![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
circulatory system
|
Responsible for the transportation, distribution, and circulation of substances such as nutrients, gasses, hormones, and metabolites.
|
|
|
blood
|
A connective tissue with a fluid matrix called plasma in which red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and cell fragments called platelets are suspended.
|
|
|
plasma
|
the fluid part of blood that contains nutrients, glucose, proteins, minerals, enzymes, and other substances
|
|
|
erythrocytes
|
red blood cells that are anucleated in mammals and nucleated in other vertebrates that carry oxygen and carbon dioxide away from tissue
|
|
|
leukocytes
|
white blood cells that aid in fighting disease
5 types: 1) neutrophil 2) eosinophil 3) basophil 4) lymphocyte |
|
|
erythrocytes (slide 1)
|
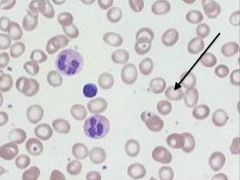
|
|
|
erythrocytes (slide 2)
|
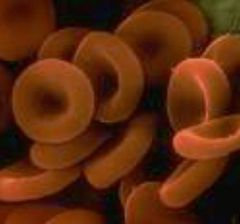
|
|
|
erythrocytes (slide 3)
|
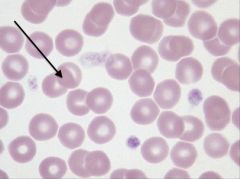
|
|
|
neutrophil
|
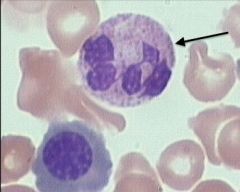
40-70% of WBC, 3-7 lobe nucleus, pale lilac cytoplasm with fine granules
|
|
|
eosinophil
|
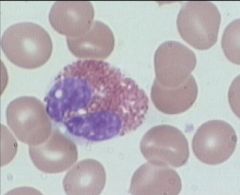
2-4% of WBC, Figure 8 or bilobed nucleus, large cytoplasmic granules
|
|
|
basophil
|
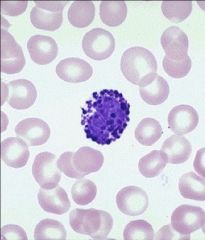
<1% of WBC, Large U or S shape nucleus with indentations, granules are coarse and stained a deep purple
|
|
|
lymphocyte
|
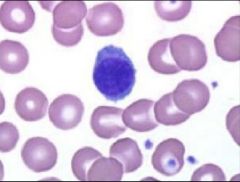
Smallest WBC, Nucleus is stained dark blue/purple and spherical; accounts for most of the cell mass
|
|
|
monocytes
|
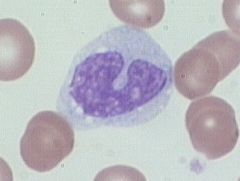
Largest of WBC, makes 3-8% of WBC, Dark blue nucleus, kidney shaped, cytoplasm stained gray-blue
|
|
|
the heart
|
Primary organ of the circulatory system, located in the pericardial cavity.
amphibians have a 3-chambered heart mammals have a 4-chambered heart |
|
|
arteries
|
tubes that carry usually oxygenated blood from the heart to all parts of the body
|
|
|
veins
|
tubes that carry usually oxygen-depleted blood from the body back to the heart
|
|
|
capillaries
|
fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the veins and arteries
|
|
|
lymphatic system
|
Because the exchange of fluids between tissues and capillaries are not 100% efficient, vertebrates have evolved the lymphatic system to return fluids back into the circulatory system.
This fluid is called Lymph and is filtered through lymph nodes, lymph glands, and tonsils before being dumped into veins |
|
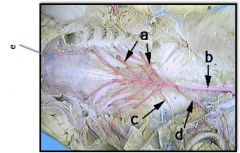
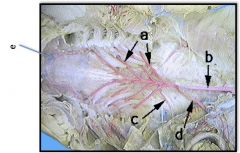
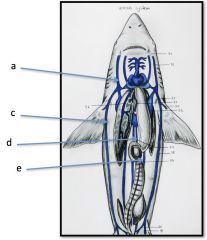
a) Efferent Branchial Arteries
b) Dorsal Aorta d) Subclavian Artery e) Carotid Artery |
Dogfish Arteries
|
|
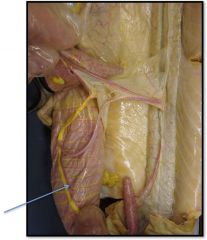
interstitial artery
|
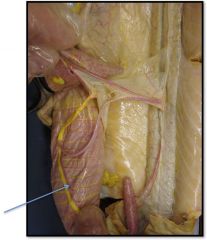
dogfish artery
|
|
a) Subclavian Vein
c) Abdominal Vein d) Cardinal Vein e) Intestinal Vein |
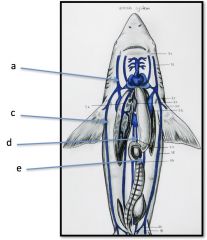
Dogfish Veins
|
|
|
Dogfish Lymphatic System
|
The lymphatic system is thought to be absent in the chondrichthyes. There are, however, a number of sinuses that drain fluids into the veins similar to the lymphatic system in other vertebrates.
