![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
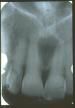
unilocular radiolucency at apex of NON-vital tooth. Most common radiolucency
|
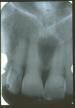
Periapical granuloma
|
|
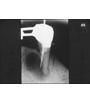
unilocular radiolucency at apex of NON-vital tooth +/- root resorption. Most common jaw cyst and odontogenic cyst (rests of Malassez).
|
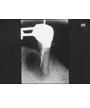
Periapical (radicular) cyst
|
|
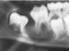
Found on buccal aspect of mandibular 1st molars of VITAL teeth in children displacing the roots lingually
|
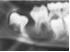
3. Inflammatory Buccal Cyst aka buccal bifurcation cyst
|
|
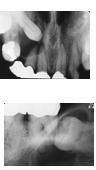
most common developmental odontogenic cyst, second most common odontogenic cyst. Fluid accumulation between REE and follicle unilocular >4mm radiolucency assoc w/ crown impacted tooth (3rds and canines = teens) inc size/bone destruction w/o tx
|
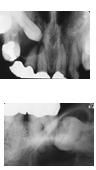
Dentigerous (Follicular) Cyst
|
|
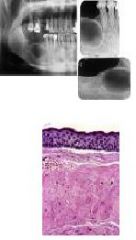
remnants of dental lamina aggressive unilocular (small) or multilocular (large) smooth/cloudy (keratin) radiolucency. Causes tooth displacement > resorption, found in jaw esp. post mandible associated with impacted/ erupted teeth or by itself. Comprise 10% of odontogenic cysts
|
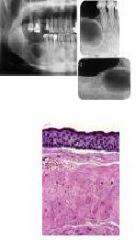
Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC) aka Primordial Cyst
|
|

mutation of Patched gene Major criteria: multiple odontogenic keratocysts (2nd decade), multiple basal cell carcinomas (3rd decade), calcified falx cerebri (by age 20) and palmar/plantar pits. Minor criteria: macrocephaly, bifid rib
|

Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
|
|
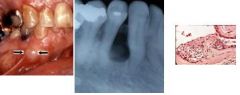
rests of Serres asymptomatic, non-inflammatory, round-tear drop shaped, unilocular, radiolucency in bone adjacent to root of a VITAL tooth.
|
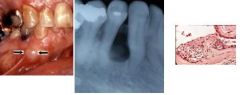
Lateral periodontal cyst
|
|
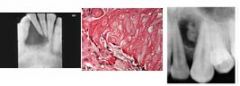
rests of Serres uni/multilocular, +/- scattered radiopacities with well defined margins commonly found intra-osseous of anterior jaws.
adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, odontoma, calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor, ameloblastic fibroodontoma diff dx = |
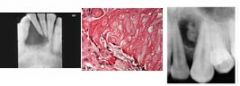
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst
|
|
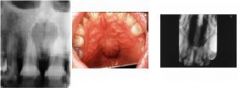
epithelial remnants form fusion of palate w/in nasopalatine canal asymptomatic, well-defined heart shaped radiolucency between max CI’s +/- root divergence.
|
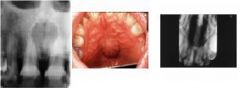
Nasopalatine duct cyst, aka incisive canal cyst
(1) variant: cyst of palatine papilla: solft tissue only (2) variant: median palatal cyst: posterior presentation |
|
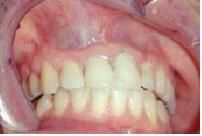
cystic change of epithelial rests extra osseous soft tissue cyst commonly found on the canine-mucobuccal fold (upper lip).
|
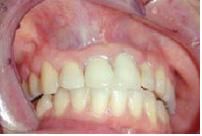
Nasolabial cyst; Tx: curettage
|
|
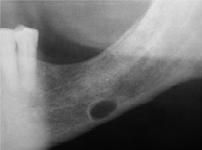
indentation of lingual surface of posterior mandible below IAN by normal salivary gland tissue. Common (males), How do you treat?
|
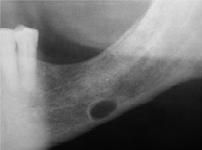
NO Tx
Lingual Mandibular salivary gland depression aka Stafne bone cyst, static bone cyst |
|
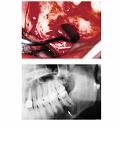
trauma (post mandible of teenage males) interradicular scalloping, empty intrabony cavity lacking epithelial lining, Also, Is this a true cyst?
|
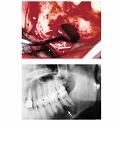
Solitary Bone Cyst aka Traumatic (Simple) Bone Cyst. NOT a true cyst (aka pseudocyst)
|
|

