![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
All of the cysts are odontogenic except this one, what is it, and what is it classified as?
|
the nasopalatine duct cyst; nonodontogenic (also there is a cyst-like lesion called a simple bone cyst)
|
|
|
characteristics of an odontogenic keratocyst
|
non-inflammatory, arises from dental lamina, has benign tumor growth potential, epithelial lining is keratinized, contains a viscous/cheesy material (keratin) derived from the epithelium
|
|
|
DD for lateral periodontal cyst?
|
small OKC, mental forament, radicular cyst at accessory pulp canal
|
|
|
DD for odontogenic keratocyst?
|
simulates other RL lesions like dentigerous cyst and other multilocular lesions
|
|
|
DD for SBC:
|
cysts, especially OKC
|
|
|
Define "residual cyst"
|
a cyst that remains after incomplete removale of the original cyst
|
|
|
Effects on surrounding tissues of nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
Divergence of roots of CI, occasional root resorption, expansion and displacement
|
|
|
how do you manage a nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
enucleate from palatal side to aviod the nasopalatine nerve
|
|
|
how do you manage an SBC?
|
conservative opening into the lesion and curattage; this initiateds bleeding and subsequent healing.
|
|
|
Radiographic features of a nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
NP canal or foramen; anterior between CI's; divergence of roots may be caused; expands posteriorly to the hard palate; corticated; RL interior
|
|
|
Radiographic features of SBC?
|
almost all occur in mandible; often in ramus or posterior; well defined to ill-defined that blends into surrounding bone; shape is smooth and curved like a cyst with a oval or scalloped border; RL interior, may appear multilocular
|
|
|
T/F the dentigerous cyst never gets very large
|
False, it has the potential to grow very large if left untreated
|
|
|
T/F the dentigerous cyst can be eccentric and develop from lateral aspects of the follicle, instead of above the crown
|
True
|
|
|
t/f the odontogenic keratocyst grows along the internal aspect of the jaws with maximal expansion, which usually occurs in ramus area
|
false; minimal expansion...may cause perforation of the cortex and can displace/resorb structures
|
|
|
what are some characterisics of the SBC?
|
A cavity within bone that is line by CT; no epithelial lining; not a true cyst; may be empty or fluid filled; etiology is unknown: may be localized aberration in normal bone remodeling or metabolism
|
|
|
what are some characteristic of an eruption cyst?
|
odontogenic, with histological features of a dentigerous cyst that surrounds a tooth that has erupted through bone, but not soft tissue.
|
|
|
what are some clinical features of the SBC?
|
relatively common; 2nd decade; male predominance; asymptomatic (discovered by chance on radiograph); occassional pain/discomfort; expanision of jaws and tooth displacement; teeth are vital; multiple SBC's my develop in cemento-osseous dysplasia
|
|
|
what are some synonyms for the simple bone cyst (SBC)
|
traumatic bone cyst; hemorrhagic bone cyst; solitary bone cyst
|
|
|
what are the characterisics of a dentigerous or follicular cyst?
|
forms around the crown of an unerupted tooth; fluid accumulation b/w crown and epithelium; eruption cyst is soft tissue counterpart or variant of the dentigerous cyst that occurs close to the alveolar crest
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of a lateral periodontal cyst?
|
Arise from epithelial rests in peridontium lateral to the root; unicystic/unilocular; Asymptomatic, less than 1cm in diameter; no sexual predilection, wide age distribultion (2-9th decades), may become lateral PD abscess
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin-Golz Syndrome)?
|
Appears early in life b/w ages of 5 and 30; skin abnormalities; skeletal abnormalities (bifid ribs); CNS abnormalities (calclification of falx cerebri); multiple cystic lesions of the jaw
|
|
|
what are the clinical features of a dentigerous cyst?
|
2nd most common cyst around the crown of an unerupted tooth; occurs in 1st-2nd decade; missing tooth; slow-growing; hard swelling, facial asymmetry; typically no pain
|
|
|
what are the clinical features of a nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
4-6th decade; 3X greater occurance in males; asymptomatic; small, well-defined, fluctuant swelling posterior to palatine papilla, can expand= salty fluid; burning sensation may be reported due to pressure on adjacent nasopalatine nerves
|
|
|
what are the clinical features of a residual cyst?
|
Asymptomatic; often discovered in an edentulous region; may show expansion; may be associated with pain in case of secondary infection
|
|
|
what are the clinical features of an odontogenic keratocyst?
|
