![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sepsis
|
SIRS due to infection
|
|
|
SIRS- systemic inflammatory response syndrome
|
2 or more of the following:
-Temp >38 C, <36 C -HR >90 -Resp >20/min or PaCO2<32 mmHg -WBC >12,000 cells/m3, or <4000cells/ml, or >10%band PMN |
|
|
Sepsis Syndrome
|
Sepsis + evidence hypoperfusion/organ dysfnx + one of the following:
-mottled skin -hypoxemia -elevated lactate -oliguria -mental status change (abrupt) -abnormal EEG -low platelets -DIC -acute lung injury -cardiac dysfnx |
|
|
Septic Shock
|
Sepsis Syndrome + hypotension despite fluid resuscitation which may require vasopressors
|
|
|
Bacteremia
|
viable bacteria in blood, confirmed by culture; may be transient
|
|
|
Septicemia
|
severe bacteremia
|
|
|
MODS- multiple organ dysfnx
|
presence of altered organ fnx in an acutely ill patient such that homeostasis cannot be maintained without intervention
|
|
|
bacterial agents of sepsis:
community-acquired pneumonia |
Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
|
|
bacterial agents of sepsis:
deep tissue wound |
Bacteroides, Clostridium, other anaerobes
|
|
|
bacterial agents of sepsis:
UTI |
E. coli, Klebsiella, other Gram negative bacteria
|
|
|
bacterial agents of sepsis:
infection from intravascular device |
Staphylococcus areus, coagulase negative Staphylococci
|
|
|
bacterial agents of sepsis:
severe burns |
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
Common Bacterial Agents of Sepsis
|
Gram negative rods
Encapsulated pyrogens Staphylococci Beta-hemolytic streptococci Anaerobes |
|
|
Special considerations for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
-Gram negative bacilli
-Ubiquitous; opportunistic pathogen -Oxidase + -Pigments & toxins -Burn victims, hot tubs, cystic fibrosis (URI) |
|
|
Sepsis due to Pseudomonas infection . . .
|
-Immunocompromised patient
-Neutropenic patient -Higher mortality rate -Special consideration for antimicrobials- resistance |
|
|
Ecthyma gangrenosum lesion
|
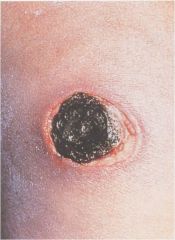
Characterisitic for pseudamonas infections… kill endothelia cells and sub Q vessels
|
|
|
Factors that predispose to sepsis and septic shock
|
-Alteration in host defenses
-Severe underlying illnesses -Major surgery -Presence of foreign bodies -Obstructive process -Treatment with cytotoxic or anti-metabolites -Prior antibiotic therapy -Prolonged hospitalization; invasive procedures |
|
|
Cardiovascular and Hemodynamic aspects of sepsis: SVR and CO
|
Initial vasodilation and capillary leakage result in decreased SVR; compensatory cardiac output
|
|
|
Cardiovascular and Hemodynamic aspects of sepsis: Hypotension
|
Marked hypotension initially responsive to volume replacement; later becomes refractory
|
|
|
Cardiovascular and Hemodynamic aspects of sepsis: CV insufficiency
|
Generalized CV insufficiency due to vascular and myocardial abnormalities, from maldistribution of blood, endothelial damage, and hypoperfusion
|
|
|
Cardiovascular and Hemodynamic aspects of sepsis: Coagulation
|
Coagulation abnormalities with organ damage
|
|
|
Septic shock coagulopathy
|
-Increased pro-coagulant state
-Decreased fibrinolysis -DIC -Fibrin deposition in small blood vessels and microvascular thrombosis in critical tagretorgans leads to organ failure. -Consumption of clotting proteins may lead to bleeding , thus both clotting and bleeding can occur simultaneously |
|
|
Endogenous mediators of sepsis
|
TLR 4
TNF-a IL-1 IL-6 NO Kinins PAF PGs Complement Coag Factors |
|
|
Patient Management in Sepsis
|
-AGRESSIVE VOLUME REPLACEMENT
-Tissue oxygenation -Immediate empirical anti-microbial therapy -Drainage of localized infection -Re-evaluate and focus aM therapy -Vasopressors and Inotropics if fluid replacement doesn't increase BP -corticosteroids, insulin |
|
|
Blood cultures for suspected sepsis patients
|
2-3 sets of cultures w/in 24hrs, optimally 20-30ml
|
|
|
Early events in sepsis
|
-Vasodilation, decreased PR & increased CO
-Fever -Flushing -Capillary leakage, reduced volume (shock) -Hypotension -Temp irregularity -Lactic acidosis -Hyperglycemia -Coag defects -microvascular circulation changes of various organs -**Hypoperfusion** due to above |
|
|
ARDS in sepsis
|
acute respiratory distress syndrome: marked increase in dyspnea and hypoxia
|

