![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
190 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How do you find the lowest boiling point? |
Boiling point requires that the molecules of a compound in the liquid overcome the intermolecular attractive forces and escape into the gas phase: the STRONGER these interactions are, the more thermal energy one will have to pout in to pull the molecules apart, and hence the higher boiling point.
|
|
|
|
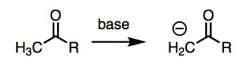
What does branching have to do with boiling point?
|
compounds will have lower boiling points with increased branching, since branching disrupts the spatial packing of molecules in the condensed phase and hence compromises intermolecular attractions.
So find the molecule with the most branching and you found your lowest boiling point. |
|
|
|
What does a longest, least branched compound have to do with highest boiling point?
|
the longer the alkane, the more it weighs and the more difficult it will be to "push" the molecule into the gas phase. Also, longer alkanes experience stronger van der Waals forces. |
|
|
|
How do you know what has the highest melting point?
|
It has the same characteristics that determine boiling point: - intermolecular attraction
- weight, and -geometry i.e compounds with hydrogen bonding have great interaction between molecules, increasing the melting point. |
|
|
|
Boiling point and cis- and trans-
ie 1,2-dichloroethene which one has a higher boiling point. |
The boiling point of the cis isomer is higher because it has a net dipole moment. |
|
|
|
True or false: Physical properties (i.e. boiling and melting point) of enantiomers are identical.
|
True
|
|
|
|
True or false: All meso compounds are optically inactive.
|
True
|
|
|
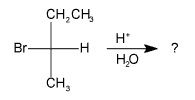
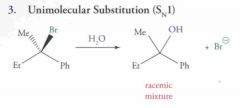
What is(are) the major organic product(s) of the SN1 reaction below?
|
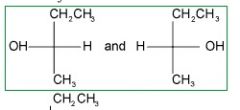
Remember the the following criteria:
1) SN1 reactions proceed through planer intermediate in which the central carbon atom is sp2 hybridized. This means that the nucleophile can attack from above or below the plane of the cation. yielding a racemic mixture of compounds. Since we started out with an optically active compound, the correct choice will have two compounds listed that differ in the configuration around one carbon atom. |
|
|
|
What should we look for in a compound with the lowest boiling point?
|
look for compounds with little or no hydrogen bonding ie to O or N
|
|
|
|
What is true of ethene?
|
Both carbon atoms are sp2 hybridized and the molecule is planar.
|
|
|
|
What is a carbonyl carbon?
|
one that is double bonded to an oxygen. So if you are asked what is the hybridization of the carbonyl carbon on N,N-Dimethylformamide. You don't need to know the structure just the definition of a carbonyl carbon.
|
|
|
|
A compound is separated from an ethereal mixture by extraction with cold, aqueous NaHCO3, then recovered by addition of HCl to the extract. What is the likely compound?
|
CHx(CH2)7 COOH
The correct answer choice has to be a compound that is hydrophobic (since it started in the ether layer), but when reacted with a weak base becomes a water soluble salt. The answer above is a nonanoic acid, will react with sodium bicarbonate and form sodium nonanoate, a water soluble salt. |
|
|
|
What does acetone do and what reactions does it promote best?
|
It is a compound that promotes SN2/E2 reactions because it is aprotic and polar. Since it cannot form strong intermolecular bonds and is of low molecular weight it has a low boiling point. Acetone exists in two forms, whith the keto form predominating by 99%. This is because the carbon-oxygen double bond (the carbonyl bond) is much stronger than the carbon-carbon double bond.
|
|
|
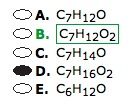
What is a formula for an ester? And what are the key characteristics of an ester?
|
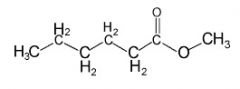
An ester MUST have at least two oxygens; both of which are bonded to the carbonyl carbon (one via double bond and another single bond).
Watch out for the number of Hydrogens. |
|
|

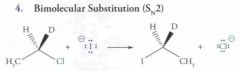
Find the rate law.
|
For SN2 and E2 reactions, the rate law is first order with respect to both the nucleophile and the substrate. In this reaction the nuc is the t-butoxide anion (T-BuO^-) and the substrate is t-butyl bromide (t-BuBr). THus B.
|
|
|
|
What are the general formulas for finding the number of hydrogens for cyclohexane and n-hexane?
|
CxH2x
CxH2x+2 |
|
|
|
WHat is heat of hydrogenation and what type of compounds will have a high heat of hydrgenation?
A. Cycloheptene B. cyclohexene C. cyclopenene D. cyclobutene E. cyclopropene |
Heat of hydrogenation is the amount of energy release when pi bonds are converted to sigma bonds by the addition of hydrogens. THe great the heat of hydro. of a molecule, the great the potential energy it has. The more potential energy a molecule has, the less stable it is. By comparing the relative stabilities of different molecules, their delta Heat of Hydrogentation can be obtained. Cyclopropene, a three membered ring, has the greatest bond strain, and is the most unstable. It will therefore release the most energy upon hydrogenation, so will have the greatest delta Hh.
|
|
|
|
What relation do Z/E and cis/Trans isomers have in relation?
|
They describe the relative positions of subtituents about a double bond. They are by definition geometric isomers. Since double boned carbons are not chiral, they cannot be enantiomers.
|
|
|
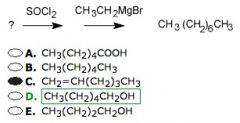
Which of the compound below would be the best starting material for the synthesis shown?
|
D.
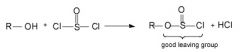
SoClx reacts with primary and secondary alcohols to generate something with a very good leaving group ClSO2^- (OH- is a very poor leaving group). |
The compound formed is reactive in nucleophilic substitution reactions. The Grignard reagent is a good nucleophile. To get the question correct, verify the number of R. Since prodcut has 8 carbons, and 2 came fro the ethyl magnesium bromide, our starting compound must have 6 carbons. Answer d
|
|

