![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
central nervous system
|
the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
peripheral nervous system
|
cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and autonomic nerves
|
|
|
neuron
|
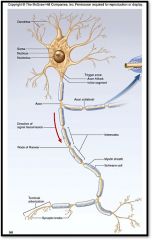
structural unit of nervous system
Highly specialized to transmit messages (nerve impulses). Made up of: - cell body - dendrites: receptive regions - axons: nerve impulse generators and transmitters |
|
|
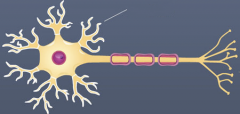
axons
|
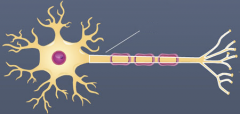
nerve impulse generators and transmitters
conducts electrical impulses AWAY from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands |
|
|
dendrites
|
receptive region of the neuron; sensing, or listening part of the neuron
branching neuron process that serves as a receptive, or input, region; transmits an electrical signal TOWARD the cell body. |
|
|
bipolar, interneuron
|
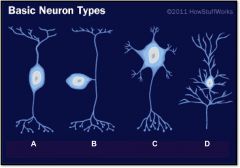
Neuron Histology:
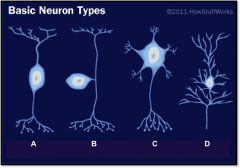
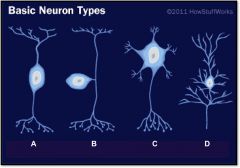
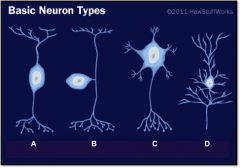
What is neuron type A? |
|
|
unipolar, sensory neuron
|
Neuron Histology:
What is neuron type B? |
|
|
multipolar, motoneuron
|
Neuron Histology:
What is neuron type C? |
|
|
pyrimidal cell
|
Neuron Histology:
What is neuron type D? |
|
|
white matter
|
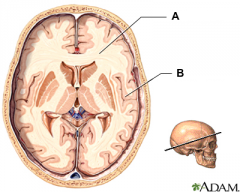
(identify object A)
a nervous system tissue; the paler tissue of the brain and spinal cord, consisting mainly of nerve fibers with their myelin sheaths |
|
|
gray matter
|
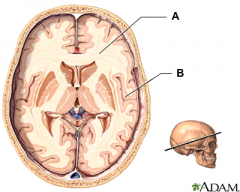
(identify object B)
a nervous system tissue; the darker tissue of the brain and spinal cord, consisting mainly of nerve cell bodies and branching dendrites |
|
|
meninges
|
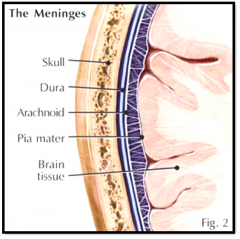
a series of enveloping membranes surrounding the central nervous system; include the dura mater, pia mater, and arachnoid
|
|
|
dura mater
|
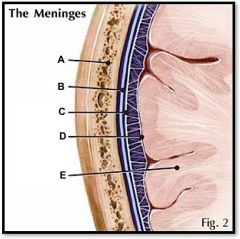
(identify B)
tough outer layer of the meninges |
|
|
pia mater
|
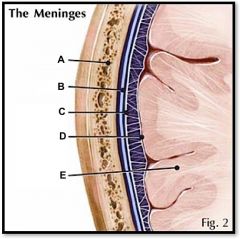
(identify D)
delicate, inner vascularized meninges |
|
|
arachnoid
|
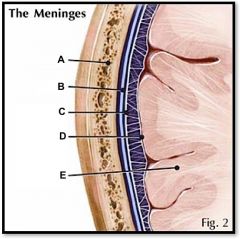
(identify C)
a cobwebby layer that separates the dura and pia mater |
|
|
sense organs
|
olfaction, vomeronasal organ, gustation, lateral line system, equilibrium and audition, vision
|
|
|
olfactory bulb
|
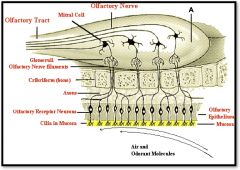
(identify A)
