![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Of the three filaments, which is the least flexible? |
Microtubules |
|
|
What kind of energy does microtubule (MT) assembly require? |
GTP |
|
|
What does dynamic instability mean? |
The rapid switching between growth and shrinkage shown by microtubules. Occurs primarily at the positive end. Allows MTs to undergo rapid remodeling, and is crucial for their function. |
|
|
What is one of the primary functions of MTs? |
To move cargo through the cell (trafficking). This requires more energy (ATP). |
|
|
What is the MT organizing center? |
The centrosome. MTs radiating out from the centrosome support the plasma membrane. This contributes to the size and shape of the interphase cell. The network created is also what traffics cargo through the cell. |
|
|
Where is the centrosome located when the cell is in interphase? |
Typically close to the nucleus. |
|
|
What is the centrosome constructed of? |
A pair of centrioles surrounded by a matrix of proteins (called the pericentriolar material). This matrix contains hundreds of ring-shaped structures formed from a special tubulin called gamma tubulin. |
|
|
What does each gamma tubulin ring complex serve as? |
The starting point, or nucleation site, for the growth of one MT. The minus end of each MT is embedded here (the centrosome). |
|
|
What is the mitotic spindle? |
Occurs when the cell enters mitosis and MTs disassemble and reassemble into this intricate structure. Provides the machinery that will segregate chromosomes equally into the two daughter cells. |
|
|
What can be seen at the poles in mitotic cells? |
Spindle poles. MTs attached to spindle poles also attach to chromosomes to drive chromosome positioning and segregation during mitosis. |
|
|
What is the basal body? |
An organizing center for MTs that form cilia in ciliated cells. It anchors cilia to the plasma membrane. It also regulated the motion of the cilia. |
|
|
What are cilia? |
Hair like structures covered by plasma membrane. They extend from the surface of many kinds of eukaryotic cells. Each contains a core of stable MTs arranged in a bundle that grow from the basal body. |
|
|
The centrosome does not play a role in what? |
Segregating chromosomes during mitosis. This is the job of spindle fibers and spindle poles. |
|
|
What DOES the centrosome play a role in? |
Supporting large organelles such as the Golgi and Endoplasmic Reticulum, supporting the plasma membrane, and organizing microtubules. |
|
|
Describe the structure of MTs. |
Hollow tubes made up of globular tubulin subunits. This subunit is a heterodimer made up of an alpha tubulin and beta tubulin protein. |
|
|
How do the MT subunits stack together? |
Through noncovalent interactions. |
|
|
What is a protofilament, and how many create the tube structure of MTs? |
They are linear chains of alternating alpha and beta tubulin dimers that form the tube like structure. 13 parallel protofilamentd make up the MT tube structure. |
|
|
True or false: each protofilament has structural polarity, giving the MT a plus and a minus end. |
True |
|
|
What do both alpha and beta tubulin proteins bind to? |
GTP. This is what helps polymerize and depolymerize MTs. The two proteins also bind to each other in head to tail fashion. |
|
|
Describe the growing process of MTs. |
GTP-bound alpha/beta tubulin subunits are fundamental to MT growth. As long as the GTP on the filaments remains unhydrolyzed (creating a GTP cap), the MT will grow. |
|
|
Describe the shrinking process of MTs. |
GTP is hydrolyzed as the filament builds. Eventually, hydrolysis will catch up to the end of the MT, transforming the GTPs in the cap to GDP. This GDP-tubulin end is unstable, leading to disassembly of the MT. When shrinking, the proto protofilaments peel away. |
|
|
What is catastrophe? |
The disassembly of an entire MT caused by GTP hydrolysis to GDP at the end of the MT because GDP-tubulin is unstable. |
|
|
True or false: the + end of an MT is unstable on its own and can't be stabilized. |
