![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are properties of organisms within the Fungal kingom?
|
Non-motile
Eukaryotic Cell walls No chlorophyll Reproduce sexually from spores |
|
|
What is the characteristic morphological feature of molds?
|
Hyphae: multiceullar branching filaments
|
|
|
What is a mycelium?
|
Masses of hyphae; grossly, fuzzy growth.
Found in molds |
|
|
What is a conidi?
|
Axequal reproductive structure on the top/sides of hyphae.
Breaks off to cause dsease |
|
|
What is the characteristic morphological feature of yeast?
|
Round, ovoid cells.
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of yeast reproduction?
|
Budding!
|
|
|
What is a pseudohyphae? What type of organism produces this?
|
A string of attached cells produced by budding yeast
|
|
|
What is unique to dimorphic fungi?
|
They have two different morphologies: one in the body and another in the environment.
|
|
|
What is the "skeletal" structure of fungi
|
Outside--> Inside
Cell wall Cell membrane |
|
|
What is a unique component of the fungal cell wall that is commonly a target of antifungal drugs?
|
Ergosterol - a sterol derivative
|
|
|
Are fungi mostly aerobic or anaerobic?
|
Aerobic
|
|
|
What is the mechanism by which fungi obtain nurients?
|
Consuming dead matter in the environment
Bumming off of us! |
|
|
What are ideal growth conditions for fungi?
(Temperature, pH?) |
Can grow from 25-50 C, prefer 25-35; human pathogens at 37
pH < 6 |
|
|
What are some of the problems in the laboratory with culturing fungi?
|
They grow S-L-O-W!
Often, there's contamination by fungi that are all over the place |
|
|
What is the one type of fungi that infects the skin?
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
What part of the body does Malassezia furfur live on?
|
The skin!
Think furfur: fur is on the SKIN! |
|
|
Where in this part of the body does Malassezia furfur live?
|
Skin
Inside the stratum corneum. |
|
|
What are the clinical diseases caused by Malassezia furfur?
|
Tinea versicolor
Suborrheic dermatitis |
|
|
Tinea versicolor is caused by what pathogen?
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
What is the appearance of Tinea versicolor?
|
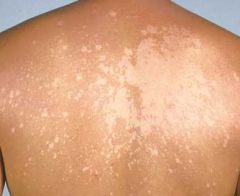
Depigmentation of dark skin.
Typically on the back. |
|
|
What is a fungi that can cause Suborrheic dermatitis?
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
What type of an organism is Malassezia furfur
|
Yeast-like organism
|
|
|
What is the presentation of a patient with Seborrheic dermatitis?
|
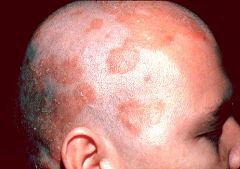
Red, flaky, itchy skin.
Typically localized to places where there are sebaceous glands Can show up in the head, back, etc. |
|
|
What molds can cause cutaneous mycoses?
|
Trichophyton
Microsporum Epidermophyton |
|
|
What kind of an organism is Trichophyton? Where does it infect?
|
Mold
The skin |
|
|
What kind of an organism is Microsporum? Where does it infect?
|
Mold
The skin |
|
|
What kind of an organism is Microsporum? Where does it infect?
|
A fungus. The skin. "Ringworm"
|
|
|
What is a typical host for an infection by a cutaneous mycoses?
|
Healthy male
|
|
|
What areas of the body are typically targeted by a cutaneous mold?
|
Feet
Genital area Hair shafts Nails |
|
|
What is the colloquial term for an infection by a cutenous mold? Why is this wrong?
|
Ringworm
THERE AREN'T ANY WORMS! |
|
|
Where is Tinea capitis localized? What are the symptoms?
|
The head!
Reversible hair loss |
|
|
What is the location of tenia corporus?
|
The body
|
|
|
What is the location for tinea cruris? What is the colloquial name of this?
|
Genital area
"Jock itch" |
|
|
What population is typically affected by Tinea cruris?
|
Men!
|
|
|
Whhat is the location of a tinea pedis infection?