detecting chemicals and odors in the environment (aquatic or terrestrial) through moist olfactory epithelia, a brain structure located above the nasal cavity beneath the frontal lobes, gathers messages from the smell neurons and transmits them to the brain |
|
|
vomeronasal, Jacobson's organ
|
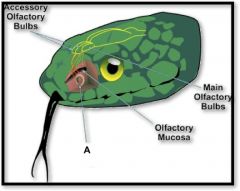
(identify A)
a chemoreceptor separate from olfaction that is used to follow food trails and find potential mates through phermones |
|
|
gustation
|
tastebuds; usually confined to the mouth and pharynx but can cover the entire body in fish
|
|
|
lateral line system
|
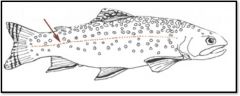
receptors which detect movement, water currents, pressure changes, etc,
A mechanoreceptor system consisting of a series of pores and receptor units (neuromasts) along the sides of the body of fishes and aquatic amphibians; detects water movements made by an animal itself and by other moving objects |
|
|
skull
|
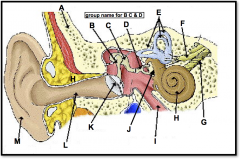
identify A
|
|
|
malleus, incus, stapes
|
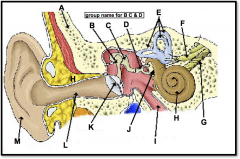
(identify B, C, and D)
bones of the middle ear auditory ossicles |
|
|
auditory ossicles
|
What is the grouping term for the malleus, incus, and stapes?
|
|
|
semicircular canals
|
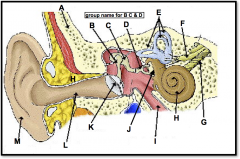
(identify E)
3 fluid-filled canals in the inner ear attached to the cochlea; responsible for our sense of balance; detect movement and gravity. contain specialized receptor cells that generate nerve impulses with body movement |
|
|
vestibular nerve
|
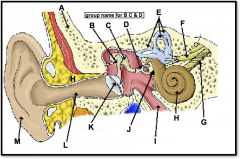
(identify F)
nerve that conducts impulses related to maintaining balance to the brain |
|
|
cochlear nerve
|
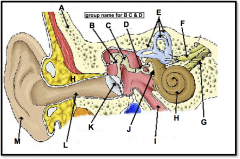
(identify G)
branch of the auditory nerve responsible for transmitting auditory info from the cochlea to the brain |
|
|
ear
|
used for equilibrium and audition; the inner apparatus of vertabrates
|
|
|
cochlea
|
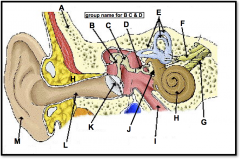
(identify H)
A coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses |
|
|
eustachian tube
|
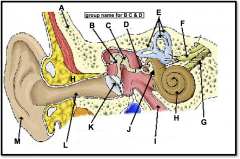
(identify I)
A narrow tube between the middle ear and the throat that serves to equalize pressure on both sides of the eardrum |
|
|
round window
|
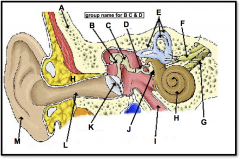
(located on the cochlea, to the left of H)
a membrane-covered opening in the inner wall of the middle ear that compensates for changes in cochlear pressure. releases the pressure |
|
|
oval window
|
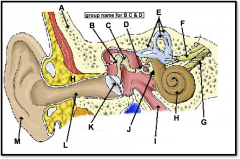
(identify J)
Opening in bone structure surrounding cochlea; stapes presses against membrane behind it to transmit sound into cochlear fluid. |
|
|
eardrum
