![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
154 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the US radiographic findings of a cystic hygroma
|
bilobed cystic mass on back of neck with a midline septum
|
|
|
What is cystic hygroma associated with
4 |
Assoc w/Turner (XO), trisomies 13, 18, 21, and 22
|
|
|
What is the cause of cystic hygroma
|
lymphatic obstruction
|
|
|
How does localized cystic hygroma present
|
solitary cytic lesion
|
|
|
How does diffuse cystic hygroma present
2 |
fetal skin thickening
fluid in body cavities (pleural/pericardial/ascites) which indicates hydrops |
|
|
What are the risk factors of an ectopic pregnancy
3 |
previous ectopic
PID IUD + pregnancy |
|
|
What is the limitation of transvaginal US "seeing" a gestional sac based off B-HCG
|
1000 or more it should be visible
|
|
|
What are the findings of ectopic pregnancy
4 |
Extrauterine anechoic gestational sac containing a fetus with or without a heartbeat or an empty gestational sac outside the uterus
empty endometrial canal Thick hyperechoic band surrounding a small hypoechoic core donut or ring Echogenic free fluid if ruptured |
|
|
What does the tissue surrrounding a gestational sac look like
|
thick hyperechoic band surrounding a small hypoechoic core
|
|
|
What is the outside of the decidual reaction
|
hyperechoic (surrounds an inner hypoechoic area)
|
|
|
What are the risk factors associated with heterotopic pregnancy
|
ovulation induction, history of abx use PID, endometriosis, previous ectopic
4 |
|
|
Why is a US used to evaluate the adnexa
|
evaluate for torsion, PID, ectopic, and neoplasm.
|
|
|
Size simple cyst can be ignored if a patient is premenopausal
|
less than 3cm
|
|
|
What if a premenapausal women has a unilocular cyst that is 5-7cm
|
1 year follow up
|
|
|
What if a premenopausal women has a simple cyst that is greater than 7cm
|
remove
|
|
|
What is the general rule of thumb for postmenopausal women and adnexal cyst
|
For postmenopausal, anything not a simple cyst needs to be removed
|
|
|
What is the follow up if a women is post menopausal and has a simple cyst that is less than 1 cm
|
1 year follow up
|
|
|
What are malignant features of a adnexal cyst
4 |
irregular walls
mural or septal nodules thick/multiple septations solide |
|
|
Generally speaking what are the resitive index of a malignant ovarian tumor
|
less than 0.4
|
|
|
What is the pulsatility index of a malignant tumor
|
less than 1
|
|
|
Besides a decreased RI and a decreased pulsatility index what are other doppler features of suggest malignancy
|
diastolic notch and flow in solid portions of a mass
|
|
|
What is the cause of a hemorrhagic cyst
|
Acute hemorrhage in a follicular or corpus luteal cyst
|
|
|
What are the features of a hemmorrhagic cyst
|
They can have a variety of appearances depending on the stage of evolution of the clot. The most typical appearances are that of lace-like reticular echoes or an intracystic solid clot.
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a endometrioma
|
In the typical situation there is acoustic enhancement with diffuse homogenous low-level internal echoes as a result of the haemorrhagic debris. This appearance occurs in 95% of cases and is considered the classic finding on ultrasound examination. Features of multi-locularity and hyper-echoic wall foci may be present. Anechoic cysts may occur, but they are rare.
|
|
|
What is the MR appearance of a endometrioma
|
T1 : typically, lesions appear hyper-intense while acute haemorrhage occasionally appears hypo-intense
T2 : typically hypo-intense owing to the presence of deoxyhaemoglobin and methaemoglobin. Old haemorrhage occasionally appears hyper-intense. |
|
|
What is the appearance of a tubo-ovarian abscess
|
often shows complex retro-uretine / adnenal mass(es)
|
|
|
What are the findings of ovarian torsion on non-doppler US
|
-enlarged hypo or hyperechoic ovary
-peripheraly displaced follicles -free fluid in pelvis -whirlpool sign of twisted pedicle |
|
|
What percent of women with ovarain torsion have free fluid in the pelvis
|
80%
|
|
|
What are the doppler findings of ovarian torsion
|
little or abscent venous flow
absent arterial flow (less common) absent or reduced diastolic flow |
|
|
Does normal doppler exclude ovarian torsion
|
no
|
|
|
What side does ovarian torsion usually occur
|
right side
|
|
|
What is the main feature of ovarian torsion
|
ovarian enlargement due to engorgement, edema or hemorrhage.