What is its colloquial name? |
The feet
Athletes foot |
|
|
What is the location of Tinea unguum/onchomycosis?
|
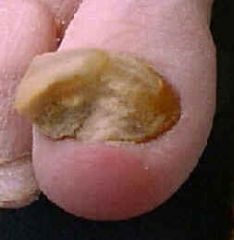
The nails
|
|
|
What is the method of treatment for Tinea unguum? Why?
|
Systemic drugs; can't get to the infection with topical creams.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a cutaneous mold infection?
|
Creams or pills
Itriconizol/Sporinox Turbinifen/Lanamicil |
|
|
What is an example of a fungi that can cause a subcutaneous mycoses?
|
Sporothrix schenckii
|
|
|
What kind of disease does Sporothrix schenckii?
|
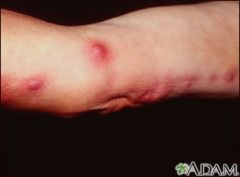
Sporotrichosis, a subcutaneous mycoss
|
|
|
What is the lifecycle of Sporothrix schenckii?
|
Dimorphic fungus:
Mold at 25C Yeast at 37C |
|
|
Where in the environment is Sporothrix schenckii found?
|
Soil
Wood Decaying material Sphagnum moss - think rose gardens |
|
|
Who are the typical hosts for Sporothrix schenckii?
|
Healthy people who spend time in the outdoors.
STEREOTYPICAL: ROSE GARDNER WHO WAS PRICKED! |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Sporothric schenckii?
|
Innoculation into the skin followed by spread up the lymphatics
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of someone with an infection of Sporothrix schenckii?
|
Open wound on the extremities
Non-painful Lesions following the path of draining lymphatics up the extremity. |
|
|
What is the treatment of an infection by Sporothrix schenckii?
|
Itriconizol
KI |
|
|
What are the most common endemic mycoses?
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
Blastomyces dermatitdis Coccidoides immitis, posadasii |
|
|
What kind of disease does Histoplasma capsulatum cause? What are the symptoms?
|
An endemic fungal infection, Histoplasmosis.
Short term symptoms: Fever and chills Cough, Chest pain upon inspirarion Long term: Swelling of heart lining Headache, neck stiffness High fever |
|
|
What kind of disease does Blastomyces dermatitidis cause?
|
An endemic fungal infection:
Blastomycosis, a pulmonary infection. |
|
|
What kind of disease does Coccidioides immitis and posadasii cause? What are the symptoms?
|
An endemic fungal infection of the lungs:
Coccidioidomycosis. Swelling in extremities Chest pain Cough Fever, night sweats Lumps on lower legs |
|
|
Histoplasmosis is caused by what kind of bug?
|
A fungus, Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
|
Blastomycosis is cause by what kind of bug? What are the diseases caused?
|
A fungus, Blastomyces dermatitidis. Lung diseases.
|
|
|
Coccidioidomycosis is caused by what kind of bug?
|
Coddidioides immitis or Coddidioides posadasii
|
|
|
Are endemic mycoses able to infect a healthy person?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
What is the morphology of an endemic mycoses?
|
Dimorphic; have an environmental and tissue form
|
|
|
What is the source of an endemic mycoses?
|
Environmental; not a part of the normal flora
|
|
|
What is the growth rate of an endemic mycoses?
|
Slow
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of diagnosis of an endemic mycoses?
|
Serology; chronic infections can have an Ab response
|
|
|
What is the immune response to an endemic mycoses?
|
Cell-mediated immune responses
|
|
|
What are the most common organisms to cause an opportunistic fungal infection?
|
Aspergillus fumigatus and flavus
Mucor, Rhizopus species Candida albicans Cryptococcus neoformans Pneumocystis jiroveci |
|
|
Aspergillus fumigatus or flavus causes what type of an infection?
|
A moldy opportunistic fungl infection, aspergillosis.
|
|
|
Mucor species and Rhisopus species cause what type of an infection?
|
A moldy opportunistic fungal infection, mucormycosis
|
|
|
Candida albicans causes what type of an infection?
|
An opportunistic yeast infection, candidiasis
|
|
|
Cryptococcus neoformans causes what type of an infection?
|
An opportunistic yeast infection, cryptococcosis
|
|
|
Pneumocystis jiroveci causes what type of an infection? What are the symptoms?
|
Pneumocystosis.
