![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
244 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If a patient has acute onset SOB and a peripheral consolidation what should be suspected
|
pulmonary infarct
|
|
|
What is the ddx for bronchiectasis
6 |
CAPT KANGAROO HAS MOUNIER KUHN
Cystic fibrosis ABPA Postinfectious TB Kartagener’s Mounier Kuhn |
|
|
What is the ddx of chronic interstial disease of the upper lobe
5 |
Pneumoconiosis
Ankylosing spondylitis Granulomatous (TB) Eosinophillic Sarcoid/Silicosis |
|
|
What are the typical findings of EG
|
young smokers, nodules, bizarre cysts, hyperinflation
|
|
|
What type of TB occurs in the upper lungs
|
reactivation
|
|
|
What are the findings of reactivation TB
|
nodules, cavities, apical volume loss, hilar retraction
|
|
|
What are the plain film findings of CF
|
has hyperinflation and predominantly upper lobe bronchiectasi
|
|
|
What are the findings of EG (LHC)
|
typical combination of nodules, cavitated nodules, and thick- and thin-walled cysts
|
|
|
Does EG have an upper lobe predominance
|
yes
|
|
|
What demographic classicaly gets EG
|
young to middle aged smokers (.90%)
|
|
|
Does EG predispose you to PTX
|
yes (25%)
|
|
|
What are the size of the lungs in a pt with EG
|
normal to increased in size
|
|
|
Are the costophrenic angles involved in EG
|
no they are spared
|
|
|
What demographic typical gets lymphangioleimyomatosis
|
premenopausal women
|
|
|
What are the complicaitons of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
2 |
PTX
chylous effusion |
|
|
What disease may produce Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in men
|
TSC
|
|
|
What are the XR findings of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
2 |
fine reticular pattern
increased lung volume |
|
|
What are the HRCT findings in Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
|
diffuse uniform cyst that eventually replace the parenchyma
|
|
|
What are 4 conditions that may produce cystic lesions of the lung
|
sjogrens
LIP (lymphocytic interstial pneumonitis) LAM EG |
|
|
What is the ddx of increased lung volumes
|
cysti lung disease
airway disease (asthma, BO, dysmotility cilia, CF, ABPA) COPD |
|
|
Name 5 airwasy diseases that cause an increase in lung volume
|
asthma
CF BO dysmotility ABPA |
|
|
What is the rib knotching of aortic coarctation caused by
|
the dilated intercostal arteries
|
|
|
What is the radiographic 3 sign from
|
coarctation or pseudocarctation
|
|
|
What is pseudocoarctation
|
this is the radiographic appearance of coarctation without a gradient.
|
|
|
What are the radiographic findings of aortic stenosis
|
-Dilated ascending aorta best seen on frontal, right of midline
-LVH or normal-sized heart -Calcification of aortic valve on the lateral -Normal pulmonary vascularity |
|
|
What is a common congenital cause of aortic stenosis
|
bicuspid aorta
|
|
|
What is a hint that there may be aortic stenosis on plain film
|
dilated ascending aorta with calcifications of the valve
|
|
|
What is seen on MR cine if there is aortic stenosis
|
stenotic jet through the valve
|
|
|
What are the findings of infantile aortic stenosis
|
CM and pulm edema
|
|
|
What are 3 types of aortic stenosis
|
supravalvular
valvular subvalvular |
|
|
What type of aortic stenosis is nealy always congenital
|
supravalvular (note that subvalvular is always congenital)
|
|
|
What type of aortic stenosis is isolated or part of williams syndrome
|
supravalvular
|
|
|
Can valvular aortic stenosis be congenital
|
yes, but this one can also be aquired
|
|
|
Name the causes of valvular aortic stenosis
|
bicuspid
unicuspid rheumatic disease degenerative change |
|
|
What is the MCC of valvular aortic stenosis in adults
|
degenerative stensosis
|
|
|
Descibe subvalvular aortic stenosis
|
MC thin membrane situated w/in 1 cm beneath cusps
Muscular stenosis caused by asymmetric HCM |
|
|
What type of aortic stenosis is causes by rheumatoid
|
valvular
|
|
|
What is the westermark sign
|
an abrupt cut off of pulmonary vascularity distal to a large central pulmonary embolism
|
|
|
What is the fleischner sign
|
enlargement of pulmonary artery
|
|
|
What is hampton hump
|
peripheral wedge shaped density representing a pulmonary infarct
|
|
|
Besides oligemia distal to an infarct, a wedge shaped peripheral consolidation, and enlargement of the pulmonary arteries are there any other signs of PE
|
yes, ATX and pleural effusion
|
|
|
