET-f18, n13, o15, c11 generator isotopes, Ga68, others |
|
|
units of dose
|
absorbed dose
1 rad 0.01 gray 100 rad 1 gray dose equivalent 1 rem 0.01 sv 100 rem 1 sv |
|
|
activity measurements
|
1 mCi = 3.7 MBq
1 curie = 3.7 x 10^10 distintegrations/second 1 bequerel = 1 distintegration/second |
|
|
signage requirements
|
unrestricted area: <2 mrem/hr and <100 mrem over 7 consecutive days
more than this control required |
|
|
radiation area sign
|
>5 mrem/hr at 30 cm from source
|
|
|
high radiation sign
|
>100 mrem/hr at 30 cm from source
|
|
|
badge requirements
|
personell likely to receive > 10 % of occupation dose limits
any minor or pregnant female likely to receive more than 100 mrem (1mSv) TLD or other device on upper torsa ring dosimetry |
|
|
acceptance and monitoring packages
|
monitor external surface of labeled package for radioactive contamination (>6600 dpm 300 cm2)
monitor for external radiation levels of a labeled package -radiactive yellow white I- max 0.5 mrem/hr radioactive yellow II-max 50 mrem/hr radioactive yellow III-max 200 mrem/hr if contamination or radiation level >200 mrema/hr or 10 mrem at 1 m, notify delivery carrier and NRC or state by telephone |
|
|
public dose limit
|
100 mrem effective dose equivalent
|
|
|
annual occupational
|
5 rem effective dose to body
15 rem to the eye 50 rem to any organ or tissue |
|
|
fetal
|
500 mrem during pregnancy
|
|
|
doses to visitors
|
500 mrem for all visits to hospitalized patient
|
|
|
doses at 1 meter from patient (tc99m)
|
tc-99m 20 mCi (740 MBq)
0.9 mrad/hr at 0 time 0.35 mrad/hr at 3 hrs |
|
|
doses at 1 meter from patient (th201)
|
10 mCi (370 MBq)
2.0 mrad/hr at 0 time |
|
|
doses at 1 meter from patient (f18)
|
10 mCi (370 MBq)
-30 mrad/hr at 0 time 5 mrad/hr at 1 hr |
|
|
doses at 1 meter from patient (I131)
|
cancer tx 100 mCi (3.7 GBq)
-22 mrad/hr at 0 time 12 mrad/hr at 12 hours -1.8 mrad/hr at 72 hours |
|
|
release of radioisotope therapy patients
|
release on calculations- not likely to exceed 500 mrem to any other individual
if dose to other >100 mrem written instructions to minimized dose to others relased based on retained activity-<33 mCi of I131, no limits for Sr-89, P-32, or Samarium 153 general instructions-avoid pregnant people for 2 weeks, stay away from people by about 1 m for 5-7 days |
|
|
breast feeding
|
f18-none
tc99m 0-24 hours gal, indium 1-4 weeks i131 stop |
|
|
major spill
|
100 mCi Tc99m, TI 201
10 mCi Ga-67 or I-123 1 mCi I-131, Sr-89 |
|
|
major spill actions
|
call RSO, do not clean up. clear and secure area, cover spill, radiactive signage, potentially shield, decontaminate persons
|