Pneumoia. Only found in people with AIDS. |
|
|
What type of patient is a target for an opportunistic fungal infection?
|
Immunocompromised hosts:
Cancer patients Transplants AIDSers |
|
|
What is the morphology of an opportunistic fungal infection?
|
Not dimorphic - one form in tissue or the environment
|
|
|
What is the normal environment of an opportunistic fungal infection?
|
Normal flora of the body
|
|
|
What is the growth rate of an opportunistic fungal infection?
|
Easy to grow: fast and easy.
|
|
|
What is the host defense against an opportunistic fungal infection?
|
Neutrophils
|
|
|
Cell mediated immunity is important against these two opportunistic fungl pathogens:
|
Cryptococcus
Pneumocystis |
|
|
What is the morphology of Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Dimorphic:
Mold in the environment that can be inhaled In the tissue at 37 it forms a yeast |
|
|
What is the host for Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Healthy kids and adults
Immunosuppressed |
|
|
What is the geographic locale of Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Mississipppi and Ohio River valleys
|
|
|
What type of soil does Histoplasma capsulatum like? What type of soil normally is this?
|
Soil high in nitrogen content.
Soil that birds/bats have crapped on! |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Inhalation of the mold from the environment
|
|
|
What is the epidemiology of Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Many have it,few show symptoms.
|
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Very similar to Tb.
Lungs->Lymph->Hematogenous to reticuloendotelial system |
|
|
What organs can Histoplasma capsulatum localize to?
|
Liver
Spleen Lymph nodes Bone marrow |
|
|
What is the immune response to Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Cell-mediated response: T-lymphocytes and macrophages activated by interferon gamma.
|
|
|
In what types of patients do you see a chronic Histoplasma capsulatum infection?
|
Patients with emphysema
|
|
|
In what types of patients do you see a disseminated Histoplasma capsulatum infection?
|
Immunocompromised patients
|
|
|
What is the distribution of Blastomycosa dermatidis?
|
Similar to histoplasmosis, except that it extends north into Canada and farther east into the Carolinas.
|
|
|
What is the habitat of Blastomycosa dermatidis?
|
Soil
Decaying wood Near the water |
|
|
What is the morphology of Blastomycosa dermatidis?
|
Dimorphic.
In tissue forms a round cell filled with pinkish cytoplasm. |
|
|
What disease processes does Blastomycosa dermatidis cause?
|
Lung disease
Painless purlent skin lesions |
|
|
What is the immune response to Blastomycosa dermatidis?
|
PMNs
Macrophages |
|
|
What is the geographic locale for Cocciodies immitus and posadasii?
|
In the deserts of the southwest
|
|
|
Are Cocciodies immitus or C. posadasii very contagious?
|
Yes! If you even open the plate, the entire lab is going to come down with Coccidioidomycosis.
|
|
|
What are the morphologies of Cocciodies immitus and posadasii?
|
Mold in the environment
Sperules inside the tissues |
|
|
What kinds of diseases can Cocciodies immitus and posadasii cause?
|
Severe skin ulcers
Chronic uncurable, but controllable, meningitis Joint disease |
|
|
What is the best way to diagnose an endemic mycosis?
|
Antibody titers for Coccy, histo
Culture Antigen detection Histopathology |
|
|
What drug is used in severe fungal infections?
|
Amphotericin B
|
|
|
What is the length of therapy for an endemic mycoses?
|
LONG! Months - years.
|