What is a tumor that may cause a PE
|
pulmonary artery sarcoma
|
|
|
What are the findings of mitral stenosis
|
Left atrial enlargement
cephalization of upper lobe vessels calcification of mitral valve |
|
|
What are 2 complications of severe mitral stenosis
|
atrial fib
atrial thrombus |
|
|
What are the radiographic findings of mitral stenosis
4 |
displacement of left main stem bronchus superiorly on frontal and posteriorly on lateral, splaying of carina, posterior displacement of barium-filled esophagus, double density along right side of spine
|
|
|
What is the luftsichel sign
|
The luftsichel sign involves hyperextension of the superior segment of the left lower lobe, which then occupies the left apex in a pt with LUL collapse
|
|
|
Describe the findings of RUL collapse
|
Collapses superomedial creating a wedge opacity
Minor fissure displaced upward on frontal Major fissure displaced anteriorly on lateral Right hemidiaphragm, hilum elevated If central mass, convex bulge in medial aspect of fissure Hyperaeration of RML and RLL is typical |
|
|
Describe the findings of LUL collapse
|
Looks different than RUL b/c no minor fissure
Hazy density silhouettes upper left heart border on frontal May be periaortic lucency due to compensatory hyperinflation of LLL Leftward tracheal shift and elevated left hemidiaphragm and hilum On lateral view, major fissure is shifted anteriorly parallel to sternum |
|
|
What is the appearance of the periaortic region in a LUL collapse
|
periaortic lucency due to compensatory hyperinflation of LLL
|
|
|
Which way is the major fissure shifted on lateral films
|
anteriorly
|
|
|
What are the findings of a RML collapse
|
Best seen on lateral view
Triangular opacity over heart with depression of minor fissure and elevation of major fissure On frontal, hazy density silhouetting right heart border An apical lordotic view is helpful |
|
|
Where is the best view to visualize a RML collapse
|
lateral view
|
|
|
What is seen on frontal view in a pt with RML collapse
|
On frontal, hazy density silhouetting right heart border
|
|
|
What are the findings of Lower lobe collapse
|
Similar on both sides
Both collapse posteromedial and inferior On lateral, upper half of major fissure swings down and lower half swings back On frontal, silhouetting of medial hemidiaphragm and on lateral, silhouetting of posterior hemidiaphragm Heart shifted toward collapsed side and hilum is depressed |
|
|
What is the ddx of lobar collapse
|
Tumor (extrinsic compression, intrinsic): bronchogenic carcinoma, carcinoid
Mucous plugging Foreign body Broncholith (TB) RML syndrome Compressive atelectasis |
|
|
What is the appearance of Left lower lobe atx on lateral films
|
the left lower lobe is seen as a posterior opacification
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a RML of collapse on frontal and lateral films
|
lateral fim approximation of the minor and major with increased density between seen anterior
front-triangular shape approximating the right hear border |
|
|
What does a RML and RLL colapse resemble
|
plerual effusion
|
|
|
What is the MC manifestation of asbestos exposure
|
pleural plaques
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of pleural plaques
|
asymptomatic
|
|
|
Do pleural plaques calcify
|
yes they typicaly do
|
|
|
What are 3 types of asbestos related diseasee
|
pleural plaques
diffuse pleural thickening rounded atx |
|
|
Describe diffuse pleural thickening
|
Smooth and does involve CP angles
Involves visceral pleura and lung parenchyma |
|
|
What is the measurement for the pleura to be considered thickened
|
Must measure 8 cm craniocaudal, 5 cm wide, and 3 mm thick
|
|
|
Does pleural thickening ever involve the CP angles
|
no
|
|
|
What is typicaly seen adjacent to diseased pleura
|
rounded atx: roundly sharply marginated lung mass abutting pleura
|
|
|
What are the radiographic findings of rounded atx
|
Volume loss, ipsilateral pleural disease (plaque, thickening, effusion), broad area of pleural contact, comet tail sign (swirling vessels)
|
|
|
What is the commet tail sign
|
swirling vessels seen with rounded atx
|
|
|
Where does rounded atx most commonly occur
|
bases
|
|
|
should a pt with rounded atx get a f/u to exclude CA
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the classic findings of a transposition of the great vessels in peds
2 |
Anteroposterior radiograph will show an "egg"-shaped heart, narrow mediastinum.