What is the realtionship
|
Both compounds have the same atoms, but the connectivity among them is different. THese are structural or constiutional isomers by definition.
|
|
|
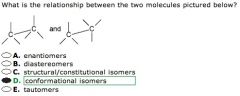
WHat is the realationship?
|
THe two compounds are chemically identical, differing only in their rotation about a single bond, in this case the central c-c bond. THese are referred to as conformational isomers.
|
|
|
|
What are addition reactions?
|
Addition reactions involve, as the name suggests, an addition of a molecule to a double bond, which are made of pi bonds and sigma bonds.
|
|
|
|
Why can pi bonds be broken?
|
THe pi bond is in some ways weaker than the sigma bond; therefore the pi bond can be broken without breaking the sigma bond. A further advantage of the pi bond is that the electrons are exposed and are easily attacked by electrophiles (molecules that are seeking an electron pair)
|
|
|
|
What are electrophiles?
|
are species that "love" electrons. They are often positively charged and seek electrons to fill their outershells. Many typical electrophiles are Lewis acids.
Lewis acids are electron acceptors because they "love" to accept love/electrons. |
|
|
|
What is the Markovnikov Rule?
|
This rule states that the addition of a protic acid (HX) to an alkene occurs such that the proton attaches to the carbon with the smallest number of alkyl substituents, and thus producing the most stable carbocation. The proton will add to the carbon with the greatest number of hydrogens.
Confusing? In other words when we are adding an alkyl halide to an alkene we add the halide to the most substituted carbon atom in the double bond and the proton to the least substituted carbon atom of the double bond. |
|
|
|
What disobeys Markovnikov's rule? And why?
|
Free redical intermediates also play a role in addition of alkyl halides. Free radical additions occur when PEROXIDES, OXYGEN, UV light or other radical causing conditions are present. Free radical additions disobey Markovnikov's rule because the Xdot adds first to the double bond, and the hydrogen radical then adds second.
|
|
|
|
What happens when peroxides are present?
What is a peroxide? |
expect free radical reactions that do not follow Markovnikov's rule.
A peroxide is a oxygen-oxygen single bond i.e. hydrogen peroxide H-O-O-H |
|
|
|
Where does the radical land on during anti-Markovnikov addition?
|
In the presence of peroxides, the addition of HBr to the double bond takes place in an anti-Mark. manner in a series of free radical reactions initiated by the presence of the peroxides. Free radical additions disobey Mark.'s rule because the radical adds to the double bond so as to produce the most stable alkyl radical. The most stable alkyl radical is the most substituted alkyl radical, thus in the next step the hydrogen radical will add to the most substituted carbon of the double bond.
|
|
|
|
What happens to anti addition of an X2 molecule?
|
The double bond acts as a nucleophile and attacks an X2 molecule, displacing X. Note that this addiiton is anti, becaseu the X- attacks the cyclic halonium ion in a standard SN2 displacement.
THe addition of halogens to a double bond is a rapid process. Note that this addition is frequently used as diagnostic tool to test for the presence of double bonds. |
|
|
|
How does the anti-addition of X2 proceed?
|
it proceeds via an ionic mechanism as in the case of Mark.'s addition. BUT the intermediate is a cyclic ion.
|
|
|
|
What are syn additions?
|
Syn additions are additions to the same side of a double bond.
|
|
|
|
What is a common example seen on test day regarding syn addition?
|
the catalytic hydrogenation, which is the reductive process of adding molecular hydrogen to a double bond with an acid or metal catalyst. B/c the face of the double bond is coordinated to the metal surface, the two hydrogen atoms will add to the same side of the double bond.
|
|
|
|
What doe elimination reactions introduce?
What are the used for most? |
Well if addition takes away a double bond...an elimination will insert a double bond.
They are widely used for making alkenes. |
|
|
|
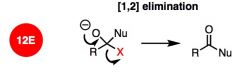
What does the rate of an E1 mechanism depend on?
|
It depends only on the concentration of one species, the substrate. Therefore, increasing the conc. of the nuc will not increase the reaction rate.
It is also dependent by the formation of a carbocation on the substrate, and polar protic solvents stabilize the positive charge on carbocations, E1 reactions are favored by highly polar protic solvents |
|
|
|
What factors favor E1?
|
more branched carbon chains, good leaving groups, weak nucleophiles.
|
|
|
|
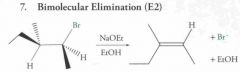
What determines the E2 mechanism rate?
|
determined by the two participating species, substrate and nucleophile. So it needs non-polar solvents so as not to disturb the nucs.
|
|
|
|
True or false. E2 reaction are favored by the presence of a weak base?
|
False, a strong base. WHen the substrate is primary halide and the base is an ethoxide ion, elimination is not favored.
|
|
|
|
Why is it important to determine basicity for a reaction?
|
In order to determine whether a reaction will proceed through E1 or E2 mechanism, you need to consider the strength of the base. In order to determine the relative strength of a base we need to relate the strength of a base to the pKa of its conjugate acid.
|
|
|
|