|
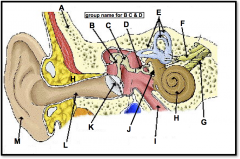
(identify K)
tightly stretched membrane located at the end of the ear canal that vibrates when struck by sound waves; tympanic membrane |
|
|
ear canal
|
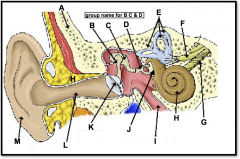
(identify L)
a narrow region leading from the outside of the human ear to the eardrum; funnels sound waves towards ear drum |
|
|
pinna (outer ear)
|
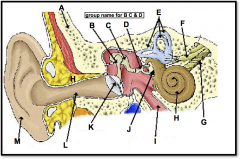
(identify M)
flexible outer flap of the ear, which channels sound waves into the ear cannal |
|
|
vision
|
with the exception of animals that have secondarily lost their vision (burrowing or cave-dwelling species) all vertebrates have bilateral, image-forming eyes
|
|
|
sclera
|
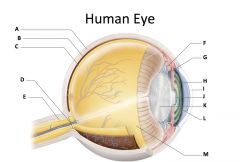
(identify A)
dense fibrous, protective, opaque outer coat enclosing the eyeball except the part covered by the cornea; containing collagen and elastic fibers; known as the white or white of the eye |
|
|
choroid
|
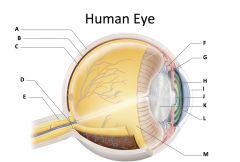
(identify B)
A highly vascular membrane in the eye between the retina and the sclera in the uveal tract. Provides nourishment to the retina |
|
|
retina
|
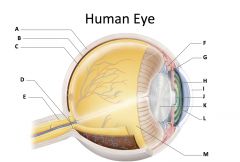
(identify C)
Light sensitive layer of the eye; contains rods and cones |
|
|
optic disc (blind spot)
|
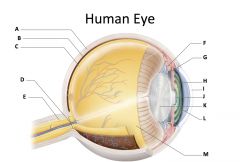
(identify D)
site where optic nerve leaves the eye and lacks photoreceptors |
|
|
optic nerve
|
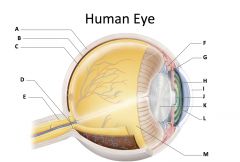
(identify E)
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain |
|
|
cilliary body
|
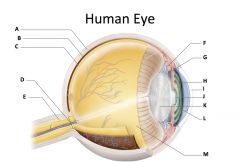
(identify F)
Contains a ring of muscles that surround the lens and control its shape |
|
|
suspensory ligament
|
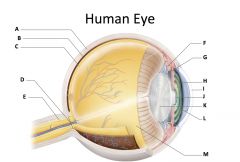
(identify G)
Attaches the lens to the ciliary body and hold it in place. |
|
|
iris
|
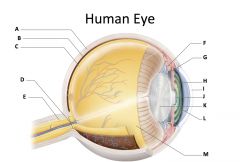
(identify H)
A ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening. |
|
|
cornea
|
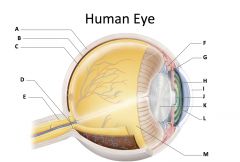
(identify I)
Contained in the sclera. It is transparent to allow light rays to pass into the eye. It has a curved surface that allows it to bend the entering light waves to focus them on the surface of the retina. |
|
|
pupil
|
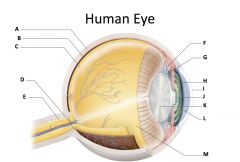
(identify J)
Behind the cornea; Opening in the center of the iris that permits light to pass into the rear chamber of the eye; Is adjusted to control the amount of light that enters the eye |
|
|
lens
|
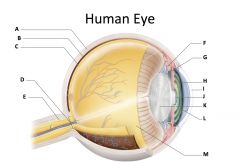
(identify K)
Behind the pupil; focuses the incoming rays into an image on the eyes light sensitive back surface |