|
|
|
What is the normal relationship of the aorta and pulmonary artery in the AP direction
|
the pulmonary artery is anterior to the aorta
|
|
|
What is the relationhip of the pulmonary artery and aorta in D transposition
|
anteriorly-placed aorta, connected via infundibulum to right ventricle, and posteriorly-placed pulmonary artery, directly connected to left ventricle.
|
|
|
What is D-type transposition of the great vessels
|
aorta arises from the RV
PV arises from the LV |
|
|
How are babies with TGV able to survive
|
they have a shunt
(ASD, PDA, VSD |
|
|
Are children with TGV cyanotic
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the cause of the narrow mediastinum in TGV
|
thymic involution and abnormal relationship of aorta and pulm art
|
|
|
What is a typical name of a XR sign of TGV
|
egg on a string
|
|
|
Is there increased pulmonary blood flow in TGV
|
yes
|
|
|
What happens if ther is right sided injection in angio
|
the aora will fill
|
|
|
What is the treatment for TGV
|
Jatene procedure, an arterial switch with reimplantation of coronaries
|
|
|
What is L type transposition of the great vessels
|
Congenitally corrected transposition
Morphologic (smooth) LV on right side serving as RV Morphologic RV (trabeculated) on left, serving as LV |
|
|
How do you differentiate right ventricle from the left
|
smooth on the left ventricle
more trabeculated on the right ventricle |
|
|
Is the relationship of the aorta and pulmonary artery still switch in L-TGA
|
yes (aorta is anterior and the pulm artery is posterior) Morphologic (smooth) LV on right side serving as RV (pumping to the pulmonary artery)
Morphologic RV (trabeculated) on left, serving as LV |
|
|
What is the angiogaphic findings of L-TGA
|
Smooth ventricle supplies pulmonary artery
Trabeculated ventricle supplies Ao |
|
|
What is the ages of the common neural based posterior mediastinal masses
|
Age related: Neuroblastoma < 3, ganglioneuroblastoma 3-10, ganglioneuroma > 10
|
|
|
Describe a neuroblastoma
|
Neuroblastomas heterogeneous due to hemorrhage, cystic degeneration and necrosis
|
|
|
What percent of neuroblastomas have calcifications
|
85%
|
|
|
What may a neuroblastoma mature to
|
Neuroblastoma may mature to a ganglioneuroblastoma, then ganglioneuroma
|
|
|
What are the causes of middle mediastinal masses
|
HABIT
Hernia, Hematoma Aneurysm Bronchogenic cyst/duplication cyst Inflammation (sarcoidosis, histoplasmosis, coccid- ioidomycosis, primary TB in children) Tumors–remember the five Ls: Lung, especially oat cell Lymphoma Leukemia Leiomyoma Lymph node hyperplasia |
|
|
What are the clues that a lesion is in the posterior mediastinum
3 |
Displacement of paraspinal lines or azygoesophageal line
Does not obscure heart border or hilum Rib spreading or posterior rib erosion |
|
|
What is the best way to conferm that a mass is in the posterior mediastinum
|
lateral view
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a posterior mediastinal mass
|
neurogenic
vebral body relaed vascular esophageal LN Neurenteric cyst bochldalek hernia extramedullary hematopoiesis |
|
|
What is the MC reason for a posterior mediastinal mass
|
neurogenic
|
|
|
What are 3 tumors of the sympathetic chain
|
neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma and ganglioneuroma
|
|
|
What are 2 types of peripheral nerve tumors
|
swhannoma and neurofibroma
|
|
|
What is a a paraganglioma
|
"Extraadrenal pheochromocytoma"
Usually syndromic (e.g., von Hippel-Lindau) and benign |
|
|
Where do schwannomas arise from
|
Benign tumor arising from nerve sheath of peripheral nerves
|
|
|
Where do neurofibromas arise from
|