How do we know a reaction will go through an E2 mechanism by looking at the pKa of the conjugate acid?
|
The LARGER the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base. The stronger the base, the more likely that the reaction will proceed through an E2 mechanism.
|
|
|
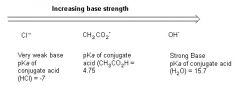
The LARGER the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base. The stronger the base, the more likely that the reaction will proceed through an E2 mechanism.
|
We see that the hydroxide ion is the strongest base among the compounds described on the other side b/d its conjugate acid (water) has a high pKa and is thus very weak.
|
|
|
|
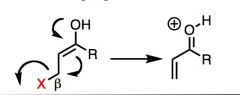
WHat is a dehydration reaction?
Draw an example |
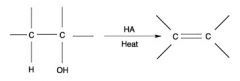
a dehydration reaction is usually defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule. Dehydration reactions are a subset of elimination reactions.Because the hydroxyl group (–OH) is a poor leaving group, having a Brønsted acid catalyst often helps by protonating the hydroxyl group to give the better leaving group, –OH2+. The reverse of a dehydration reaction is a hydration reaction.
|
|
|
|
What is the most important reaction for aromatic compounds?
|
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
In this reaction an electrophile replaces a proton on an aromatic ring, producing substituted aromatic compound |
|
|
|
What are the most common example of aromatic substitution?
|
1) Halogenation
2) Sulfonation 3) Nitration 4) Acylation |
|
|
|
pKa = -logkKa
Strong acids have what |
They have high Ka's and small pKa's
|
|
|
|
What happens to acidity when there are electron-withdrawing groups or electron-donating groups?
|
electron-donating groups: Acidity DECREASES as more alkyl groups are attached becaseu the electron-donating alkyl groups destabilize the alkoxide anion.
Electron-withdrawing: stabilize the alkoxy group anion, making the alcohol more acidic. |
|
|
|
What are the four most common methods for synthesizing aldehydes and ketones?
|
1) Oxidation of Alcohols
2) Ozonolysis of Alkenes 3) Friedel-Crafts Acylation |
|
|
|
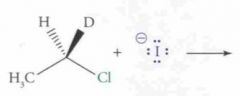
How do you know a reaction will be racemic?
|
IN order for a reaction to produce a racemic mixture, the product formed must possess at least one chiral center and its enantiomers must form in a one-to-one ratio.
|
|
|
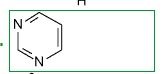
What is this?
|
pyrimidine
|
|
|
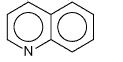
What is this?
|
quinoline
|
|
|
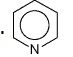
What is this?
|
pyridine
|
|
|
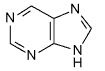
What is this?
|
purine
essential component of nucleic acids |
|
|
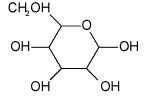
What is this?
|
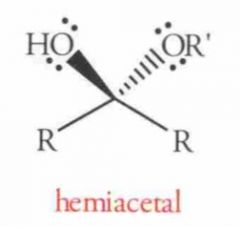
This is a hemiacetal. by definition, contain a carbon atom which is bonded to one -OR group, one-0H group, and a hydrogen.
|
|
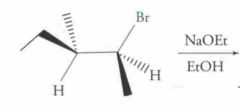
|
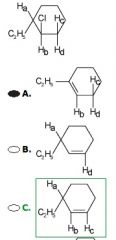
This goes through E2. Why is answer C the correct answer?
|
E2 Elimination occurs in the anti configuration, requiring that the proton abstracted be in a position trans to the leaving group. As, drawn, only the proton labeled Hd is in the proper position for anti elimination.
|
|
|
|
What groups are make the iodoform test positive?
|
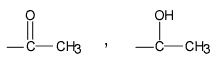
|
|
|
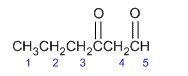
Which carbon is the most acidic?
|
4
It is easy to resonance stabilize with the other double bonds. Making it also easier to leave if a base comes around. Acidic means that it can give away a Hydrogen the easiest. |
|
|
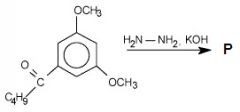
What is the product? And what is this an example of?
|
This is an example of Wolff-Kishner reduction of a ketone to an alkene (conversion of -C=0 groups into -CH2 groups)
|
|
|
What type of reaction will an electron-donating group promote?
|
electrophilic substitution. There are more electrons added to the ring.
|
|
|
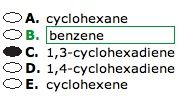
A compound to be analyzed is known to be a six carbon cyclic hydrocarbon. The compound is found to be inert to bromine in water and to bromine in dichloromethane, yet it decolorizes bromine in carbon tetrachloride when a small quantity if FeBr3 is added. Which of the following is the identity of the compound?
|
THe question stem informs us that the unknown cyclic hydrocarbon does not react with bromine in dichloromethane, carbon tetrachloride, or water. This means that the unknown cannot contain any non-conjugated double or triple bonds, otherwise the bromine would have added across the pi bonds. Since the unknown did react with Febr3 was added, it must be benzene. THe FeBr3 acts as a lewis acid and catalyzes aromatic nucleophilic substitution reactions. Bromine is not strong enough electrophile to disrupt the conjugated double bonding in the benzene ring, but the addition of the iron(III) bromide catalyst converts the bromine into a strong enough electrophile that can add to the benzene ring.
|
|
|
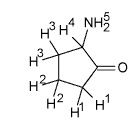
Which of these Hydrogens below are the most acidic? And why is it important to identify those things.
|
Hydrogens 1, 4, and 5 are the most acidic because they are alpha-hydrogens (a-hydrogens). Alpha hydrogens are 1 bond away from the carbonyl bond.
THe oxygen is electron withdrawing making the H's easier to dissociate or be replaced with something else. |
|
|

