![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Applications of cytopathology
|
Screening - i.e. pap smear, at risk populations (esp asymptomatic)
Dx - nearly any organ for symptomatic cancers Surveillance - i.e. bladder cancer urine cytopathology follow up Rule out cancer (why this is different from diagnosis i have no idea) |
|
|
Cytological Methods
|
Abrasive (brushing)
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)(imaging guidance) - initial smear to assess adequacy then cell block to Dx Exfoliative (look in fluids) *combine w/ FISH! |
|
|
Pap Smear
|
Abrasive sampling of cervix, Diff Quick stain for air dried or EtOH for Pap stain fixing
Residual material used to detect high risk HPV DNA, chlamydia, gonorrhea |
|
|
Morphologic parameters affecting Dx
|
Cell arrangement
Cell size & shape Cytoplasm Nucleus Background |
|
|
Cell Arrangement
|
groups, sheets, clusters
papillary - papillary transitional cell carcinoma, papillary adenocarcinoma, malignant mesothelioma glandular/tubular - adenocarcinoma follicles - follicular adenoma of the thyroid rosettes - retinoblastoma pearls - squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
Cell Size & Shape
|
variable (small, large, giant)(polygonal, round, oval, elongate)
malignant neoplasms tend to vary more than benign neoplasms (some exceptions) |
|
|
Cytoplasmic Features
|
Color, texture, presence of inclusions, vacuoles, pigments, other cell products
pap smear: pink/blue keratin=orange helps identify cell type viral & chlamydial infections form inclusions KOILOCYTOTIC ATYPIA in HPV |
|
|
Nuclear features
|
Size & Shape (variation = malignancy), Chromatin (darker=hyperchromatic=cancer), Inclusions, Nucleolus (larger & numerous = malignancy)
many explanations for multinucleation |
|
|
Extracellular Background
|
Inflammation, microorganisms, cell necrosis, blood, colloid, crystals
|
|
|
Cytology Report
|
Should follow the Bethesda System
should contain: statement regarding adequacy of specimen, general categorization, and an interpretation |
|
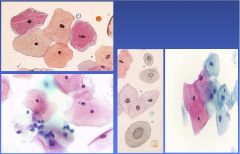
|
Normal Pap Smear
|
|
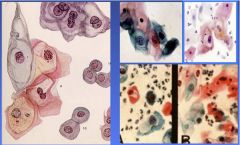
|
Low Grade Intraepithelial Lesion
|
|
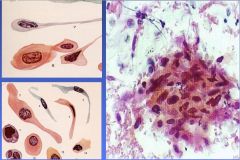
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|