Solitary or multiple lesions arising from nerve sheath
Benign or malignant; isolated or syndromic (NF1) Malignant degeneration common, especially in NF1 |
|
|
Can a paraganglioma cause a posterior mediastinal mass
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the 6 neurogenic tumors that may cause posterior mediastinal masses
|
ganglioneuroma
ganglioneuroblastoma neuroblastoma schwannoma neurofibroma paraganglioma |
|
|
What are 3 broad categories of vetebral body related posterior mediastinal masses
|
trauma
infection tumor |
|
|
Can esophageal lesion be both a posterior or middle medistiinal mass
|
yes
|
|
|
Can a bochdalek hernia, extramedullary hematopoeisis, LN, vascular and neurenteric cyst be posterior mediastinal mass
|
yes
|
|
|
What finding is extramedullary hematopoesis associated with
|
associated diffuse marrow hypointensity in patient with chronic anemia
|
|
|
Can a pt with thalasemia present with extramedullary hematopoiesis
|
yes
|
|
|
What does extramedullary hematopoeisis look like on CT
|
CT image shows abnormal bilateral paraspinal soft-tissue masses in the lower thoracic region
|
|
|
What are the radiographic findings of a neurogenic tumor
|
Usually vertical, fusiform paravertebral masses +/- vertebral body erosion and paraspinal extension
|
|
|
What is the most common signal characteristic of an posterior neurogenic tumor causing a mass
|
slightly higher than muscle on T1, very bright on T2, homogeneous enhancement
|
|
|
Do neurogenic tumors typically enhance homogenously
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the radiographic findings of a neurogenic tumor
|
Usually vertical, fusiform paravertebral masses +/- vertebral body erosion and paraspinal extension
|
|
|
If you see a well circumscribed subcarinal mass what should be suspected
|
a bronchogenic cyst
|
|
|
What is the most common signal characteristic of an posterior neurogenic tumor causing a mass
|
slightly higher than muscle on T1, very bright on T2, homogeneous enhancement
|
|
|
What is the one do not biopsy lesion that may occur in the posterior mediastinum and should be considered always
|
aneurysm
|
|
|
Do neurogenic tumors typically enhance homogenously
|
yes
|
|
|
If you see a well circumscribed subcarinal mass what should be suspected
|
a bronchogenic cyst
|
|
|
What is the one do not biopsy lesion that may occur in the posterior mediastinum and should be considered always
|
aneurysm
|
|
|
Where do bronchogenic cyst arise from
|
the foregut
|
|
|
What are 2 possible complications of a bronchogenic cyst
|
infection
compression of adjacent structures |
|
|
What are the 2 classic locations for a bronchogenic cyst
|
subcarinal
right paratracheal |
|
|
What is the radiographic appeareance of a bronchogenic cyst
|
Usually smooth, round, homogeneous with very thin wall
|
|
|
What is a hint that a bronchogenic cyst may be infected
|
air fluid level
|
|
|
What is the CT appearance of a bronchogenic cyst
|
fluid density, but often higher due to protein, hemorrhage, mucin
|
|
|
What are the MR signal characteristics of a bronchogenic cyst
|
T1 dark or bright for same reason, bright on T2 (bc may contain protein or mucin)
|
|
|
Can calcification occur in the walls of bronchogenic cyst
|
yes
|
|
|
If a pt has thick calcifications at the margin of the heart what should be suspected
|
current of history of TB pericarditis
|
|
|
What is the cause of complications in constrictive pericarditis
|
Thickening of pericardium which restricts diastolic filling
|
|
|
What are the causes of constrictive pericarditis
|
infection (TB), uremia, prior heart surgery, radiation, hemorrhage
|
|
|