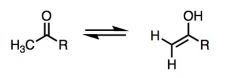
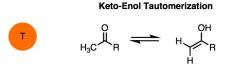
WHat kind of relationship is this? Which is which?
|
Keto-enol Tautomerism.
The left is keto and the right is enol. A tautomer ar two isomers which differ only in the placement of a proton. |
|
|
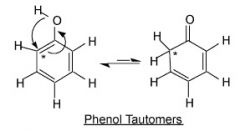
Which compound is more stable and why?
|
Phenol is one of few aldehyde/ketones that exist predominately in the enol form as part of their keto-enol tautomer equilibrium. The conjugated benzene ring system of phenol provides the stability of the enol form. WHen the molecule assumes the keto form, the conjugation is lost, and the molecule become lest stable.
Therefore the molecule on the left, enol, is more stable than the keto form, on the right. |
|
|
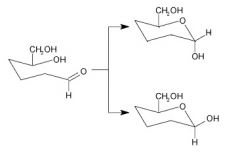
What is this called?
|
mutarotation
Cyclic hemiacetal forms of monosaccharides with different configurations around the first carbon-that is, anomers--are easily broken in aqueous solutions. |
|
|
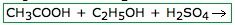
What will this form?
|
an Ester
Esterification is a process in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acidic or basic catalyst to form an ester plus water. |
|
|
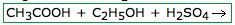
What will this form?
|
an Ester
Esterification is a process in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acidic or basic catalyst to form an ester plus water. |
|
|
|
What do electron donating and withdrawing groups do to the reactivity for electrophilic aromatic substitution?
|
Electron-dontating groups INCREASE the rate by stabilizing the intermediate
ELECTRON-WITHDRAWIG GROUPS decrease THE REACTIVITY. |
|
|
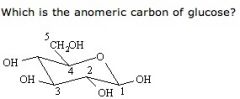
ANd what is the definition of anomeric carbon
|
Carbon 1
Anormeric carbon is the carbon directly bonded to two oxygen atoms. O-C-O |
|
|
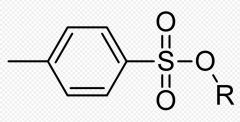
WHat is this and what why would we need this?
|
Tosylate ion is an excellent leaving group
|
|
|
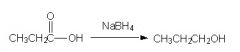
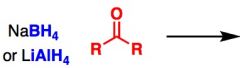
Is this correct?
|
No, Sodium Borhydride is not strong enough to reduce a COOH to and OH
|
|
|
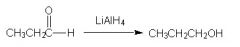
Is this correct?
|
Yes, LiAlH4 is a strong reducing agent. Stronger than NaBH4
|
|
|
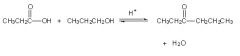
Is this rxn correct?
|
No, b/c under acid catalyzed conditions a COOH will react with an alcohol to form an Ester not a ketone.
|
|
|
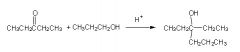
Is this rxn, correct?
|
No, b/c a reaction between an alcohol and an ketone makes a ketal, not a tertiary alcohol (as shown)
|
|
|
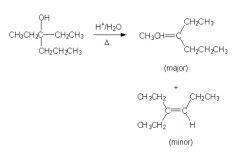
Is this rxn correct?
|
No, b/c the major elimination product is the second one.
|
|
|
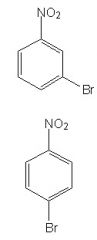
In the EAS reaction of nitrobenzene with bromine, what is the expected product, and what is the rate relative to that for the bromination of benzene?
|
Well, first since the nitro group is meta directing the correct product will be the top one. And since it is meta the reaction will proceed at a slower rate.
|
|
|
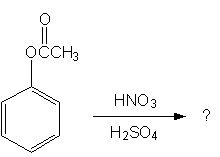
Predict the following reaction
|
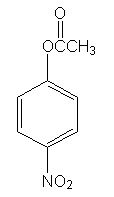
|
|
|
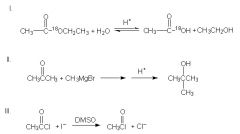
Which of the following reaction schemes are correct?
|
ONly II
Rxn I: In the hydrolysis of an ester to form carboxylic acid, the bond between the carbonyl and the -OR group is cleaved. In other words, the isotopic label will be found in the alcohol product instead. Rxn III: incorrect b/c iodide is a better leaving group than chloride, since it is a weaker base. The acetyl chloride on the reactant side is thus more favored. |
|
|
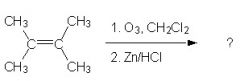
What is the product?
|
The rxn shown is an ozonolysis. Since the alkene is not a terminal alkene, the product is two ketones.
(The ozonolysis of a terminal alkene yields carbon dioxide as one of the products. |
|
|
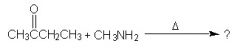
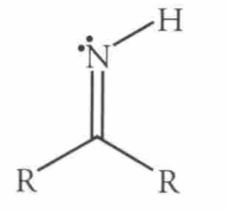
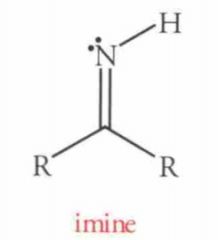
WHat is the major product shown?
|
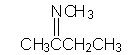
Amines react with aldehydes and ketones to form imines (functional group C=N-)
|
|
|
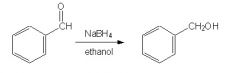
Is this reaction correct?
|
Yes, b/c NaBH4 (sodium borohydride, effectively reduces aldehydes and ketones
|
|
|
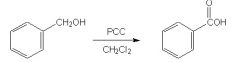
Is this reaction correct?
|
No, b/c PCC is not strong enough to oxidize a primary alcohol past the aldehyde stage.
|
|
|
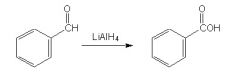
Is this reaction correct?
|
No, b/c Lithium aluminum hydride is a strong reducing agent and will reduce the aldehyde into a primary alcohol.
|
|
|
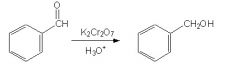
Is this reaction correct?
|
No, b/c the reagents shown will oxidize, not reduce, the material
|
|
|
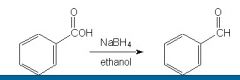
Is this reaction correct?
|
No, b/c Sodium borohydride is too weak to reduce a COOH. There would be no reaction.
|
|
|
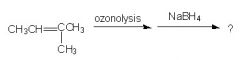
WHat will this yield?
|
ethanol and 2-propranol
|
|
|
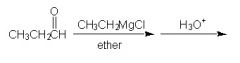
WHat is the major product of this reaction sequence?
|
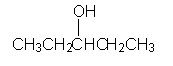
|
|
|
|
True or false: The molecule that give off the least energy is the most stable?
|
False. THe molecule that gives off the most energy is the least stable.
|
|
|
|