rare, destructive, well defined, rapid expansile lesion often associated with antecedent bone lesion of posterior jaws. 50% painful. Histo: similar to CGCG w/ sinusoidal blood spaces. Is this a true cyst?
|

Aneurysmal Bone Cyst; Not a true cyst (pseudocyst)
|
|
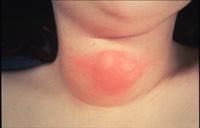
epithelial remnants; midline swelling (most below hyoid); MOST COMMON developmental cyst of the neck.
|
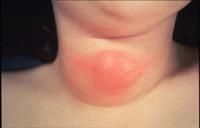
Thyroglossal Tract (Duct) Cyst
|
|
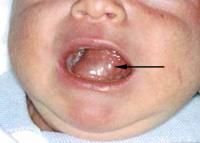
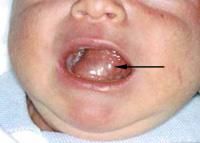
developmental cyst of anterior floor of mouth above(displaces tongue)/below(midline swelling) the mylohyoid. Histo: epithelial lining + CT wall contains skin appendages
|
Dermoid Cyst
|
|
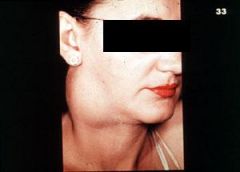
proliferation of epithelial islands in cervical lymph nodes; asymptomatic enlargement of lateral neck, teens-20’s. Histo: epithelial lined cyst + lymphoid tissue in wall.
|
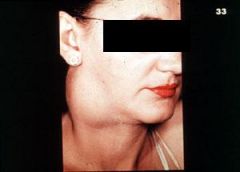
Branchial Cleft Cyst aka Cervical Lymphoepithelial Cyst
|
|
|
What do PA granuloma, PA Cyst and Inflammatory buccal cyst have in common?
|
They are all inflammatory odontogenic cysts
|
|
|
Dentigerous cysts, odontogenic keratocysts, lateral periodontal cysts, calcifying odontogenic cysts, and glandular odontogenic cysts are all what group of cysts?
|
Developmental odontogenic cysts
|
|
|
Name the 2 developmental Non-odontogenic cysts
|
Nasoplatine duct cyst; nasolabial cyst
|
|
|
Static Bone cyst, Focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect, traumatic bone cyst, and aneurysmal bone cyst are all what type of cyst?
|
Pseudocyst
|
|
|
What do the following have in common: thyroglossal tract cyst, dermoid cyst, branchial cleft cyst
|
soft tissue cysts of the neck
|
|
|
What is the fancy name for remnants of the dental lamina?
|
rests of serres
|
|
|
What is the fancy name for remnants of Hertwig's root sheath?
|
Rests of Malassez
|
|
|
T or F: Most developmental odontogenic cysts are derived from epithelial remnants of the rests of Malassez.
|
False; from the rests of serres
|
|
|
T or F: Periapical cysts are derived from rests of serres.
|
False; generally from rests of malassez
|
|
|
T or F: Dentigerous cysts are derived from the reduced enamel epithelium
|
true
|
|
|
What are the rests called associated with reduced enamel epithelium?
|
enamel organ rests
|
|
|
What is the difference between a cyst and a pseudocyst?
|
Pseudocyst has no epithelial lining
|

