![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Data model |
Method for organizing the data involved. This method in most cases specifies or implies the ways in which data is accessed. Each database system (DBS) supports usually one such data model at the conceptual level for the database designer (DBA) to plan the structure of the database. |
|
|
Database languages |
The language provides the designer with a data language that includes two components. 1. Data definition language, that is used to design the structure of the database 2. Data manipulation languages, that is used to access our manipulate database content |
|
|
5 data models used commercially |
1. Hierarchical data model 2.network 3. Relational data model 4. Object oriented days model |
|
|
Entity set |
A set of entities of the same type (all persons with an account at s certain bank |
|
|
Degree of relationships |
This means how many of one entity can be related to how many of another set |
|
|
Binary |
Relationship where there is only two entity sets. Becomes terniary, for three etc. |
|
|
Type of relationships |
Self explanatory. 1 to 1 1 to many Many to many |
|
|
Relational database |
A relational database organizes datasets in tables (relations). A table is made up of does and columns. A row is also called a record (or tuple). A column is also called a field or attribute. A database take is similar to a spreadsheet. |
|
|
Union |

Adds to tables |
|
|
Intersection |
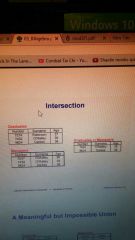
New table of the common elements between two different tables |
|
|
Differencr |

New table composed of the differences between two tables |
|
|
Renaming |

|
|
|
Selection and projection |

|
|
|
Selection |

|
|
|
Projection |

|
|
|
Join |

Most used operand. Similiar to union, but drops the uncommon tuples |
|
|
Natural join |

|