Comparing neopentane (heat of combustion = 3250 kJ/mol) and pentane (heat of combustion 3269 kJ/mol) which one is more stable?
|
neopentane. because the molecule that gives off the least amount of energy, neopentane, is the most stable.
|
|
|
|
On which type of element is the positive charge most stable?
On which type of element is the negative charge most stable? |
+ charge is most stable on the least electronegative element
- charge is most stable ont he the most electronegative element. |
|
|
|
Which value is closest to the internal C-C-C bond angle in cyclohexane?
|
110
|
|
|
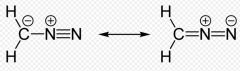
These are resonance structures of what molecule?
|
diazomethane. Notice that it is okay to have the negative charge on the Carbon atom in this case.
|
|
|
|
True of false: when comparing acid strength...the most electronegative atom with the + charge will be the most acidic?
|
True (ie. O+ vs. N+)
|
|
|
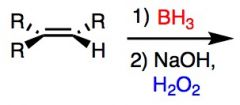
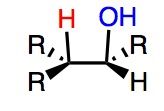
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
Reaction Name: Hydroboration
What's Added?: H+ and OH- Regioselectivity: Anti-Markovnikov Stereoselectivity: Syn Intermediate:N/A Rearrangements: Not Possible |
|
|
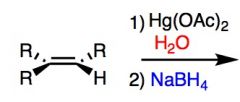
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
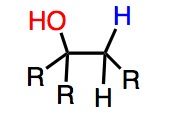
What's Added?: H+ and OH-
Regioselectivity: Markovnikov Stereoselectivity: Anti Intermediate: Mercurinium ion (from three membered ring) Rearrangements: Not Possilbe |
|
|
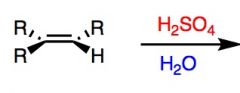
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
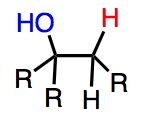
What's Added?: H+ and OH-
Regioselectivity: Markovnikov Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
|
|
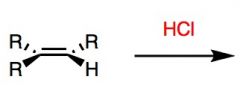
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
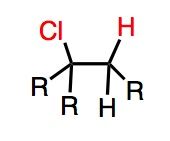
What's Added?: H+ and Cl-
Regioselectivity: Markovnikov Stereoselectivity: N/A Intermediate: Carbocation Rearrangements: Possible |
|
|
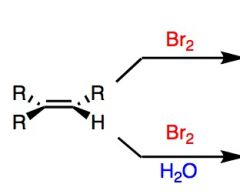
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
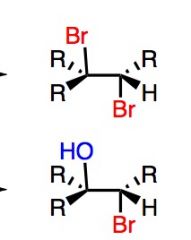
Top Reaction: Is usually accompanied with CCl4 (orCl2), which is inert. This will add both Br.
What's Added?: Br+ and Br- Regioselectivity: N/A Stereoselectivity: Anti Intermediate: bromonium ion Rearrangements: Not Possible Bottom Reaction Note this specific reaction can also be Cl2 What's Added?: Br+ and OH- Regioselectivity:Markovnikov Stereoselectivity: Anti Intermediate: bromonium ion Rearrangements: Not Possible |
|
|
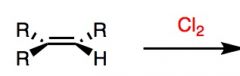
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
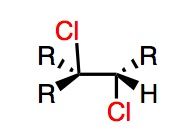
What's Added?: Cl- and Cl+
Regioselectivity: N/A Stereoselectivity: Anti-addition Intermediate: Chlorine ion (brief three membered ring) Rearrangements: Not Possible |
|
|
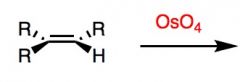
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
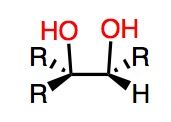
Note: OsO4 = osmium (transition metal)
What's Added?: OH and OH Regioselectivity:N/A Stereoselectivity: Syn-addition Intermediate: N/A Rearrangements: Not Possible |
|
|
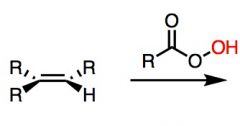
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
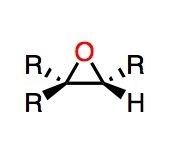
Reaction Type: Epoxidation
Reagent name: mcpba Note: If the reaction above is accompanied by Hot H3O+ then the epoxide ring opens and you get a diol. What's Added?: OH and OH Regioselectivity: N/A Stereoselectivity: Anti Intermediate: N/A Rearrangements: Not possible |
|
|
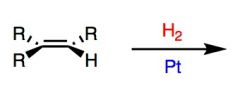
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
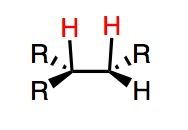
Reaction Name: Catalytic hydrogenation
What's Added?: H and H Regioselectivity: N/A Stereoselectivity: Syn Intermediate: N/A Rearrangements: Not Possible |
|
|
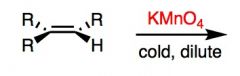
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
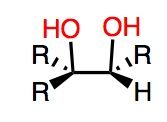
What's Added?: OH and OH
Regioselectivity: N/A Stereoselectivity: Syn Intermediate: N/A Rearrangements: Not possible |
|
|
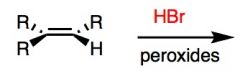
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
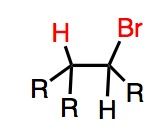
Reaction Mnemonic: ROOR !!! (peroxide) scares the H and Br into anti-Markovnikov
What's Added?: H and Br Regioselectivity: Anti-Markovnikov Stereoselectivity: N/A Intermediate: Radical Rearrangements: Not Possible |
|
|
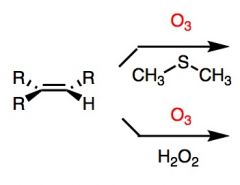
What's Added?:
Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
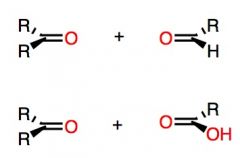
Top Reaction: CH3SCH3 (dimethyl sulfide) is a reducing agent, it will be oxidized to dimethyl sulfoxide.
Bottom Reaction: Hydrogen Peroxide is used to obtain the carboxylic acid instead of the aldehyde. What's Added?: Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Intermediate: Rearrangements: |
|
|
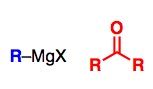
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Grignard Reaction
|
|
|
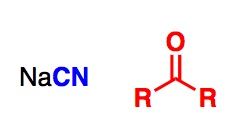
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Cyanohydrin formation
|
|
|
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |
|
|
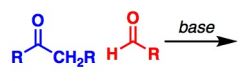
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |
Base-catalyzed aldol reaction
|
|
|
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