What is the ddx of contrictive pericarditis
|
restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
How do you differentiate restrictive cardiomyopathy and constrictive pericarditis
|
there is no peripheral calcification or thickening of the pericardium in restrictive CM
|
|
|
What are the CXR findings of constrictive pericarditis
|
Eggshell Ca+ around margin of heart, spares LA b/c pericardium does not extend posteriorly
|
|
|
Does constrictive pericarditis tend to spare the appex
|
yes (and this helps to differentiate from Ca aneurysm which does have calcification at the apex)
|
|
|
What secondary findings may be seen on CXR in a pt with constrictive pericarditis
|
Dilation of pulmonary veins and SVC/IVC, pulmonary edema, with cephalization
|
|
|
Does constrictive pericarditis tend to enlarge the atria
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the MR findings of constrictive pericarditis
|
Pericardial thickening > 4 mm
Biatrial enlargement and distension of veins |
|
|
If you see a bump along the margin of the heart (close to the apex) on CXR what should be suspected
|
cardiac aneurysm
|
|
|
Where do true cardiac aneurysms occur
|
anterior and apical walls of the heart
|
|
|
What is the cause of true cardiac aneurysms
|
Usually post transmural MI
|
|
|
What is a potential complicaiton of a true aneurysm of the heart
|
potentiall nidus for clot formation
|
|
|
What are the CXR findings of a true aneurysm
|
Smooth bulge along left heart border on frontal +/- curvilinear rim Ca+
On lateral, bulge usually projects over heart (not behind it) b/c they are anterolaterally located |
|
|
What is a false cardiac aneurysm
|
LV ruptures contained by pericardium or extracardiac tissues. These have an increased risk of rupture
|
|
|
Where do false aneurysms tend to occur
|
Usually posterolateral or at diaphragmatic wall
|
|
|
Where do false aneurysms of the heart tend to occur
|
left retrocardiac double density, and on lateral involves the posterior surface
|
|
|
What are the angiographic findings of a false aneurysm of the heart
|
: neck usually smaller than true aneurysm, often delayed filling, delayed emptying
|
|
|
Does wegners form both cavities and nodules
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the ddx for cavitary lung lesions
|
C- Carcinoma - Squamous is most common
A- Autoimmune - Wegener's granulomatosis, Rheumatoid nodules V- Vascular - Emboli (septic emboli or bland emboli) I- Infection - Lung abscess, Bacterial pneumonia, Fungal pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Pneumatocele T- Trauma - Pulmonary laceration Y- Young (congenital) - Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation, Pulmonary sequestration, Bronchogenic cyst |
|
|
What is a general rule of thumb as the thickness of a lung cavity increases
|
it is more likely to be malignant
|
|
|
What is the likelihood of malignancy with thickness of the thickest part of a cavity lesions wall
|
Cavity wall thickness (thickest part)
< 5 mm: 92% benign 5-15 mm: indeterminate (51% benign, 49% malignant) > 15 mm: 95% malignant |
|
|
What is a subtle clue that a patient may have a pneumothorax on the medial aspect of a chest x ray
|
Air commonly accumulates medially sharpening of mediastinal borders and improved visualization of cardiac margin and aortic knob
|
|
|
What is the pathway of a line that goes into a persistent left side SVC
|
Swan-Ganz in left SVC: left SVC to the coronary sinus to the RA to the RV to the PA
|
|
|
What are the two main causes of pulmonic stensos
|
Mostly congenital, rarely acquired in carcinoid syndrome
|
|
|
What is the radiographic appearance of pulmonic stenosis
|
