![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Key |
A set of attributes is a key if it is a minimal set of identifying attributes - removing any one attribute would make it no longer uniquely identifiable. |
|
|
Super Key |
A set of attributes is a superkey for an entity if those attributes, taken together, always uniquely identify every entity instance. |
|
|
Composite Key |
A Primary Key made up of multiple attributes. |
|
|
Primary Key |
A single key that is unique and not-null. It is one of the candidate keys. |
|
|
Candidate Key |
A candidate key can be uniquely and used to identify a database record. They are Not Null and Unique. |
|
|
Representative Sample |
The corpora should contain a similar mix of text to the language variant for which it is being developed. For example using Shakespeare's works is not a good representation of Elizabethan English. |
|
|
Finiteness |
A copora should be finite. When building a corpora it is usually decided at the outset how the language is to be sampled and how much data to include. |
|
|
Monitor Corpora |
These capture the growth and change of a language. They remain finite but extend over time. |
|
|
Name 4 distinctive features of a Machine Readable Corpus compared to books with printed text |
• They can be huge in size; up to a billion words • They can be searched and analysed efficiently • They can be made available to many users simultaneously, at large distances • They can easily (and sometimes automatically) be annotated with additional useful information. |
|
|
What is the advantage of using a standard reference? |
Having a standard reference allows competing theories about the language variety to be compared against each other on the same sample data. |
|
|
Name 4 notable English Language Corpora |
• Oxford English Corpus (OEC) • Corpus of Contemporary American English (COCA) • British National Corpus (BNC) • Brown Corpus |
|
|
Balancing |
Balancing ensures that the linguistic content of a corpus represents the full variety of the language sources for which the corpus is intended to provide a reference. For example a balanced text corpus includes materials from sources such as books, newspapers, magazines, letters, etc. |
|
|
Sampling |
Sampling ensures that the material is representative of the types of source. For example, Sampling from the newspaper text involves selecting texts randomly from different newspapers, issues and sections. |
|
|
List some of the "dimensions" of the source material that balancing would affect. |
• Language Type: Editied Text, Spontainious, Scripted • Genre • Domain (What is the text about?) • Medium |
|
|
Tokenization |
Tokenization divides are textual data into tokens such as words, numbers and punctuation marks. |
|
|
Sentence Boundary Detection |
Identify the start and end of individual sentences. |
|
|
Why Annotate A Corpus? |
It adds informstion to the corpus that is not explicit in the data itself. This is often specific to a particular application; and a single corpus may be annotated in multiple ways. |
|
|
Annotation Scheme |
Annotation Scheme is the basis for annotation, made up of a tag set and annotation guidelines |
|
|
Annotation Guidelines |
Tells annotators - domain experts - how a tag set should be applied. It ensures consistency across annotators. |
|
|
Tag Set |
An inventory of labels for makeup. |
|
|
Relationship |
A relationship is an association between entities. |
|
|
Relationship Instance |
Each individual occurrence of the relationship is a relationship instance. |
|
|
Relationship Set |
A collection for all instances of a relationship |
|
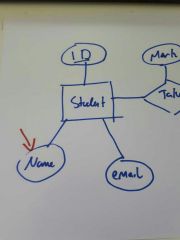
What is this in an ER diagram? |
Attribute |
|
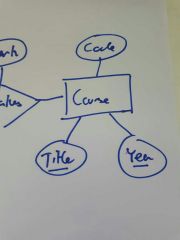
What sort of key is used to identify Course? |
Composite Key |
|
|
What is Atomicty? |
All or Nothing: a transaction eitehr runs to completion, or fails and leaves the database unchanged. This may involve a rollback mechanism to undo a partially-complete transaction |
|
|
What is Consistency? |
Applying a transaction in a valid state f the database will always give a valid result state. |
|
|
What is Isolation |
Concurrent transactions hav eht esame effect as sequential ones: the outcome is as if they were done in order. (NOTE: Transactions may, in fact run at the same time: but should never see each other;s imtermediate state.) |
|
|
What are the ACID properties amd why are they meeded/ |
The ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durable) are a key benchmark for assessing database systems. |
|
|
What is the symbol for total participation in an ER diagram? |
Double lines |
|
|
Which way should an arrow face in a one to many relationship in an ER diagram? |