|
|
aqueous humor
|
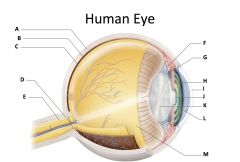
(identify L)
A clear, watery fluid that fills the space between the cornea and iris. |
|
|
vitreous humor
|
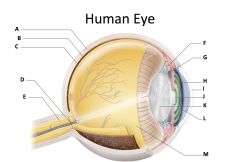
(identify M)
jellylike substance found behind the lens in the posterior cavity of the eye that maintains its shape |
|
|
cerebrum
|
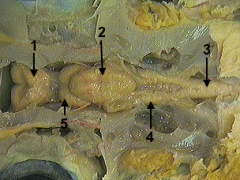
identify 1 on the dogfish
|
|
|
cerebellum
|
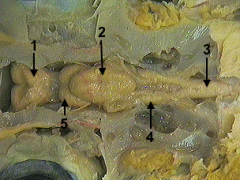
identify 2 on the dogfish
|
|
|
spinal cord
|
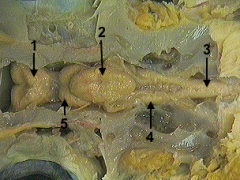
identify 3 on the dogfish
|
|
|
medulla
|
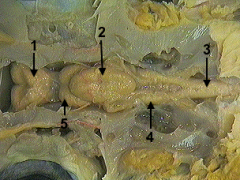
identify 4 on the dogfish
|
|
|
optic lobe
|
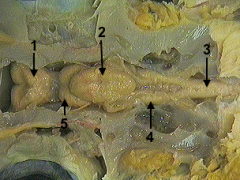
identify 5 on the dogfish
|
|
|
nostrils
|
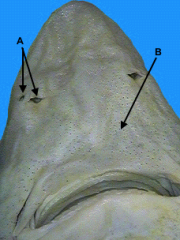
identify A on the dogfish
|
|
|
ampullae of lorenzini
|
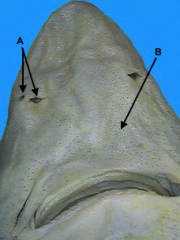
(identify B) on the dogfish
nerve receptors found in a shark's snout which sense the electric fields generated by the muscles of fish and other potential prey. |
|
|
pupil, cornea, sclera
|
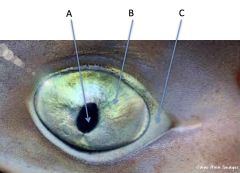
identify A, B, and C on the dogfish
|
|
|
right cerebral hemisphere
|
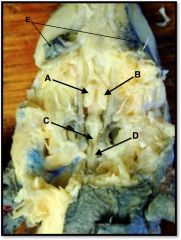
identify A on the mudpuppy
|
|
|
left cerebral hemisphere
|
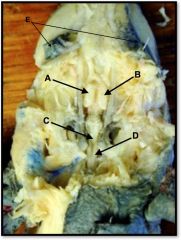
identify B on the mudpuppy
|
|
|
cerebellum and medulla oblongata
|
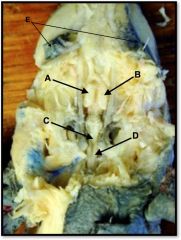
identify C on the mudpuppy
|
|
|
spinal cord
|
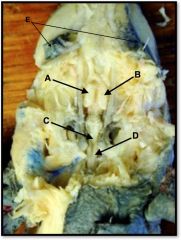
identify D on the mudpuppy
|
|
|
eyes
|
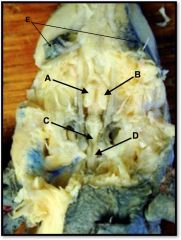
identify E on the mudpuppy
|
|
|
cerebral hemisphere
|
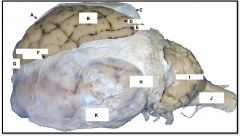
identify A on the mammal brain
|
|
|
parietal lobe
|
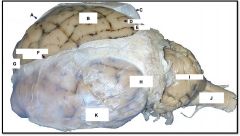
identify B on the mammal brain
|
|
|
gyrus
|
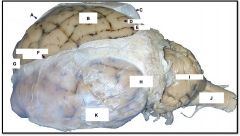
identify D on the mammal brain
|
|
|
sulcus
|
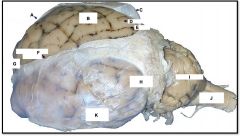
identify E on the mammal brain
|
|
|
dura and arachnoid matter
|
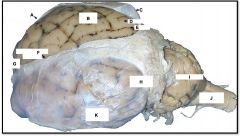
identify C on the mammal brain
|
|
|
temporal lobe
|
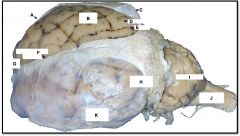
identify K on the mammal brain
|
|
|
occipital lobe
|
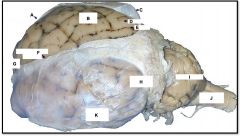
identify H on the mammal brain
|
|
|
cerebellum
|
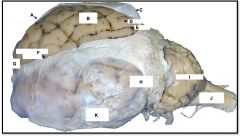
identify I on the mammal brain
|
|
|
medulla oblongata
|
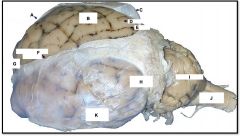
identify J on the mammal brain
|
|
|
frontal lobe
|
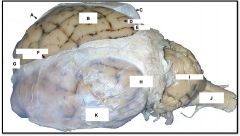
identify G on the mammal brain
|
|
|