Dilated main and left PA, normal-sized right PA
|
|
|
Does the right pulmonary artery enlarge in pulmonic stenosis
|
no
|
|
|
Do you expect to see increased vascularity in pulmonic stenosis
|
no
|
|
|
What ventricle is usually enlarged in pulmonic stensosis
|
the right ventricle
|
|
|
What are secondary causes of ascending aortic dilation
|
dissection, postenotic dilation, coarctation
|
|
|
What are the congenital/infectious causes of ascending aortic dilation
|
marfans, syphillis, takayasus
|
|
|
What is the MCC of an ascending aortic aneurysm
|
atherosclerotic disease or trauma
|
|
|
What is the characteristic appearance of the ascending aortic aneurysm in marfans syndrome
|
sinotubular ectasia with tulip bulb appearance, related to cystic medial necrosis
|
|
|
What is the characteristic appearance of an aortic aneurysm in marfans syndroem
|
saccular (like most infectious aneurysms), spares aortic root
|
|
|
Does takayasu tend to have stenotic areas in addition to the aneurysm
|
yes
|
|
|
What is an ascending aortic aneurysms treated
|
surgery when > 5.5 cm, enlarging > 1 cm/y, or symptomatic (> 5 cm in Marfan)
|
|
|
What findings are consistent with a solitary pulmonary nodule
|
Well-defined round or oval lesion < 3 cm
|
|
|
What is the likelihood of malignancy if a patient has a solitary pulmonary nodule
|
50% lung CA, 40% benign, 10% solitary mets
|
|
|
What is the most cost effective way to make sure a nodule is not malignant
|
get old film and if it is stable for 2y it is benign
|
|
|
If there is no old films then what should be done
|
get a CT
|
|
|
What 2 characteristics will indicate that a nodule is benign
|
if it is completly calcified and is therefore a granuloma or if it has fat (hamartoma)
|
|
|
What type of lung nodule will contain fat
|
hamartoma
|
|
|
What are benign types of calfications in a nodule seen on CT
|
Benign Ca+ patterns: diffuse, central, laminar, popcorn
|
|
|
What are the indeterminate patterns of calcification seen on CXR
|
no Ca+, stippled or eccentric Ca+
|
|
|
What is the work up for a solitary nodule on CT
|
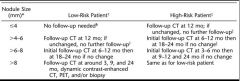
|
|
|
What is the technique for biopsing a centrally located pulmonary nodule
|
Central endobronchial: bronchoscopic
|
|
|
What is the technique for biopsying a more peripheral pulmonary nodule
|
percutaneous CT guided
|
|
|
How sensitive is a FNA for detecting primary or metastic cancer
|
greater than 90%
|
|
|
If lymphoma or thymoma is suspected what is the pathologic method of choice
|
Core bx may be needed for dx of thymoma, lymphoma
|
|
|
What are the potential complications of lung biopsy
|
PTX (25%; of pts w/PTX, 25% require chest tube), minor hemoptysis (common), air embolism, significant pulmonary hemorrhage (rare)
|
|
|
What are the causes of a thoracic aortic aneurysm
|
atherosclerotic (MC; fusiform +/- thrombus & Ca+), trauma (pseudoaneurysm), mycotic (saccular), dissection
|
|
|
Is the risk of rupture of a descending aortic ruputure large if a patient has a 5cm aortic aneurysm
|
Degenerative thoracic aneurysms have a low risk of rupture if < 5 cm, with risk increasing after 5 cm
|
|
|
When is a ascending aortic aneurysms surgically repaired
|
Usually repaired if > 6.5 cm (risk of rupture > surgical risk), enlarging > 1 cm/y, or symptomatic (> 6 cm in Marfan)
|
|
|
What is a sign of impending aortic rupture on CT
|
Impending rupture produces high density crescent sign within aortic thrombus or between thrombus and aortic wall
|
|
|
What is the ddx of an intracardiac mass
|
Thrombus (MC in adults)