|
|
|
Mudpuppy Heart
|
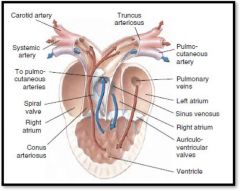
Amphibians have a 3 chambered heart that consists of:
1 Ventricle, Left Atrium, Right Atrium, and Conus Arteriosus |
|
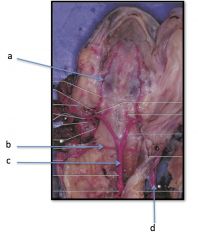
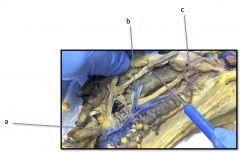
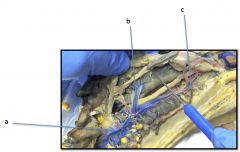
a) Carotid Artery
b) Subclavian Artery c) Dorsal Aorta d) Pulmonary Artery |
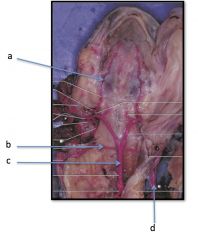
Mudpuppy Arteries
|
|
a) Vena Cava
b) Hepatic Portal Vein c) Pulmonary Vein |
Mudpuppy Veins
|
|

a) Abdominal Vein
|

Mudpuppy Veins
|
|
|
Mudpuppy Lymphatic System
|
Amphibians possess a well developed lymphatic system in subcutaneous tissue but it is not possible to dissect it out
|
|
|
Cat Heart
|
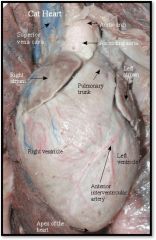
Typical mammalian heart with 2 ventricles and 2 atria.
|
|
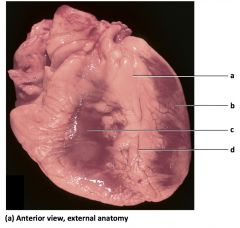
a) fat in interventricular
sulcus b) left ventricle c) right ventricle d) anterior interventricular artery |
Mammalian Heart
|
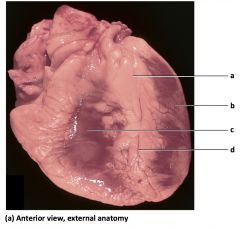
|
a) left atrium
b) left ventricle c) right atrium d) right ventricle |
Mammalian Heart
|
|
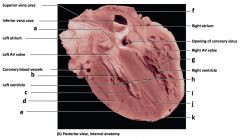
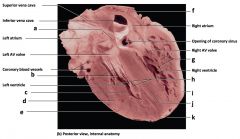
a) superior vena cava
b) inferior vena cava c) left AV valve d) coronary blood vessels e) opening of coronary sinus f) right AV valve |
Mammalian Heart
|
|
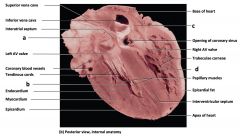
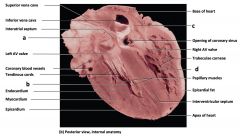
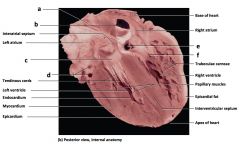
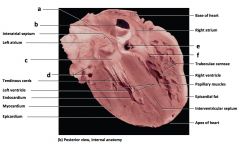
Mammalian Heart
a) interatrial septum b) tendinous cords c) endocardium d) myocardium e) epicardium f) base of heart g) trabeculaeg carneae h) papillary muscles i) epicardial fat j) interventricular septum k) apex of heart |
Mammalian Heart
|
|
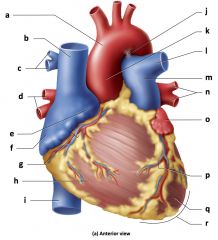
a) Aortic arch
b) Superior vena cava c) Branches of the right pulmonary artery d) Right pulmonary veins e) Right auricle f) Right atrium g) Coronary sulcus h) Right ventricle i) Inferior vena cava j) Ligamentum arteriosum k) Ascending aorta l) Left pulmonary artery m) Pulmonary trunk n) Left pulmonary veins o) Left auricle p) Anterior interventricular sulcus q) Left ventricle r) Apex of heart |
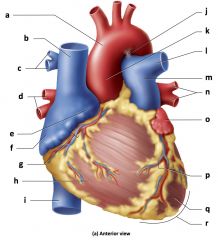
Mammalian Heart
|
|
a) aorta