|
|
|
What is tubo-ovarian abscess a complication of
|
PID
|
|
|
What are the clinical SS of TO abscess
|
fever,
WBC lower abodminal pain |
|
|
Can a TOA be present with out increased WBC and fever
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the ddx of TOA
|
pelvic malignancy
diverticulosis appendicitis endometriosis |
|
|
What is a dermoid plug
|
this is an echogenic mural nodule associated with posterior acoustic shadowing in a complex adnexal mass.
|
|
|
What is a dermoid
|
cystic lesion with echogenic shadowing nodule projectin into the lumen
|
|
|
What is the 'tip of the iceberg"
|
Diffusely or partially echogenic mass usually demonstrating sound attenuation (sebaceous material & hair within cyst cavity)
|
|
|
What is the dermoid mesh
|
Multiple thin, echogenic lines and dots caused by hair in the cyst cavity (dot-dash appearance)
|
|
|
What percent of dermoid contain teeth on CT
|
50%
|
|
|
What percent of dermoids contain fat on CT
|
90%
|
|
|
What is the treatment of a dermoid
|
excision
|
|
|
What is a TOA
|
painful complex adnexal ms
|
|
|
What does a pyosalpinx look like on US
|
serpiginous mass with echogenic material
|
|
|
Are TOA often bilateral
|
yes (infection spreads from one side to the other)
|
|
|
What is pyosalpinx
|
an upper genital infection and part of the PID spectrum
|
|
|
What is PID
|
s an extremely broad term and essentially means is infection - inflammation of the upper female genital tract, resulting in a spectrum of abnormalities.
|
|
|
What is a hydrosalpinx
|
A hydrosalpinx is a descriptive term and refers to a fluid filled dilatation of the fallopian tube.
|
|
|
What are the causes of a hydrosalpinx
|
endometriosis
ovulation induction PID post-hysterectomy tubal ligation tubal malignancy |
|
|
What are the US findings of hydrosalpinx
|
May be seen as a thin-or thick-walled (in chronic cases), elongated or folded, tubular, C shaped or S shaped fluid-filled structure that is distinct from the uterus and ovary.
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a hyperechoic hepatic lesion
4 |
hemangioma, focal fat, met, hcc
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a hemangioma on US
|
-homogenous hyperechoic
-occasional posterior acoustic enhancement -no detectable flow on doppler |
|
|
How may a hemangioma appear in a fatty liver
|
hypoechoic
|
|
|
How may a hemangioma appear if it is large
|
heterogenous (if larger than 3cm)
|
|
|
What do you do in a pt with a hemangioma that has normal LFTs, no known primary, non cirrhotic, asymptomatic
|
then f/u US in 6 m
|
|
|
What are 4 causes of hyperechoic mets
|
Usually from GI tract (esp colon CA) RCC
islet cell carcinoid chorioCA |
|
|
What is the ddx of calcified mets of the liver
|
colon
mucinous ovary breast stomach |
|
|
What are the classic appearance of mets on US
|
hyperechoic center with a hypoechoic periphery
|
|
|
Why does hcc have a hypoechoic component
|
due to fat (usualy hyperechoic but i gues compared to the hyperechoic portion of hcc its dark)
|
|
|
Where do most pancreatic adenocarcinoma occur
|
head of the pancreas
|
|
|
What is the usual appearance of a pancreatic adenocarcinoma
|
hypoechoic
|
|
|
What are characteristics of a pancreatic adenocarcinoma that make it unresectabe
4 |
hepatic or peritoneal mets
involvement of pancreatic vessels invasion of adjacent organs besides duodenum malignant asites |
|
|
What is the ddx for a hypoechoic pancreatic head mass
4 |
pancreatic adenocarcinoma
focal pancreatitis lymphoma mets |
|
|
What is the double duct sign o
|
dilation of the CBD and pancreatic duct
|
|
|
What are the 3 number values looked at during ICA stenosis