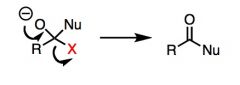
Addition of neutral nucleophiles to acid halides or anhydrides (e.g. amines, alcohols, water)
|
|
|
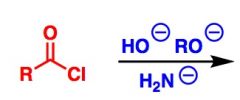
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |
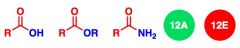
Addition of anionic nucleophiles to acid halides or anhydrides (e.g. RO-, H2N-, OH-)
|
|
|
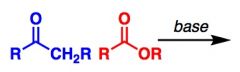
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Claisen condensation
|
|
|
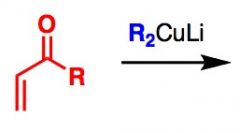
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

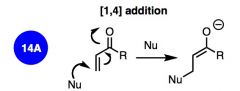
1,4 addition of GILMAN reagent
|
|
|
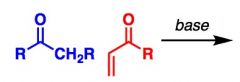
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Michael Reaction
|
|
|
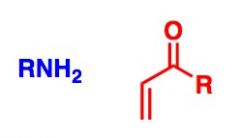
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |
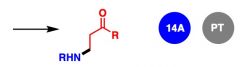
1,4 addition of neutral nucleophiles
|
|
|

What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |
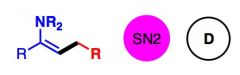
Reactions of neutral nucleophiles with alkyl halides
|
|
|

What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |
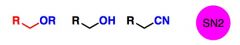
Reactions of anionic nucleophiles with alkyl halides
|
|
|
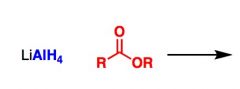
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Reduction of esters
|
|
|
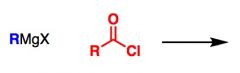
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Grignard Reaction + acid chloride, ester or anhydride
|
|
|
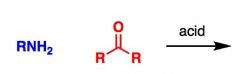
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

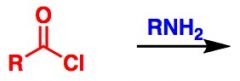
Imine formation
|
|
|
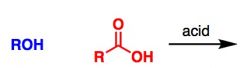
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Fischer esterification
|
|
|
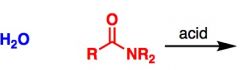
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Amide hydrolysis
|
|
|
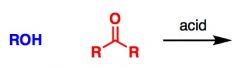
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Formation of acetals
|
|
|
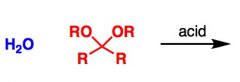
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Hydrolysis of acetals
|
|
|
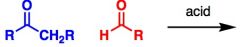
What General type of reaction is this?
2) Predict the Product (answer on image) 3) Describe the general mechanistic steps (answer on image) |

Acid catalyzed aldol
|
|
|
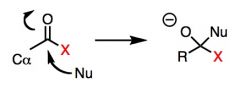
What general type of reaction is this?
|
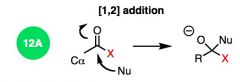
|
|
|
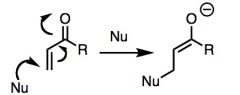
What general type of reaction is this?
|
|
|
|
What general type of reaction is this?
|
|
|
|
What general type of reaction is this?
|
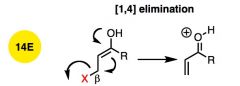
|
|
|
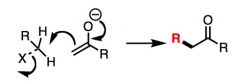
What general type of reaction is this?
|
|
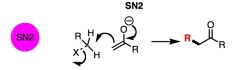
|
|
What general type of reaction is this?
|
|
|
|
What general type of reaction is this?
|
|
|
|
What general type of reaction is this?
|
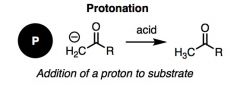
|
|
|
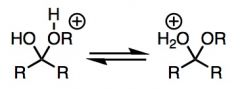
What general type of reaction is this?
|
|
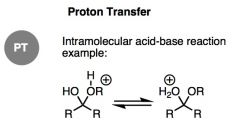
|
|
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
|
|
|
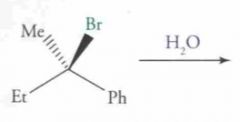
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
|
|
|
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
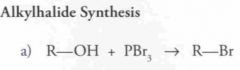
|
|
|
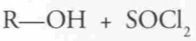
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

|
|
|
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
|
|
|
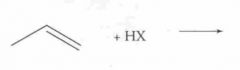
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

|
|
|

What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes and Alkynes
|
|
|
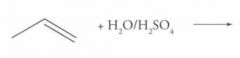
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
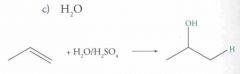
Electrophilic addition to alkenes and Alkynes
|
|
|
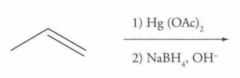
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

|
|
|
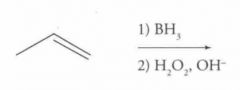
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
|
|
|
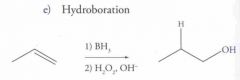
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
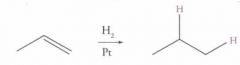
Hydrogenation
|
|
|