False. While it is unstable on its own, other proteins can stabilize it. |
|
|
What are the two typed of protein that regulate MT + end stability? |
1. MAPs (Microtubule associated proteins). Regulate length and stability.
2. TIPs (Microtubule tracking proteins). Mediate end dynamics and attachments |
|
|
What is an example of a MAP protein? |
Tau. Found in neurons. It binds to the side of the MT, but stabilizes the + end. |
|
|
Give an example of a disease caused by improper function of the MAP tau. |
Alzheimers. Tau fails to bind properly to neuron MTs. This causes the tau proteins to aggregate and form neurofibrilary tangles. Contributes to neurodegeneration. |
|
|
True or false: Cargo can only move away from the MT organizing center. |
False. Cargo can move toward or away from the MTOC. |
|
|
What are the two types of MT motor proteins? |
1. Dyneins (move cargo inward toward MT negative end). 2. Kinesins (primarily move cargo outward toward plus end of MT). |
|
|
What are the structures/mechanisms of dyneins and kinesins? |
They are similar in both. They have two head domains, two stalk domains that twist together to form a coiled coil, and two tail domains. The head domains attach to the MT while the tail domains attach to the cargo (vesicles, organelles, other MTs). |
|
|
What kind of energy do motor proteins require? |
ATP hydrolysis. |
|
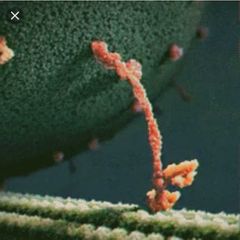
What is this an image of? |
A motor protein "walking" it's cargo along an MT. Think of the head domains as feet. |
|
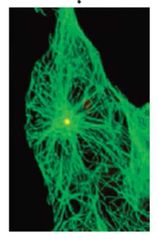
What is this an image of? |
Green = MTs Yellow = Centrosome |
|
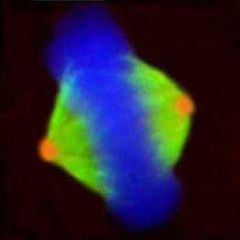
What is this an image of? |
Green = MTs Blue = DNA Orange = Spindle Poles |
|
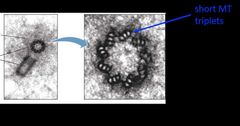
What is this an image of? |
TEM of a centrosome Left: Light gray is the pericentriolar material. Dark gray/black are the centrioles. Right: Hi magnification of short MT triplets in centriole. |
|

What is this an image of? |
A side view and cross section of an MT protofilament. |
|
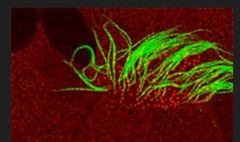
What is this an image of? |
Green = MTs Red = Basal Body |
|
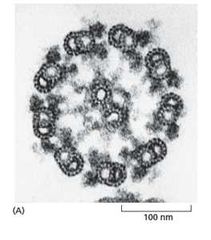
What is this an image of? |
The 9+2 array that MTs form in cilia and flagella. |
|
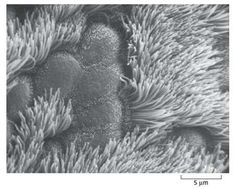
What is this an image of? |
Cilia of a lung cell. |
|
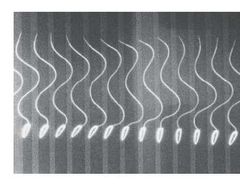
What is this an image of? |
Flagella of sperm cells. |
|
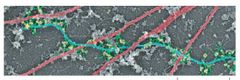
What is this an image of? |
Green: Plectin Cyan: IFs Red: MTs SEM image. |
|
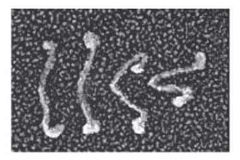
What is this an image of? |
A kinesin motor protein. |
|
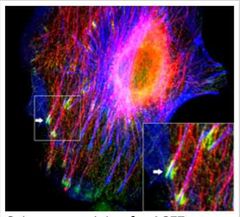
What is this an image of? |
Red: MAPs (MT-associated protein) Green: TIPs (MT tracking protein) |
|
|
What is the standard structure of cilia and flagella? |
9 doublets of MTs surrounding 2 single MTs. Called the 9+2 array. |
|
|
What motions does dynein cause in isolated doublet MTs? In a normal flagella? |
1. The MTs slide passed each other. 2. Linking proteins hold MTs together so they won't slide. Instead they bend. |
|
|
What is the 1⁰ cilium? What cells have it? |
The primary cilium is non-motile and functions in signaling. Most cells lack beating cilia but have this instead. |