1/10 of all jaw cysts; 2nd and 3rd decade with male predomination (3:2); may or may no arise from an unerupted tooth; no symptoms to mild swelling; pain with 2' infection; high recurrance due to satelline cysts of fragements left behind
|
|
|
what are the effectos on surrounding tissue with an SBC?
|
no effects in most cases; often lesion involves all the bone around the roots, but leaves the LD intact; minimum expansion along the axis of the bone
|
|
|
what are the most commonly effected teeth for a dentigerous cyst?
|
3rd Molars and Maxillary Canines
|
|
|
what are the radiographic features of a dentigerous cyst?
|
Pericoronal; well-defined cortex with a curved or circular outline; RL interior; attaches at CEJ; can displace and resorb adjacent teeth; can expand outer cortical boundry of the involved jaw
|
|
|
what are the radiographic features of a lateral periodontal cyst?
|
75% develop in the mandible, mostly extedning from CI to 2PM, corticated, round/oval; RL; may effect LD of adjacent tooth or displacement of adjacent teeth
|
|
|
What are the radiographic features of a residual cyst?
|
Occurs in both arches; slightly more often in the mandible; epicenter is located in PA region, in mandible, above the IAC; oval or round; of variable size; periphery may be corticated
|
|
|
what are the radiographic features of an odontogenic keratocyst?
|
common is posterior mandible; 90% occur posterior to canines, and 50% occur in ramus; epicenter is above the IAC; corticated, resembles other cysts; RL interior, uni or multilocular with curved septa
|
|
|
what are the synonyms of a nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
NP canal cyst, incisive canal cyst, median palatine cyst
|
|
|
what characteristic effects does a residual cyst have on surrounding tissues?
|
may cause tooth displacement or resorption; expansion or displacement of structres.
|
|
|
what characteristic internal structure does a residual cyst have?
|
RL; may have dystrophic calcifications in long standing cases
|
|
|
what is a good DD for a dentigerous cyst?
|
Hyperplastic follicle if less than 5mm in diameter; odontogenic keratocyst
|
|
|
what is reported to arise from the cyst lining of a dent. cyst?
|
squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
what is the eruption cyst clinically visible as?
|
a soft fluctuant mass on the alveolar ridges; blue to dark red due to blood in the cystic fluid.
|
|
|
what is the normal tx for a dentigerous cyst?
|
surgical removal; enucleantion and removal of tooth if indicated. Needle aspiration may reveal straw-colored fluid, takes 3-12 months to resolve
|
|
|
what is the typical DD for a nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
large incisive formen (if less than 6mm), or a redicular cyst
|
|
|
what is the typical management for a LPC?
|
excisional biopsy or enucleation; do not tent to recur
|
|
|
what is the typical management of an odontogenic keratocyst?
|
accurate determination of borders using advanced imaging, surgical resection, curettage or marsupialization to reduce size before excision, periodic post tx and radiographic exam, recurrance is usually within 5 yrs.
|
|
|
what is the usual cause of a Nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
cystic degeneration of epithelial remnants
|
|
|
what is the usual tx for a residual cyst?
|
excision and histopathological exam; should be followed radiographically for recurrance; recurrance rate is low.
|
|
|
what is this?
|
Residual cyst (above the IAC, which is what the arrow is pointing to)
|
|
|
what type of lesion is this?
|
A residual cyst (mandibular arch)
|
|
|
where is the eruption cyst most common?
|
molars and canines
|
|
|
Dentigerous cyst
|
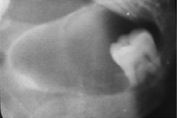
Identify
|
|
|
SBC
|

Identify
|
|
|
SBC
|

Identify
|
|
|
SBC
|

Identify
|
|
|
nasopalatine duct cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
nasopalatine duct cyst
|
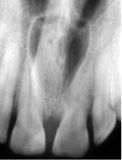
Identify
|
|
|
nasopalatine duct cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
nasopalatine duct cyst
|
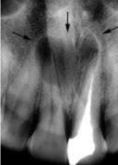
Identify
|
|
|
residual cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
residual cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
nasopalatine duct cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
dentigerous cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
odontogenic keratocyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
odontogenic keratocyst
|
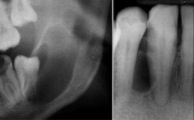
Identify
|
|
|
lateral periodontal cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
lateral periodontal cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
basal cell nevus 2' characteristics
|
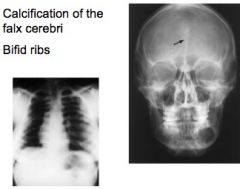
Identify
|
|
|
eruption cyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
characteristics of basal cell nevus syndrome
|

Identify
|
|
|
odontogenic keratocyst
|

Identify
|
|
|
dentigerous cyst
|

Identify
|