b) left pulmonary artery c) left pulmonary veins d) left atrium e) coronary sulcus f) coronary sinus g) fat h) left ventricle i) apex of heart j) superior vena cava k) right pulmonary artery l) right pulmonary veins m) right atrium n) inferior vena cava o) posterior interventricular sulcus p) right ventricle |
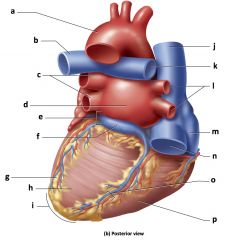
Mammalian Heart
|
|
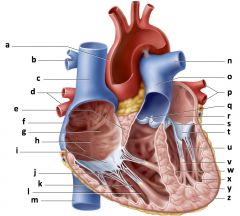
a) aorta
b) right pulmonary artery c) superior vena cava d) right pulmonary veins e) interatrial septum f) right atrium g) fossa ovalis h) pectinate muscles i) right AV (tricuspid) valve j) tendinous cords k) trabeculae carneae l) right ventricle m) inferior vena cava n) left pulmonary artery o) pulmonary trunk p) left pulmonary veins q) pulmonary valve r) left atrium s) aortic valve t) left AV (bicuspid) valve u) left ventricle v) papillary muscle w) interventricular septum x) endocardium y) myocardium z) epicardium |
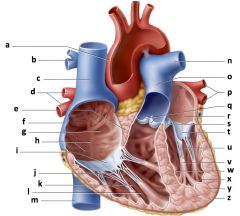
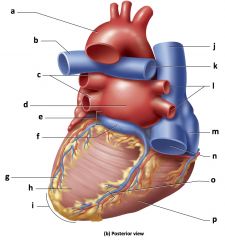
Mammalian Heart
|
|
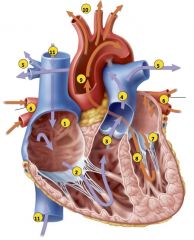
1) Blood enters right atrium from superior
and inferior venae cavae. 2) Blood in right atrium flows through right AV valve into right ventricle. 3) Contraction of right ventricle forces pulmonary valve open. 4) Blood flows through pulmonary valve into pulmonary trunk. 5) Blood is distributed by right and left pulmonary arteries to the lungs, where it unloads CO2 and loads O2. 6) Blood returns from lungs via pulmonary veins to left atrium. 7) Blood in left atrium flows through left AV |
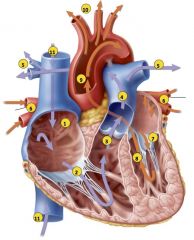
What is the path of blood flow through the heart?
|
|
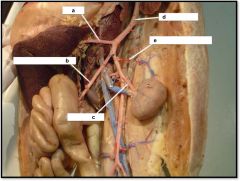
a) celiac
b) superior mesenteric c) renal artery d) dorsal aorta e) adrenolumbar artery |
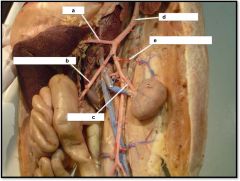
Cat Middle Arteries
|
|
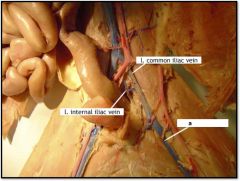
a) l. femoral vein
|
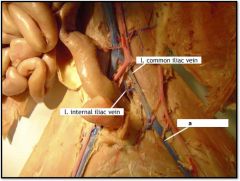
Cat Lower Veins
|
|
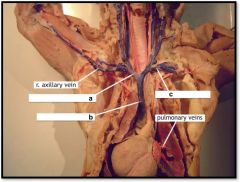
a) r. brachiocephalic brain
b) superior vena cava c) l. subclavian vein |
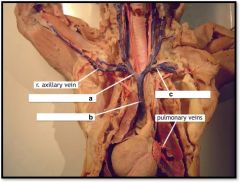
Cat Upper Veins
|
|
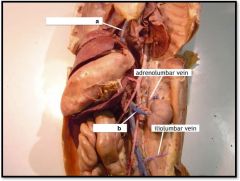
a) inferior vena cava
b) renal vein |
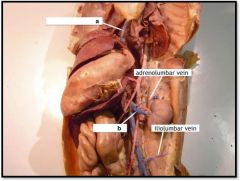
Cat Middle Veins
|
|
|
dogfish aka condrichthyes
|
Which vertebrate classes do not lymphatic systems?
|
|
|
amphibians, mammals, aves
|
Which vertebrate classes do not have lymphatic systems?
|