|
PSV-peak systolic velocity
SVR-systolic velocity ratio (ICA/CCA) EDV-end diastolic velocity |
|
|
What are the values for less than 50% stenosis
|
PSV < 125 cm/s
EDV < 40 cm/s SVR < 2.0 |
|
|
What are the values for 50-69% stenosis
|
PSV 125-229 cm/s
EDV 40-99 cm/s SVR 2-3.9 |
|
|
What are the values for >70% stenosis
|
PSV ≥ 230 cm/s
EDV ≥ 100 cm/s SVR ≥ 4.0 |
|
|
What happens if the value of either PSV, EDV or SVR increase
|
there is increased stenosis
|
|
|
What is the NASCET criteria for tx
|
NASCET: symptomatic, 70-99% (> 50% in select pts)
|
|
|
What is the ACAS criteria for tx
|
ACAS: asymptomatic, 60-99%
|
|
|
When is stenting approved according to SAPPHIRE
|
high risk pt > 70% stenosis
|
|
|
What causes aliasing
|
inability to detect true peak velocity bc doppler sampling rate is too slow
|
|
|
What is pulse repitition frequency
|
When pulses are transmitted at a given sampling frequency
|
|
|
What is the maximum doppler frequency that can be measured
|
the maximum Doppler frequency fd that can be measured unambiguously is half the pulse repetition frequency
|
|
|
What is aliasing
|
If the blood velocity and beam/flow angle being measured combine to give a fd value greater than half of the pulse repetition frequency, ambiguity in the Doppler signal occurs. This ambiguity is known as aliasing.
|
|
|
What is the artifact that occurs during aliasing
|
Highest velocities are cut off and wrap around, appearing below the baseline
|
|
|
How is aliasing prevented
|
Prevention: decrease probe frequency or increase PRF or Doppler angle
|
|
|
What signal is typical just proximal to an occluded artery on a spectral doppler US
|
'to and fro'
|
|
|
What are the findings of cholecystitis
5 |
gallstones
murphys sign pericholecystic fluid GB wall thickening >3mm GB dilated (>5cm transverse) |
|
|
What are findings of gangrenous cholecystitis
4 |
-Sloughed membranes forming intraluminal membranes
-Irregular striated wall thickening -Focal interruption of GB wall (perforation) -irregularity or masslike protrusions of GB wall |
|
|
What percent of patients with gangrenous cholecystitis have an absent murphys sign
|
up to 70%
|
|
|
What is WES sign
|
The anatomic basis of the WES sign is the well-defined echogenic gallbladder wall (W), echoes (E) from gallstones located immediately beneath the gallbladder wall, and prominent posterior acoustic shadowing (S) that results from sound attenuation caused by the calculi. The hypoechoic region between the echogenic gallbladder wall and subjacent calculi represents a thin layer of interpositioned bile
|
|
|
What is mirizzi syndrome
|
The Mirizzi syndrome refers to an uncommon phenomenon which results in extrinsic compression of a extrehepatic billiary duct from one or more calculi within the cystic duct or gallbladder. It is a functional hepatic syndrome but can often present with bilirary duct dilatation and can mimic other hepatobiliary pathology such as cholangiocarcinoma
|
|
|
What can mirizzi syndrome mimic
|
cholangiocarcinoma
|
|
|
What pt most commonly get emphysematous cholecytitis
|
elderly male diabetics
|
|
|
What is the radiographic appearance of emphysematous cholecystitis
|
very bright echoes from non-dependent portion with dirty shadows
|
|
|
Does the echoes of emphysematous cholecystitis cause ring down artifact
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the ddx of emphysematous cholecytitis
|
porcelain GB
|
|
|
What do you expect to see in a emphysematous gallbladder
|
an arc of hyperechoic foci in the non-dependent portion of the gallbladder. There is ring down artifact posterior to the hyperechoic foci.