The arrow should point from the many to the one. It should go from the many to the relationship block. |
|
|
What is a weak entitiy? |
A weak entity is an entity that has attributes but may not be enough to uniquely identify its self without it's identifying relationship and identifying owner. |
|
|
In a tree of an XPath data model, what do the positions of the nodes relative to each other show? |
They show where they appear in the XML document. Those appearing first in the document will appear leftmost in the diagram. |
|
|
In a DTD declarations, what do the order of the lines mean? |
Nothing! As DTD is declarative the lines can appear in any order. |
|
|
What would the ELEMENT line for this node look like? *Insert publisher node from paper* |
<!ELEMENT publisher (name,imprint+)> The publisher may have only one name, however the plus indicates that there maybe more than one imprint. |
|
|
In a DTD document, when would you use the tag #PCDATA? |
PCDATA is used for text nodes in DTD. |
|
|
What would the attribute line(s) look like for this node? |
<!ATTLIST book code CDATA #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST book type (hardback|paperback) "paperback"> |
|
|
When is CDATA used in a DTD document? |
CDATA is used to represent an open attribute (no regex) |
|
|
When is #REQUIRED used in DTD |
#REQUIRED is used when the attribute of a node cannot be left empty. |
|
|
When should not null be used in a SQL schema? |
Not null should be used on non-primary key attribute if it cannot be left empty or on a foreign key as this must exist for a relationship to exist. |
|
|
Do primary keys require the not null tag in a SQL schema? |
No. As primary keys by nature are required to make a record in a database thus are not null by default. |
|
|
How do you create a composite key in a SQL schema? |
primary key (field1, field2,...) |
|
|
How do you create a foreign key in a SQL schema? |
foreign key x references table(y) |
|
|
How is text represented in a SQL schema? |
VARCHAR(x) where x is the number of characters |
|
|
In an SQL query, what does distinct mean? |
distinct is used after select to remove duplicate entries in the result. |
|
|
How do you create a SQL query that involves more than one table? |
select table1.field
from table1, table2 where table1.field = table2.field and ... Note: field may be called different things in different tables |
|
|
What is catagorical data? |
Categorical data/scale is data that has no numerical or natural order. |
|
|
What is ordinal data? |
Ordinal data/scale give a recognised order between data items, but there is no arithmetic content. Numbers may still be used but there is no way to apply arithmetic to them. |
|
|
What is an interval scale? |
An interval scale assigns a numeric balue to data, but where these values are relative to each other. Values can be compared, averaged and subtracted but not added together or multiplied. |
|
|
What is a ratio scale |
A ration scale uses numeric values which have an abstemious notion of zero This means they can sensibly be added, and multiples by real numbers. |
|
|
Give 3 examples of categorical data
|
Classifying words (nouns, verbs, adjective) Eye Color Places in a town |
|
|
Give 3 examples of ordinal data |
T-Shirt Size (XS,S,M,L) 1st, 2nd, 3rd Shoe size |
|
|
Give 2 examples of interval data |
Times Of Day Temperature (Celsius) |
|
|
Give 3 examples of ratio data |
Temperature (Kelvin) Height |
|
|
What is the formula for the mean? |
*insert picture* |
|
|
What is the formula for the standard deviation with large data sets? |
*INSERT PICTURE( |
|
|
What is the formula for the standard deviation for a population |
*insert picture* This is known as the Bessel Correction |
|
|
How do you calculate the median? |
Order the data (if possible) from smallest to large then find the value that lies in the (n+0.5)/2 position. If the n+0.5/2 value is not an integer then find the value between the (n/2) and (n+1)/2 value. |
|
|
How do you calculate the mode? |
Count the most frequent value. |
|
|
What is the cosine formula |
insert picture |
|
|
What is Precision? |
Precision is what proportion of the documents returned by the system are relevant |
|
|
What is Recall? |
What proportion of all the relevant documents are returned by the system. |
|
|
Name each section of the contingency table: *picture* |
a = true positives b = true negatives c = false positives d = true negatives |
|
|
How do you calculate precision? |
TP/ (TP+FP) |
|
|
How do you calculate recall? |
TP/(TP+FN) |
|
|
What is the F Score of a system? |
F Score is a measure of how balanced a system is, a score close to one has more weight on precision, and the closer to zero it gets the more weight on recall. |
|
|
How do yo calculate F Score? |
(2PR)/(P+R) |