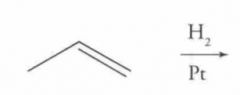
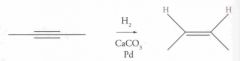
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
Hydrogenation
|
|
|

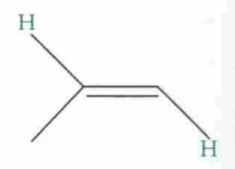
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
Hydrogenation
|
|
|

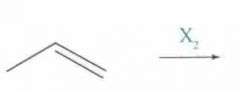
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
|
|
|
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

Halogenation
|
|
|
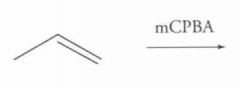
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

Epoxidation
|
|
|
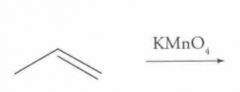
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

Oxidation
|
|
|
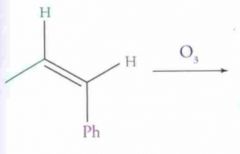
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
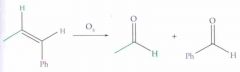
Ozonalysis
|
|
|
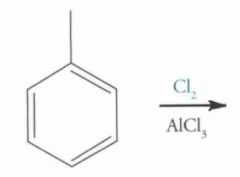
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
EAS (Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution)
|
|
|
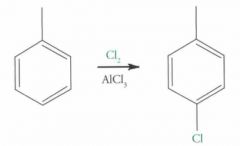
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
EAS
|
|
|
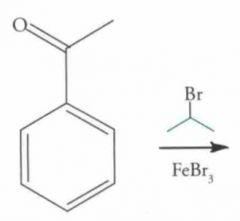
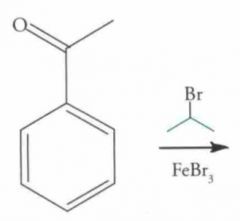
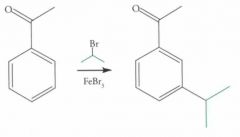
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
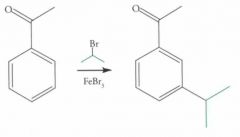
EAS
|
|
|
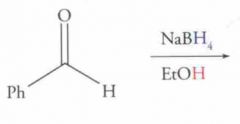
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
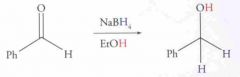
Nucleophilic Addition: Hydride Reduction
|
|
|
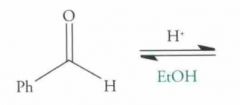
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
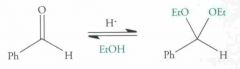
Nucleophilic addition: Acetal Formation
|
|
|
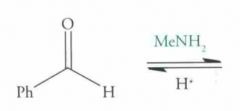
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
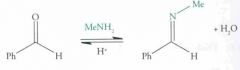
Nucleophilic addition: Imine formation
|
|
|
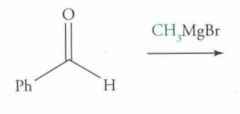
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
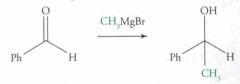
Nucleophilic addition: Grignard Reaction
|
|
|
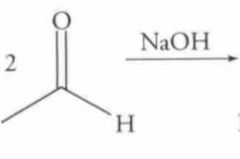
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product. (notice that this reaction continues. Full reaction found on another card)
|
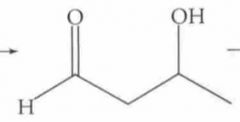
Nucleophilic Addition: Aldol Condensation
|
|
|
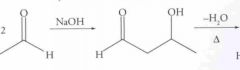
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
Nucleophilic Addition: Aldol Condesation
|
|
|
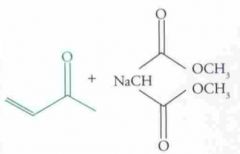
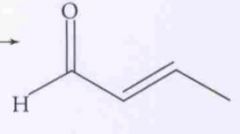
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
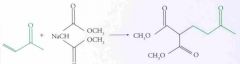
Nucleophilic Addition: Michael Reaction
|
|
|
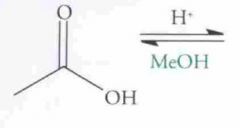
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
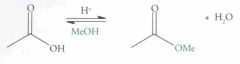
Esterfication
|
|
|
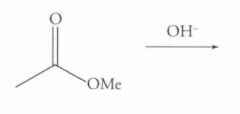
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
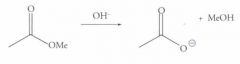
Saponification
|
|
|
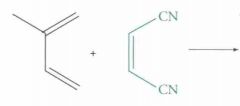
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
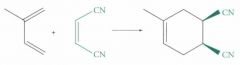
Diels-Alder Cycloaddition
|
|
|
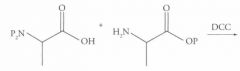
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
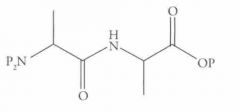
DCC coupling
|
|
|
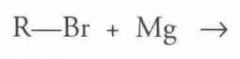
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
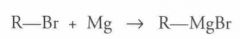
Girgnard Reagent Formation
|
|
|
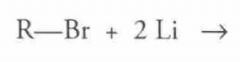
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
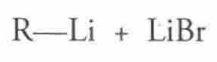
Lithium Reagent Formation
|
|
|
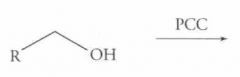
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
Oxidation of Alcohols
|
|
|
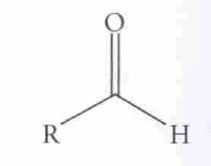
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|