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of holoprosencephaly
|
alobar
semilobar lobar |
|
|
Describe the findings in alobar holoprosencephaly
5 |
monoventricle with fused thalami
absent falx and corpus callusom brain tissue surrounding the monoventricle failure of cleavage of the prosencephalon |
|
|
What are the facial anomalies found in holoprosencephaly
3 |
proboscis (long nose)
cyclopia cleft lip |
|
|
What is the procencephalon
|
The prosencephalon is the largest part of the brain. Also called the forebrain, the prosencephalon consists of the telencephalon (includes the cerebral cortex) and the diencephalon (includes the thalamus and hypothalamus).
|
|
|
What are some congenital malformations associated with holoprosencephaly
|
omaphalocele
renal dysplasia polydactly CHD |
|
|
What are the findings of a cleft lip on US
|
Sonographic features can be variable dependant on exact type of cleft anomaly. In general an upper lip defect may be seen and is best appreciated on angled coronal scanning. A vertical hypo-echoic region through the fetal upper lip usually represents the defect in cleft lip. This finding may be corroborated by a similar defect of the soft tissues of the upper lip overlying the maxilla in the axial plane.
The palate can be examined in the transverse (axial) plane. 3D ultrasound may further assist in diagnosis. It is good practive to commonet of fetal swallowing on real time at the time the scan in performed. |
|
|
What are the findings of hydranencephaly
|
fluid-filled supratentorial space, falx is present, thalami not fused, no or very little (posterior circulation) brain tissue
|
|
|
What is the cause of hydranencephaly
|
Caused by bilateral supraclinoid ICA infarcts with loss of nearly all supratentorial brain
|
|
|
What is the ddx of hydranencephaly
|
holoprosencephaly, maximal hydrocephalus
|
|
|
How do you tell the difference between hydraneencaphly and holoprosencephaly/maximal hydrocephalus
|
mantle of surrounding tissue in holoprosencephaly and hydrocephaly
|
|
|
What are two types of portal vein thrombosis
|
bland
tumor |
|
|
What happens to the collaterals in pts with portal vein thrombosis
|
cavernous transformation
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for a bland thrombus
|
portal HTN, hypercoag state, abdominal infection/inflammation
|
|
|
What is a key to determing if there is a PV thrombus on US
|
doppler absensce of flow
|
|
|
What expands the lumen more...bland or tumor thrombus
|
tumor
|
|
|
What is the key finding in a pt with a tumor thrombus (differentiating from bland)
|
blood flow within the thrombus
|
|
|
What is the most common tumor thrombus
|
HCC
|
|
|
In portal vein thrombosis what happens to the flow
|
hepatofugal (away from the liver)
|
|
|
Name 5 causes of cirrhosis
|
alcohol
viral biliary hemochromatosis parasite |
|
|
What is pulsatile portal venous flow
|
Pulsatile portal venous flow is said to be present when the minimal portal vein flow velocity drops to or below the baseline with intermittent reversal of flow.
|
|
|
What is the ddx of pulsatile portal venous flow
|
severe cirrhosis
right heart failure tricuspid regurgitation portacaval shunt chronic hepatitis |
|
|
What is parvus tardus wave form
|
a prolonged systolic acceleration time with low PSV
|
|
|
What way is normal flow of the liver
|
hepatopetal
|
|
|
What is the normal wave form of the hepatic vein
|
triphasic with the majority below the spectral line
|
|
|
What two hepatic vessels have blood flow in the same direction
|
portal vein
hepatic artery (both above the spectral line) |
|
|
What color is towards the transducer
|
red
|
|
|
What color is away from the transducer
|
blue
|
|
|
Does severe cirrhosis have hepatofugal flow
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of monozygotic twins
|
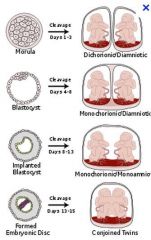
|
|
|
What is the sequence of days that each of the monozygotic twins will occur
|
diamniotic/dichorionic (within 2 days)
monoamniotic/dichorionic (split 3-8 days) monoamniotic/monochorionic (split9-12 days) conjoined twins (split after 12 days) |
|
|
What can you say about the babies if they are different sexes