Benign tumors: myxoma, lipoma, rhabdomyoma, papillary fibroelastoma Metastatic disease (second MC in adults) Malignant primary tumors: angiosarcoma, mesothelioma, fibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
What is the MC type of cardiac mass
|
thrombus
|
|
|
Name 4 types of malignant tumors of the heart
|
angiosarcoma, mesothelioma, fibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma
(sarcomas and mesothelioma) |
|
|
Name 4 benign types of tumors of the heart
|
myxoma, lipoma, rhabdomyoma, papillary fibroelastoma
|
|
|
What is a very general way of differentiated a cardiac benign and malignant tumro
|
Benign tumors tend to be well circumscribed whereas malignant are large and infiltrative, with broad attachment and pericardial effusion, and intense enhancement
|
|
|
Do malignant tumors have a broad base, cause pericardial effusion and enhance more vividly
|
yes
|
|
|
What atrium do atrial myxomas arise from
|
the left side more commonly than the right
|
|
|
Do atrial myxomas usually arise from interatrial septum
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a dumbell myxoma
|
a myxoma that grows through the fossa ovalis to the other atrium
|
|
|
What percent of mxyomas will calcify
|
10%
|
|
|
What is the typical signal characteristic of atrial myxomas
|
T1 and T2 hyperintense
|
|
|
Do atrial myxomas enhance with contrast
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the MR characteristics of a atrial thrombus
|
brighter on T1, dark on T2, GRE, no enhancement
|
|
|
What is the appearance of mitral regurgitation
|
Similar appearance to mitral stenosis, with cephalized pulmonary vessels, and enlarged left atrium and atrial appendage
|
|
|
What does mitral regurgitationn have that mitral stenosis does not
|
enlarged left ventricle
|
|
|
What are 2 functional causes of mitral regurgitation
|
muscle rupture
papillary rupture |
|
|
What disease will predispose a patient to mitral valve disease
|
rheumatic heart disease
|
|
|
What is the pulmonary finding in goodpastures disease
|
pulmonary hemorrhage
|
|
|
What are the acute causes of airspace disease
4 |
Edema
ARDS Hemorrhage PNA |
|
|
What are the chronic causes of airspace disease
|
Tumor
PNA (fungal, COP, etc) Alveolar sarcoidosis Lipoid PNA Aleovlar proteinosis Chronic Aspiration |
|
|
What kind of tumors cause chronic airspace disease
|
lymphoma
bronchoalveolar carcinoma |
|
|
What is the classic shape of the heart in a patient with TOF
|
boot shaped
|
|
|
What is a common association with TOF
|
right sided aortic arch
|
|
|
Is TOF a cyanotic congenital disease
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the 4 features of TOF
|
VSD, pulmonic stensosis, RVH, overriding aorta
|
|
|
Is the heart enlarged in TOF
|
mildly
|
|
|
Is the vasculature prominent in TOF
|
no
|
|
|
What are the plain film findings in a patient with TOF
|
Concave main PA and upturned cardiac apex (from RVH) resulting in a boot-shaped heart
↓ Pulmonary vascularity frequently there will be a right aortic arch |
|
|
What is the tx of TOF
|
VSD closure, widening RVOT (temporary fix is the Blalock-Taussig shunt to get blood to the lungs
|
|
|
What is another name for a superior sulcus tumor
|
pancoast
|
|
|
What is a pancoast tumor
|
bronchogenic Ca at the lung apex
|
|
|
What is the tumor grade if the tumor invades the chest wall
|
T3
|
|
|
What is the tumor grade if the tumor invades the neuro foramen or vetebral body
|
T4
|
|
|
What makes up the stage of a lung tumor
|
Tumor
Node Mets TNM system |
|
|
What stage is T4
|
3A or higher (depending on N or M)
|
|
|
What stage is T3
|
3A or lower (depending on N and M)
|
|
|
Subclavian artery, brachial plexus, vertebral body involvement = unresectable
|
yes
|
|
|