Oxidation of Alcohols
|
|
|
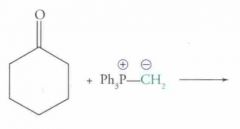
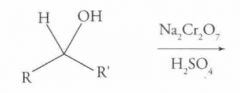
What type of reaction is this? Predict the product.
|
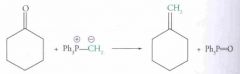
Wittig Reaction
|
|
|
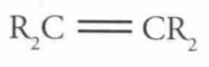
What is this?
|
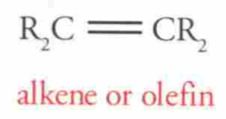
|
|
|

Name this Molecule
|
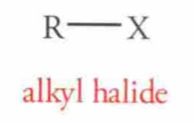
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
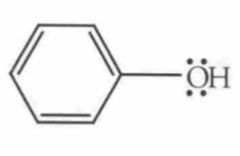
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
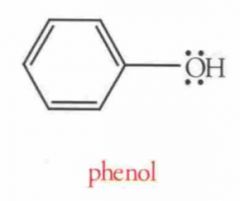
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
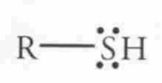
Name this Molecule
|
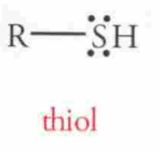
|
|
|
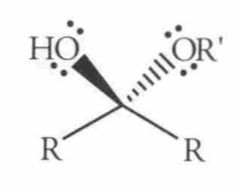
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
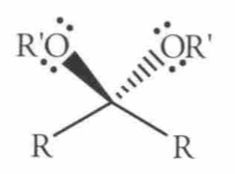
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
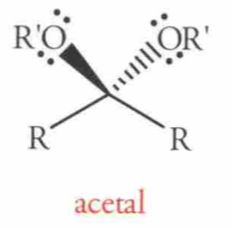
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
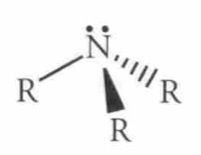
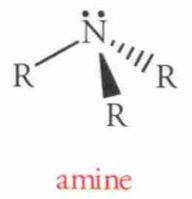
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
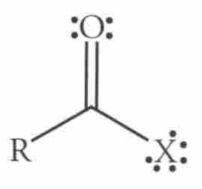
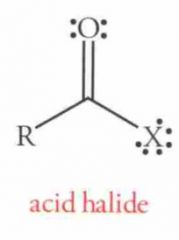
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
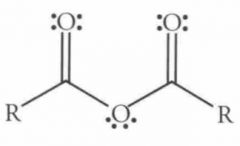
Name this Molecule
|
|
|
|
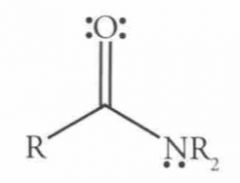
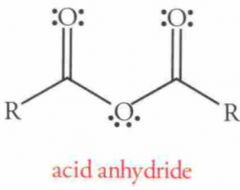
Name this Molecule
|
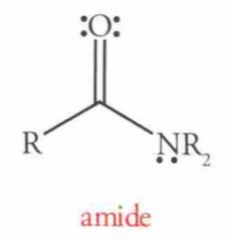
|
|
|
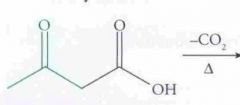
Predict the reaction and name it.
|
|
|
|
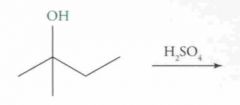
Name this Molecule
|
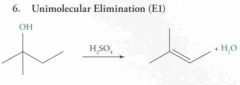
|
|
|
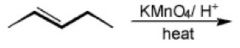
What will happen here?
|
Hot Permangenate results in cleavage of the double bond and two different sized carboxylic acids.
|
|
|
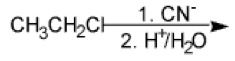
What happens here?
|
The cyanide ion displaces the chloride in an SN2 reaction and is then hydrolyzed by the acid into a carboxylic acid
|
|
|
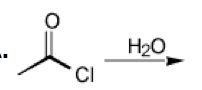
WHat happens here?
|
This will result in a carboxylic acid via an addition/elimination mechanism
|
|
|
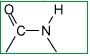
What type of bond is this?
|
A Peptide bond
The -CO - NH - linkage that arises between individual amino acids is known as an amide linkage or more commonly, a peptide linkage. THis linkgage forms when the carbonyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another. A condensation reaction = lose of water as well. |
|
|
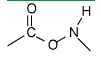
Is this a peptide bond?
|
No...This looks like one but it is not because there is an extra oxygen in the middle.
|
|
|
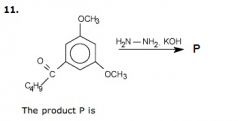
What is the product and what type of reaction is this?
|
Wolff-Kishner reduction of a ketone to an alkene (conversion of -C=) groups into -CH2 groups), often seen following a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction. This takes place in acidic conditions.
|
|
|
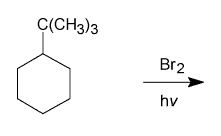
What is the major product?
|

THis is an example of free radical halogenation.
Remember: - UV splits the bromine into two radicals - radical attacks the most substituted hydrogen so that it forms the most stable/conjugated radical (3degree) - The other Br then comes in and is added to the radical |
|
|
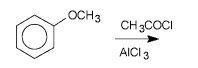
What is the product and what type of reaction is it?
|
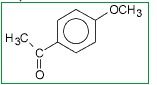
Friedel-Crafts acylation.
The AlCl3 serves as a lewis acid catalyst, and rips of the Cl from the ethanoyl chloride. The ethanone adds to the benzene para to the methoxide group, b/c -OR groups are ortho/para directing. |
|