If the fetuses are dichorionic what do they have to be |
they are dichorionic (and therefore also diamnitic)
diamniotic |
|
|
If there are 2 placentas what can you determine about the babies
|
they are dichorionic ...which means they are diamniotic
|
|
|
If there is 1 placenta can you say it is not dichorionic
|
no, bc the placenta can be close together and look as one
|
|
|
What can you say if the thickness of the membrane seperating the fetuses is greater than 2 mm
|
they are dichorionic
this is bc of villouis tissue proliferation into the intermembrane space creating spike that can be seen on US |
|
|
What can be said if the thickness seperating the twins is 1-2mm
|
monochorionic, diamniotic
|
|
|
What can be said if the thickness seperating the twins is less than 1mm
|
mono/mono
|
|
|
What is the "twin peak" sign (lamda sign)
|
chorionic tissue extending into inter-twin membrane at placenta, dichorionic
|
|
|
What as a thicker intertwin membrane
|
dichorionic
|
|
|
Describe the membrane of monochorionic diamniotic
|
In monochorionic diamniotic, intertwin membrane is very thin and inserts in a “T” junction
|
|
|
What if there is In 1st trimester 2 separate gestational sacs,
|
dichorionic
|
|
|
What is the main factor which determins pregnancy outcome during pregnancy
|
Chorionicity main factor in pregnancy outcome
Increased miscarriage and perinatal morbidity/mortality in monochorionic vs. dichorionic |
|
|
Describe the radiographic appearance of twin twin transfusion
|
one fetus has sever oligohydramnios and is much smaller that the other
One fetus appears studk to the uterus and is not moving with change in mothers position Other fetus is larger/polyhydramnios (may be hydropic) |
|
|
Can the bigger twin in twin twin transfusion be large, polyhydramniotic or hydropic
|
yes
|
|
|
What is twin embololization syndrome
|
Occurs following death of a monochorionic co-twin
Surviving co-twin “bleeds” into circulation of dead twin Results in infarction of rapidly growing tissues (brain) |
|
|
Describe acardiac twin syndrome (TRAP syndrome)
|
non-functioning cardiac pump
blood supply entirely from co-twin arterial-arterial and venous-venous anastomosis anencephalic, microcephalic, acephalic diffuse edema with hygroma UE rudimentary No heartbeat |
|
|
What are the neuro findings of twin twin syndrome
|
anecephalic, microcephalic, acephalic
|
|
|
What are the vascular anomalies that occur with TRAP syndrome
|
Arterial-arterial and venous-venous anastomoses
|
|
|
Describe the limb anomalies of TRAP syndrome (acardiac twin syndrome)
|
UE rudimentary, LE more normal
|
|
|
Does a baby with TRAP have a heart beat
|
no
|
|
|
What kind of pregnancy is it if there is two yolk sacs
|
diamniotic (can be monochorionic or dichorionic)
|
|
|
Do you expect to see a intertwin membrane in monochorionic monoamniotic
|
no
|
|
|
What is twin twin transfusion
|
Monochorionic twins with asymmetric fluid distribution and growth
|
|
|
What type of monzygotic twins have twin twin transfusion and TRAP
|
monchorionic
|
|
|
Describe the imaging findings of twin reversed arterial perfusion
|
Best diagnostic clue: Flow in umbilical artery (UA) of abnormal twin is toward fetus
Must be monochorionic gestation Acardiac twin dysmorphic with edema and cyst formation in soft tissues Ratio of EFW of acardiac to pump twin > 70% confers bad prognosis |
|
|
What is the pathognomonic finding in TRAP with doppler
|
The pathognomonic finding of reversed arterial perfusion on Doppler towards the acardiac twin
|
|
|
What happens to uterine leiomyoma during pregnancy
|
they tend to grow
|
|
|
What is the MC noncardiac abnormality
|
CDH
|
|
|
What is the postion of a bochdalek hernia
|
posterolateral
|
|
|
What is the position of a morgagni hernia
|
anteriomedial
|
|
|
What side does the stomach usually end up in a CDH
|
left chest
|
|
|
What side is the heart displaced
|
to the right or up
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of CDH
|
pulmonary hypoplasia
|
|
|
What is the ddx for non-visualization of the fetal stomach
|
swallowing abnormality
esophageal obstruction CDH oligohydramnios |