longitudinal fissure
|
identify F on the mammal brain
|
|
|
spinal cord
|
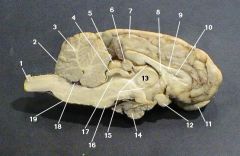
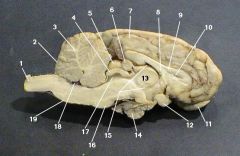
identify 1 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
cerebellum
|
identify 2 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
arbor vitae
|
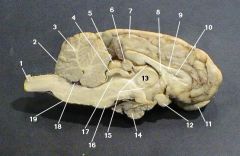
identify 3 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
inferior colliculus
|
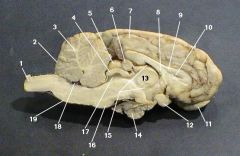
identify 4 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
superior colliculus
|
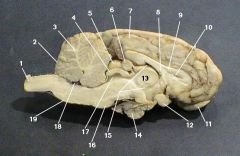
identify 5 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
pineal gland
|
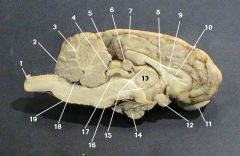
identify 6 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
cerebrum
|
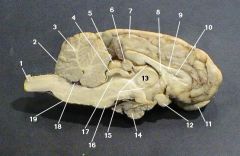
identify 7 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
corpus callosum
|
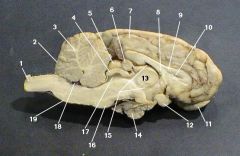
identify 9 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
olfactory bulb
|
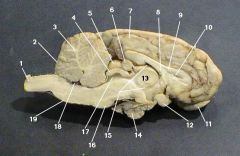
identify 11 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
optic chiasm
|
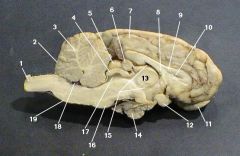
identify 12 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
thalamus
|
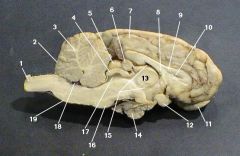
identify 13 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
pituitary gland
|
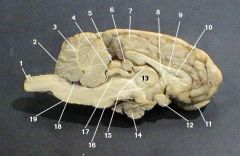
identify 14 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
pons
|
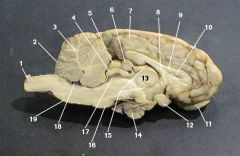
identify 16 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
medulla oblongata
|
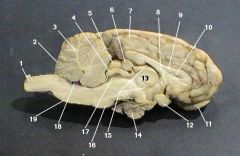
identify 19 on the mammal brain
|
|
|
endocrine system
|
glands that secrete hormones that act as regulatory chemicals and control cellular activities
known collectively as a system but in many cases they do not physically contact one another |
|
|
pituitary gland
|
located at the base of the brain; controls other endocrine glands and influences growth, metabolism, and maturation
|
|
|
pineal gland
|
located on diencephalon; secretes melatonin
|
|
|
adrenal gland
|
located near the kidneys; secrete many hormones including cortisol
|
|
|
thymus
|
in the neck; produces T-cells
|
|
|
thyroid
|
located in the neck; regulates growth and development through metabolism
|
|
|
pancreas (endocrine function)
|
produces glucagon and insulin
|
|
|
ovaries and testes (endocrine function)
|
produce estrogen and testosterone
|
|
|
placenta (endocrine function)
|
produces hormones that aid in gestation and health of fetus and birth
|