What are some of the SS of a pancoast tumor
|
Pain in shoulder or arm, weakness and atrophy of muscles of the hand, Horner syndrome, bone destruction
|
|
|
What are the CXR findings of a pancoast tumor
|
apical cap, apical mass, or bone destruction
|
|
|
What is the best study for staging of a pancoast tumor
|
MR
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of a RML and simultaneous RLL lung collapse
|
obstruction at the level of the bronchus intermedius
|
|
|
What are the CXR findings of a RML and RLL collapse
|
Major and minor fissures displaced downward and backward
On frontal, obliteration of right hemidiaphragm as well as right heart border Opacity is triangular, sharply marginated superiorly by depressed minor fissure Ipsilateral cardiac and mediastinal shift is common |
|
|
What are the 4 forms of aspergillosis
|
aspergilloma
semi-invasive aspergillosis invasive aspergillosis allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis |
|
|
Do patients with normal immune statuses get aspergillomas
|
yes
|
|
|
Where do aspergillomas occur
|
this is basically a fungal ball in a preexixting cavity, cyst or bulla
|
|
|
What 3 underlying conditions will predispose a pt to an aspergilloma
|
TB
Sarcoid CF |
|
|
What is the CXR findings of an asperigolloma
|
round opacity within a cyst or cavity that often has a crescent of air b/w fungus ball and cavity (Monad sign). The fungus ball is usually mobile and changes position with changing body position
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a aspergilloma
|
SCC (cavitating)
abscess |
|
|
If a pt is symptomatic from an aspergilloma what is the treatment
|
surgical resection
intracavitary antifungal bronchial artery embolization |
|
|
What is another name for a an aspergilloma
|
mycetoma
|
|
|
What are predisposing factors to semi-invasive aspergillosis
|
Occurs in mildly immune suppressed such as alcoholism, diabetes, chronic illness
|
|
|
Where does semi-invasive aspergillosis most commonly start
|
Starts as focal consolidation in apex
|
|
|
What is the MC natural progression of semi-invasive aspergillosis
|
It will start in the apices as a focal consolidation then progresses to a cavity, initially thick-walled, later thin-walled with fungus ball inside
|
|
|
What are the radiographic findings of semi-invastive aspergilloma
|
can look like aspergilloma, upper lobe consolidation, or thick-walled cavity
Often has extensive associated pleural thickening |
|
|
What will predispose a patient to invasive aspergillosis
|
Occurs in truly immune compromised such as AIDS, transplant, steroids
|
|
|
What causes the infarted lung of invasive aspergillosis
|
Invasive necrotizing pneumonia due to invasion of blood vessels with accompanying pulmonary infarction
|
|
|
What are the CXR findings of invasive aspergillosis
|
multiple nodular areas of peripheral subpleural consolidation which frequently cavitate and may form air crescents or masses with surrounding ground glass opacity due to hemorrhage (“CT halo” sign)
|
|
|
What causes the halo sign of invasive aspergillosis
|
consolidation with surrounding GGO
|
|
|
What is the classic CXR of ABPA
|
finger-in-glove consolidations.
|
|
|
What predisposes a patient to ABPA
|
asthma
|
|
|
Do patients with ABPA tend to have increased eosinophils and IGE
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the findings of ABPA on CXR
|
mucoid impaction in central and upper lobe bronchi (finger-in-glove pattern)
|
|
|
As the consolidation is cleared what tends to occur to the central lung on the effected side
|
As mucus plugs clear, residual central bronchiectasis
|
|
|
What is the treatment of ABPA
|
steroids
|

